Understanding the impact of the bond yield is an important element of learning how to trade in fixed income securities. If you want to learn more about bonds, interest rate and fixed-income bearing securities you may enroll in the course for Certification in Online Fixed Income and Interest rate futures.
India is currently facing a rising bond yield situation at 7.78%. Find out what it could mean for the economy?
What are bonds?
A bond is a debt instrument in which an investor loans money to an organization (typically corporate or government). The organization borrows the funds for a specified period of time at a variable or fixed interest rate. Bonds are used by governments, companies, municipalities, states to raise money to finance various activities. But, in this article, we are going to talk about government securities.
The government issues both short-term and long-term securities. Short-term government securities with maturities of less than one year are called treasury bills and long-term government securities with maturities more than one year are called government bonds.
Types of Government Securities:
Treasury bills are issued in 3 categories-91 days, 182 days and 364 days bills. Government bonds have maturities ranging from 5 years to 40 years. They are also called dated g-secs.
Bonds are usually of these types-
1. Zero-coupon bonds
2. Fixed or floating rate bonds
3. Capital-Indexed bonds
4. Bonds with a call or put option.
The most popular bonds are the conventional bonds with fixed coupon rate and defined maturity period.
How does bonds work?
Most of the dated securities have fixed coupon rates. For e.g. 7.20% GS 2028 would mean-Coupon: 7.20%, Issuer: Government of India, Maturity: 2028, Face value: Rs. 10,000.
Bonds just like equities are traded in open markets. One of the fundamental indicators of an economy is the 10-year bond yield rate and it is quoted for all major economies in major exchanges.
How is bond yield calculated?
Bond yield is the rate of interest the bond would provide on its maturity. Bond yield is calculated as cash flows from the bond divided by the price of the bond. The cash flows are constant in fixed coupon rate bond. So, the yield will depend on the current price of the bond. The yield of a bond and price of a bond are inversely related to each other, meaning if the bond prices fall the yield rises and if the bond prices rise the yield falls. Since bonds are traded in an open market.
The bond prices go up and down as per the demand and supply of the bonds. If the bond price is lower than the face value, it is yielding higher than the coupon rate and if the bond price is higher than the face value, it is yielding at a lower rate than the coupon rate.
So, we can conclude that the calculation of bond yield depends on:
1. Coupon rate and
2. Price of the bond.
Rising yields indicate worsening macros and falling markets:
If an economy has severe macroeconomic issues such as rising inflation, unemployment, fiscal deficit, current account deficit, depreciating currency, then the investors will be alarmed about the growth of the economy. The government-issued bonds are largely held by foreign investors as well. They will pull out of the economy by selling the bonds held by them.
Even the domestic investors will sell out of the G-secs because there will be serious doubts over whether the government will be able to make good on its bonds.i.e. able to pay the interest and the principal as promised. Few economies like the Greece and Ukraine defaulted on their bond repayments in the recent past. Selling of bonds means bond prices will fall and yields will rise. Thus, rising-yield can indicate worsening economy and markets.
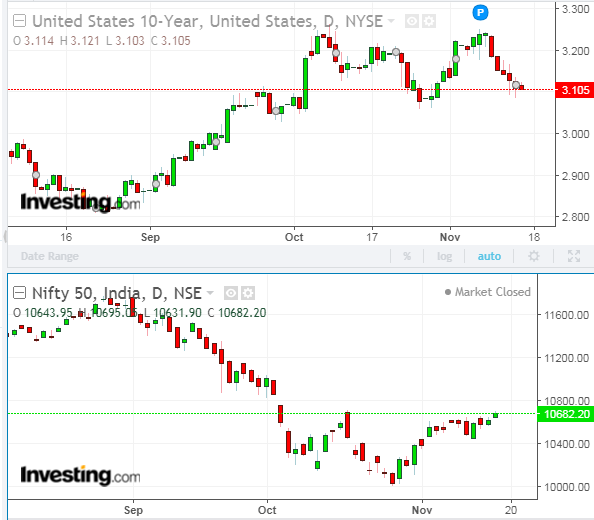
Source: www.investing.com
Why governments raise rates?
When there is low confidence in any economy. The government has to offer higher rates to attract investors. India is rated as “Baa2” by Moody’s Investor Service and “BBB -“by Fitch Ratings, so Indian government will have to offer higher rates to attract investors. When central banks raise the interest rate, there can be a demand for the new bond issue which has higher coupon rates.
Investors will try to get out of the older bonds with low coupon rates pushing the bond prices down and in effect raising the yield. If it’s such a scenario that yield from equities is close to bond yield or lower, investors will migrate from equity markets towards the bond market because they are safer. So, rising bond yield over here means falling markets.
The yield curve explanation:
The yield curve has been a near accurate indicator of the economy. The yield curve basically shows the yield of bonds of different maturities. The bonds with lower duration (say 6-month or 1 year) generally have a lower interest rate or yield than bonds with higher duration (say 10-year or 20-year) because investors expect the economy to grow a lot in future and they are going to invest in equity markets. Unless the government gives a higher rate,investors are not going to invest in long-term bonds. Also, the investors want to be compensated for inflation in long-term, so they will demand a higher rate for longer-term bonds. The yield curve should slope upwards towards the right. But, if the yield curve slopes down or stays flat it might indicate a recession ahead. Why this will be so?
If the yield curve stays flat or slopes down it means the higher duration bonds will yield lower. If the investors think that the economy or market will do worse in the future, they will shift towards the safer government bonds. Now, because there is already demand for govt. bonds, the government would not need to pay a higher interest rate for long-term bonds. So, the yield curve will be flatter or sloping downwards and it will mean the economy or market is going to face a recession in near future.
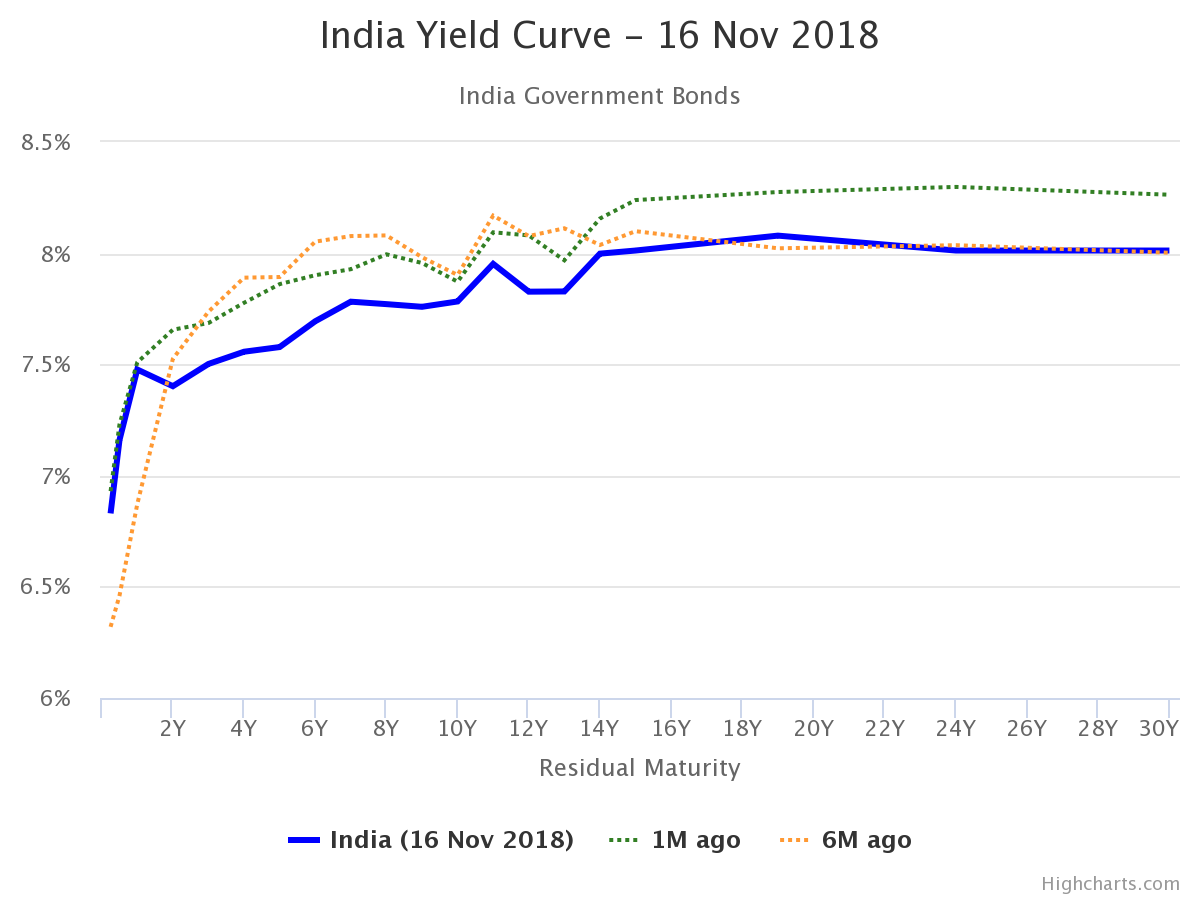
Source: www.worldgovernmentbonds.com
Current Scenario:
India is now facing a rising bond yield situation at 7.78%. The Foreign investors have pulled out massive Rs. 35,600 crores (about USD 5 billion) from the Indian capital markets in October on concerns of rupee depreciation, global trade war, and rising crude prices. They sold bonds worth Rs. 11,407 crores. Thus the markets also reacted negatively to rising bond yield. So, far this year FPIs have pulled out Rs. 60,000 crores from the debt markets. RBI is likely to conduct open market operation (OMO) purchase worth USD 40 billion by March end to provide durable liquidity and negate rising government bond yields.
Bottomline
The bond yield is a significant indicator in assessing the economic conditions of any country. So far the yield curve has successfully predicted all the major recession. Therefore understanding bond yield and yield curve is crucial in understanding the economic scenario.
In order to get the latest updates on Financial Markets visit Stockedge