- What are Government Sovereign Bonds?
- Types of Government Sovereign Bonds in India
- What is the significance of Government Sovereign Bonds for the Economy?
- What is the Issuance Process of Government Sovereign Bonds?
- Characteristics and Features of Government Sovereign Bonds
- Advantages of Investing in Government Sovereign Bonds
- Risks Associated with Government Sovereign Bonds
- How to Invest in Government Sovereign Bonds
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Consider giving the government a loan! Government sovereign bonds, or G-Secs, are all about this!
In essence, sovereign bonds are debt securities that are issued by a nation’s government to raise money for certain purposes and costs. Consider it as lending money to the government, which agrees to repay you over a predetermined time period with interest.
Because the government issuing them backs these bonds with its entire faith and credit, they are among the safest investment possibilities. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues government sovereign bonds in India on behalf of the national government.
Government sovereign bonds are essential to India’s financial system and economy. They are the main means by which the government can borrow money from the general public to fund a range of budgetary expenses, infrastructure improvements, and development initiatives. Additionally, these bonds give investors a safe place to put their extra money while receiving interest payments as a fixed income.
What are Government Sovereign Bonds?
Government sovereign bonds are financial instruments that are issued by a national government in its own currency. They are sometimes referred to as sovereign debt or government bonds. Because the issuing government’s complete confidence and credit is attached to these bonds, they are generally viewed as low-risk investments.
Sovereign bonds are issued by governments to raise money for a variety of uses, including funding public works projects, filling budget gaps, and refinancing existing debt.
Types of Government Sovereign Bonds in India
Here are three of the main types of Government Sovereign Bonds in India:
Treasury Bills (T-Bills)
The Indian government issues these short-term debt instruments, which have maturities varying from a few days to a year. Because of the government’s support, they are regarded as extremely safe investments and have attractive interest rates.
Government Securities (G-Secs)
The Central Government of India issues these medium- to long-term debt securities. Typically, maturities fall between one year and forty years. When held until maturity, G-Secs provide investors with a steady income stream in the form of fixed interest payments, or coupons, as well as the possibility of capital growth.
State Development Loans (SDLs)
These are bonds that the various Indian states have issued to raise money for development and infrastructure projects. Similar to G-Secs, SDLs have maturities of one to forty years and pay interest at a predetermined rate. They may have somewhat higher interest rates than G-Secs to offset the somewhat increased risk, but overall they are thought to be marginally less dangerous than corporate bonds.
What is the significance of Government Sovereign Bonds for the Economy?
Government sovereign bonds are essential to an economy since they fund governments and have an impact on a number of other economic variables. Below is a summary of their importance:
1. Financing Government Activities
The government issues sovereign bonds, which are effectively loans, to raise capital. This money is used to pay for a range of government expenses, including social initiatives, infrastructure improvements, and even budget deficits. By issuing bonds, governments can spread the expense of major projects over time instead of depending solely on tax revenue.
2. Bringing in Foreign Investment
Governments may be able to attract foreign investment through the issuance of sovereign bonds. These bonds are bought by investors worldwide, bringing in foreign exchange. In addition to perhaps having a favourable impact on exchange rates, this can increase the nation’s foreign exchange reserves.
3. Benchmark for Interest Rates
Investing in government bonds is generally seen as low-risk, particularly when they are issued by stable nations. These bonds’ interest rates act as a benchmark for the economy’s other interest rates, such as those on mortgages and loans.
Sovereign bonds have the potential to affect the stability of the economy as a whole. Without the need to use inflationary tactics like money printing, the government can obtain a steady supply of funds from a well-managed bond market with robust demand.
But it’s crucial to remember that relying too heavily on sovereign bonds might result in large public debt, which could be detrimental to the country’s ability to borrow money in the future.
What is the Issuance Process of Government Sovereign Bonds?
In India, the government and Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supervise a clearly defined process for issuing sovereign bonds.
Here are the steps-
1. Role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Government’s Agent: When it comes to overseeing the issuing of sovereign bonds, the RBI represents the government. They take care of the logistics and guarantee a seamless operation.
- Selecting Issue Specifics: Important components of the bond issue are decided by the RBI in cooperation with the government. This comprises: Total amount to be raised (the amount of funds required by the government).The length of the loan and the date of repayment are known as the maturity period.
- Interest rate offered: the yield that lenders will get in exchange for their loans
- Holding Auctions: The RBI holds auctions to sell bonds to investors. This guarantees openness and permits reasonable prices.
2. Auction Process
A variety of auction techniques, such as:
- In fixed-rate auctions, bidders place their highest and lowest bids for bonds at fixed interest rates.
- In yield-based auctions, bidders place their bets based on the interest rate they are prepared to pay for bonds that have a predetermined face value (cost).
Procedure for Bidding: Depending on the type of auction, investors place bids for the bonds, indicating the amount they are willing to invest and the specifics of the interest rate.
Bond Allotment: Based on the bids received, the RBI assigns bonds to certain parties. Bids with the largest yield—that is, the government’s lowest interest rate—usually get priority. This guarantees the best borrowing conditions for the government.
3. Eligibility Criteria for Investors
Investors who are residents and those who are not: The government has the authority to determine whether or not Indian residents and non-residents may participate in the bond offering’s auctions.
Investor Categories: distinct qualifying standards may be established by the government for distinct investor categories, including:
- Banks
- Insurance providers
- Individual investors
4. Subscription and Allotment Process
- Subscription Period: During a specific time frame that the RBI announces, investors place their bids. Everyone has an equal opportunity to participate as a result.
- Bond Allotment: Following the auction, the RBI notifies the winning bidders of the bonds they have been allocated. They only get the amount for which their bid was accepted.
- Payment and Issuance: Investors pay the RBI for the bonds they have been allocated, and the RBI issues the bonds in certificate form or electronic form (dematerialized), based on the investor’s option.
Characteristics and Features of Government Sovereign Bonds
Here are some Characteristics and Features of Government Sovereign Bonds-
Maturity Periods
Bonds issued by the government with sovereign characteristics range in maturity from less than a year to more than 30 years.
The bond’s maturity period establishes when the government will return the bondholder’s principal.
Interest Rates
Fixed or variable interest rates are commonly offered by government sovereign bonds.
Fixed-rate bonds give investors assurance about their income stream by paying a predefined interest rate throughout the duration of the bond.
Interest rates on floating-rate bonds are periodically adjusted in accordance with a designated benchmark, such as the yield curve on government bonds or a reference interest rate.
Liquidity and Marketability
In the financial markets, government sovereign bonds are actively traded and very liquid assets.
Because investors embrace them and they are widely available, they are seen as very marketable.
Investors can purchase and sell sovereign bonds with ease and without substantially affecting their market value thanks to their liquidity.
Taxation Policies
Depending on the nation and the particular bonds, different tax laws apply to government sovereign bonds.
Government bond interest income is taxed at the applicable tax rate for each individual investor in a number of nations.
To encourage investment, some government bonds do, however, have favorable tax treatment or may be free from some taxes.
Risk Factors
Because they are backed by the entire confidence and credit of the issuing government, government sovereign bonds are typically regarded as low-risk investments.
They are not totally risk-free, though. Sovereign bond values and returns can be impacted by a number of factors, including macroeconomic conditions, inflation, interest rate changes, and credit risk (particularly for bonds issued by governments with lower creditworthiness).
Before making an investment, investors should evaluate the risk considerations related to government sovereign bonds and adjust their investment portfolios accordingly.
Advantages of Investing in Government Sovereign Bonds
Here are some advantages of Investing in Government Sovereign Bonds-
Safety and Security
Since government sovereign bonds are guaranteed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government, they are among the safest investments available.
The ability of governments to impose taxes and generate money offers a high degree of guarantee that they will honor their debt commitments.
For conservative investors looking to protect cash, government bonds are especially enticing because of their safety and security.
Regular Income Stream
Bondholders who purchase government bonds usually get set or semi-annual interest payments, or coupons, which offer a steady source of income.
Investors looking for steady cash flows or retirees may find this monthly income useful.
Diversification of Portfolio
A diverse investment portfolio can lower overall portfolio risk by holding government sovereign bonds.
Bonds benefit from diversification since they frequently have low or negative correlations with other asset types, including equities.
Government bonds have the ability to stabilize a portfolio during times of market or economic instability.
Hedge against Inflation
A lot of government bonds have characteristics like inflation-linked bonds or floating-rate notes that protect against inflation.
Inflation-linked bonds help investors maintain their buying power by adjusting their principal and interest payments in response to fluctuations in inflation.
Because they offer a guaranteed nominal return, even conventional fixed-rate government bonds can serve as a hedge against unforeseen inflation.
Risks Associated with Government Sovereign Bonds
Here are some Risks Associated with Government Sovereign Bonds-
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is the possibility that shifts in interest rates will cause bonds’ value to vary.
Bond prices usually decrease when interest rates rise and vice versa. This is due to the fact that newly issued bonds have higher yields than older bonds, which makes the latter less appealing.
Compared to shorter-term bonds, longer-term bonds are more susceptible to changes in interest rates.
Inflation Risk
The possibility that inflation will reduce the bond’s future cash flows’ buying value is known as inflation risk.
Government bonds and other fixed-income instruments offer a set income stream, which could decrease in real terms in the event of inflation.
On the other hand, inflation-linked bonds are intended to lessen this risk by modifying principal and interest payments in response to variations in inflation.
Credit Risk
Even while credit risk is typically minimal for government sovereign bonds, it nevertheless exists to some degree.
It alludes to the possibility that bondholders could suffer losses in the event that the issuing government defaults on its loan.
Credit risk may be greater for governments with unstable economies or huge debt loads, however industrialized nation bankruptcies are uncommon.
Market Risk
The chance of suffering losses as a result of variables impacting the whole financial market is referred to as market risk, often called systematic risk.
The pricing of government bonds can be impacted by events like financial crises, economic downturns, or geopolitical unrest that enhance bond market volatility.
All investment kinds are subject to market risk, which cannot be reduced by diversification.
How to Invest in Government Sovereign Bonds
Here are some ways to Invest in Government Sovereign Bonds-
1. Direct Purchase through Primary Market
The government or its authorized issuing agencies, such as central banks or treasury departments, issue and sell government sovereign bonds to investors through the primary market.
By sending bids straight to the issuing authority during the auction period, investors can take part in primary market bond auctions.
Before newly issued government bonds are made available for trading on the secondary market, investors can bid on them in the primary market at face value, usually par.
When investing in a primary market bond auction, investors must be informed of the precise issuance parameters, such as the coupon rate, maturity date, and settlement procedures.
The investors can participate in the auction of G-Secs from the RBI Retail Direct Website. They can create an account and participate in the auction process of Government Bonds.
2. Secondary Market Trading
Government sovereign bonds are traded on the secondary market, where investors purchase and sell previously issued bonds to one another after they are first issued.
Investors can purchase or sell bonds at current market values through secondary market trading, giving them flexibility and liquidity without having to wait for fresh issuances.
Through brokerage houses, financial institutions, or computerized trading platforms, investors can access the secondary market.
To make wise investment selections, investors need take into account variables including bond prices, yields, and transaction fees while trading government bonds on the secondary market.
Here are the steps for trading G-Secs ETFs in the secondary market-
1. Examine and Select GSec Bonds
Examine variables such as the maturity period, current market price, and interest rate (coupon). You can view the bond’s details on your brokerage’s platform. Below is an example from ICICI Direct Trading Platform-
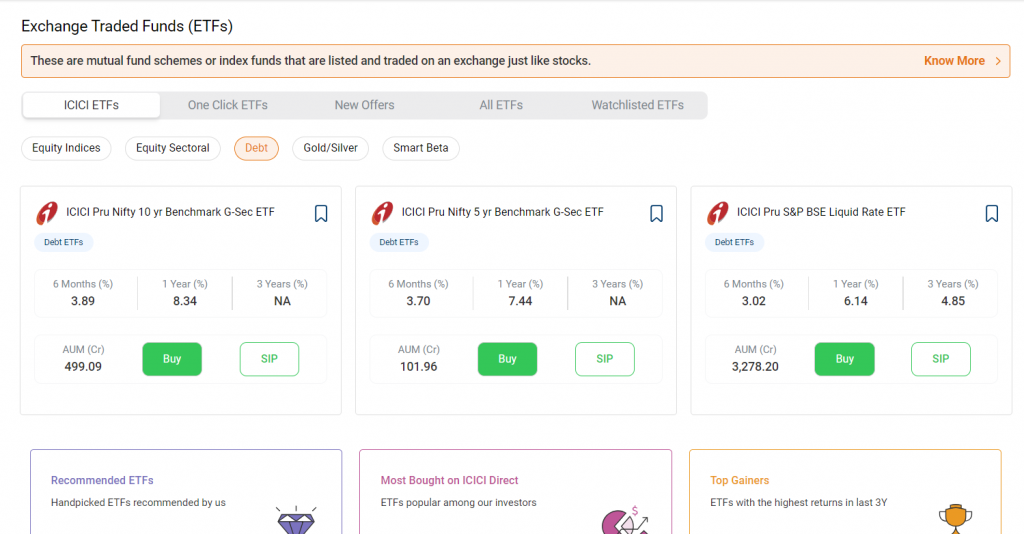
2. Place an order through your broker
To place a buy order for the particular GSec bond, log in to your online trading platform or get in touch with your broker.
Use a market order to buy bonds at the going rate, or specify how many bonds you want to buy and how much you’re ready to pay (limit order).
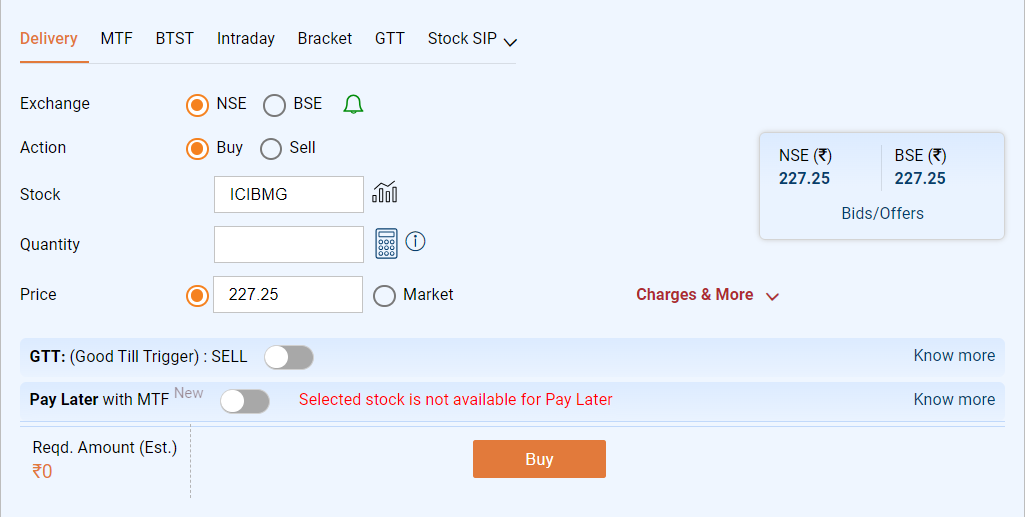
3. Order Execution and Settlement
After that, your broker will match your order with a secondary market seller to execute it. When the order is filled, money will be taken out of your trading account and credited to your demat account for the GSec bonds you bought.
3. Investment through Mutual Funds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that concentrate on fixed-income assets, such as government bonds, offer an additional avenue for investing in government sovereign bonds.
1. Through Mutual Funds
Gaining exposure to the Indian government bond market can be done conveniently and possibly with less risk by investing in GSec (Government Security) bonds through mutual funds.
Types of GSec Mutual Funds
- Pure Gilt Funds: These funds mainly make investments in government securities, exposing investors to changes in interest rates as well as possible financial gains.
- Debt funds exposed to GSecs: These funds have the potential to invest in a variety of debt instruments, including corporate bonds and GSecs. When compared to pure gilt funds, this may offer more volatility but also some diversity.
- Funds for GSecs with shorter maturities are known as short maturity GSec funds. These funds often offer lower volatility along with possibly lower returns.
- Funds for GSecs with Longer Maturities: These funds invest in GSecs with longer maturities, possibly yielding larger returns, but they also expose investors to more interest rate volatility.
Popular G-Secs Mutual Funds
Here are some Popular G-Secs Mutual Funds in India-
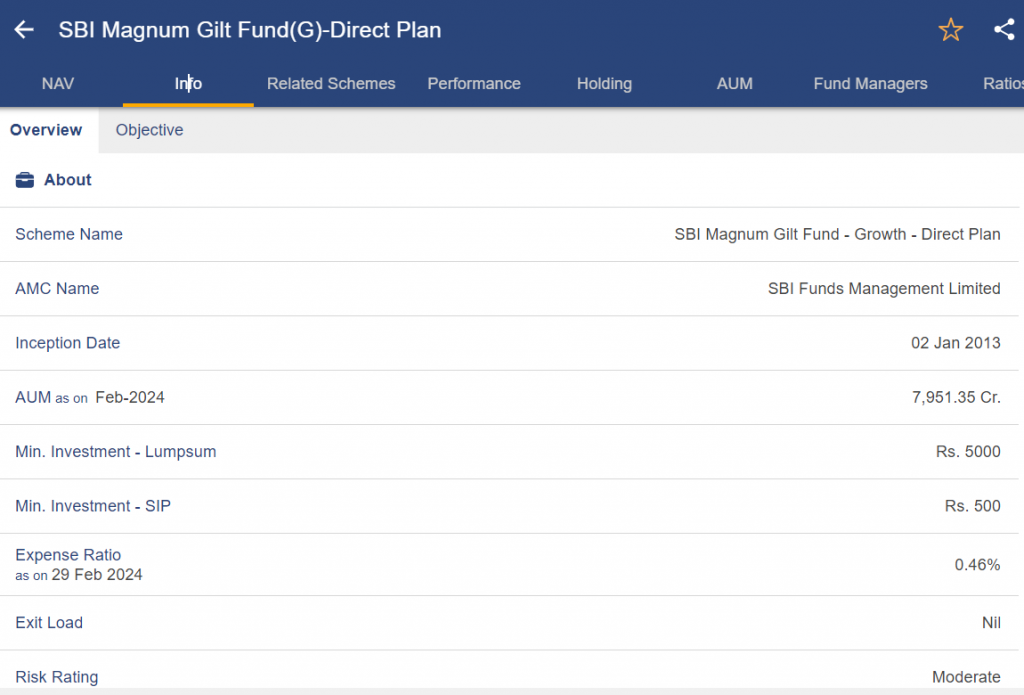
SBI Magnum Gilt Fund
- Type: Pure Gilt Fund, which mostly makes investments in government bonds
- Investment Goal: By purchasing government securities, investors want to increase their capital and earn income.
- Appropriate for: Investors looking for comparatively low risk and moderate potential returns
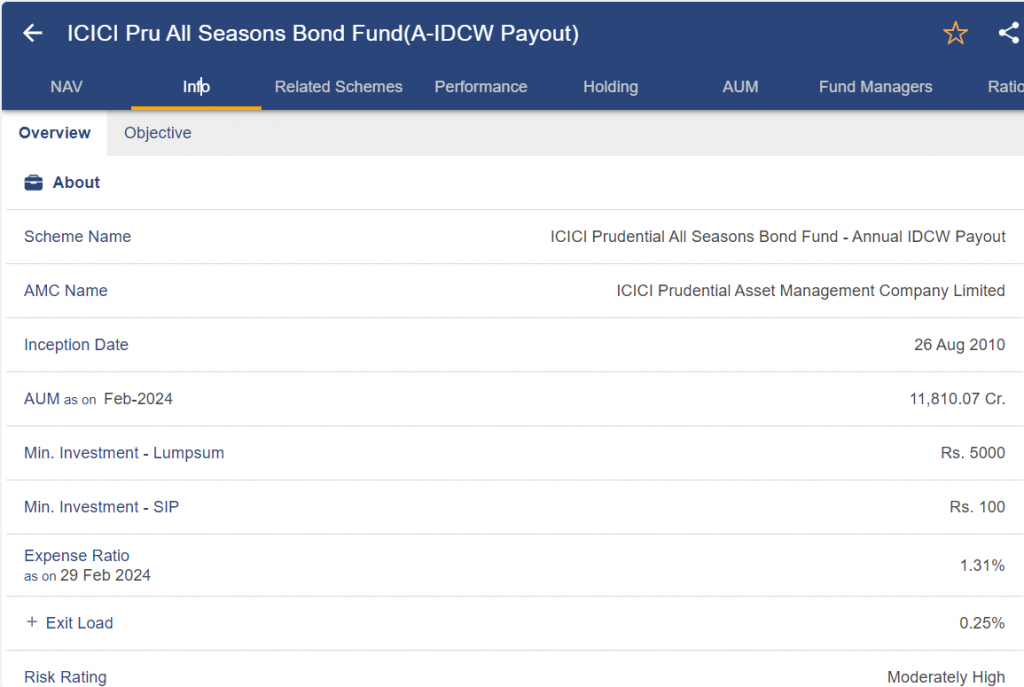
ICICI Prudential All Seasons Bond Fund
- Type: Bonds of various maturities are invested in by Dynamic Bond Funds, which are depending on market conditions.
- Investment Goal: By making investments in a diverse range of debt instruments, this strategy seeks to produce both capital growth and consistent income.
- Appropriate for: Investors who want a modest potential return with some market-condition flexibility.
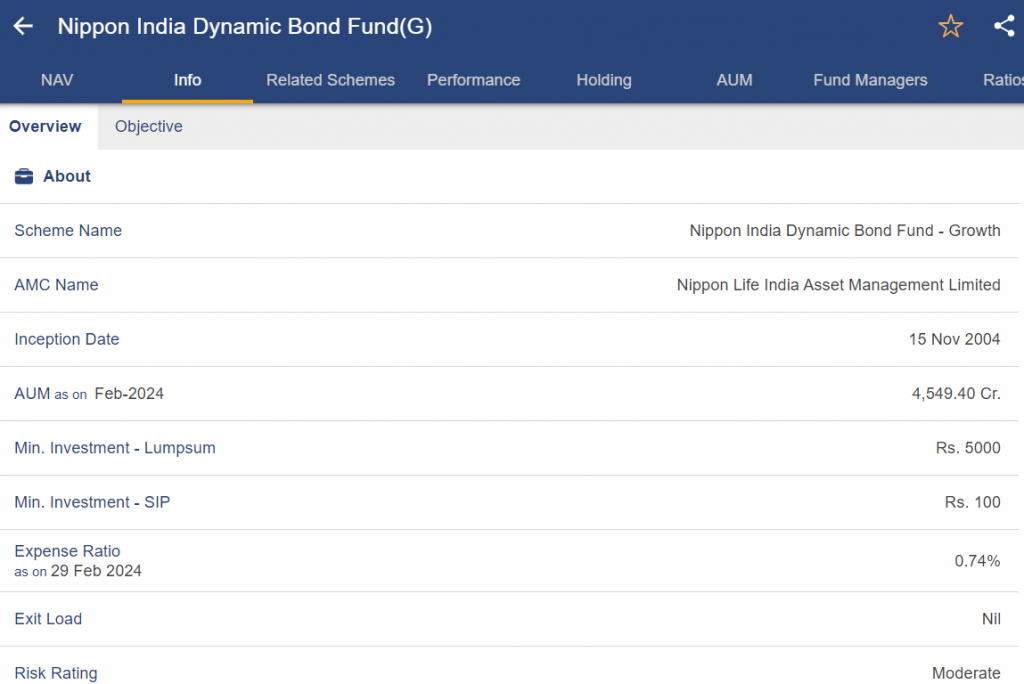
Nippon India Dynamic Bonds Fund
- Type: Bonds of various maturities are invested in by Dynamic Bond Funds, which are depending on market conditions.
- Investment Goal: Invests in a dynamic mix of debt securities spanning the maturity spectrum with the intention of producing both income and capital appreciation.
- Appropriate for: Investors looking for a moderate potential return with considerable flexibility in response to changes in the market.
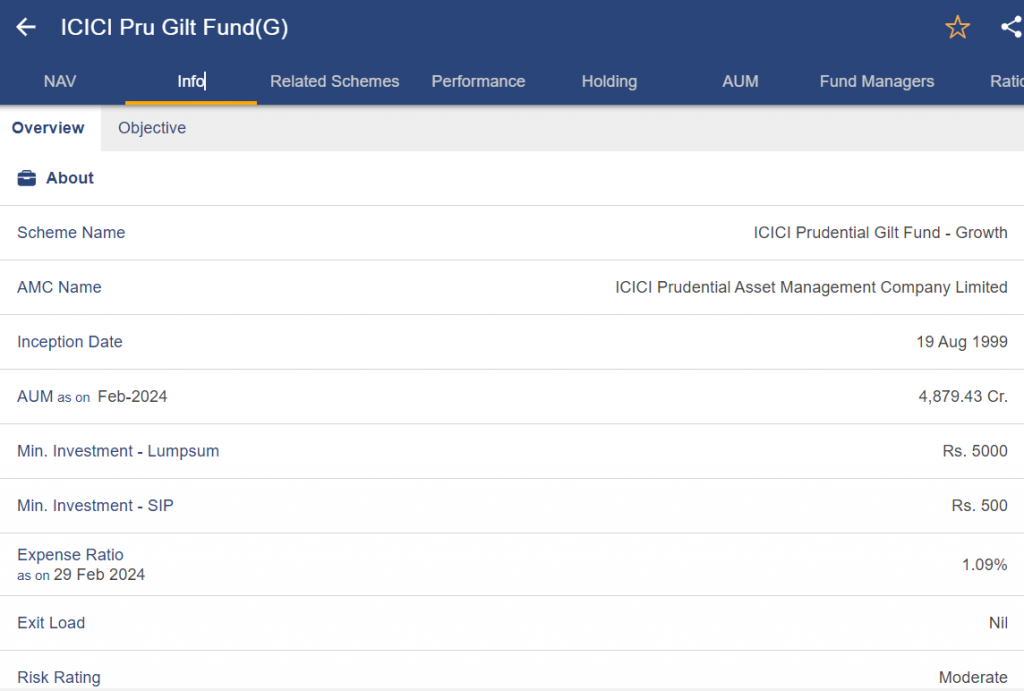
ICICI Prudential Gilt Fund
- Type: Pure Gilt Fund, which mostly makes investments in government bonds
- Investment Goal: By purchasing government securities, investors want to increase their capital and earn income.
- Appropriate for: Investors looking for comparatively low risk and moderate potential profits.
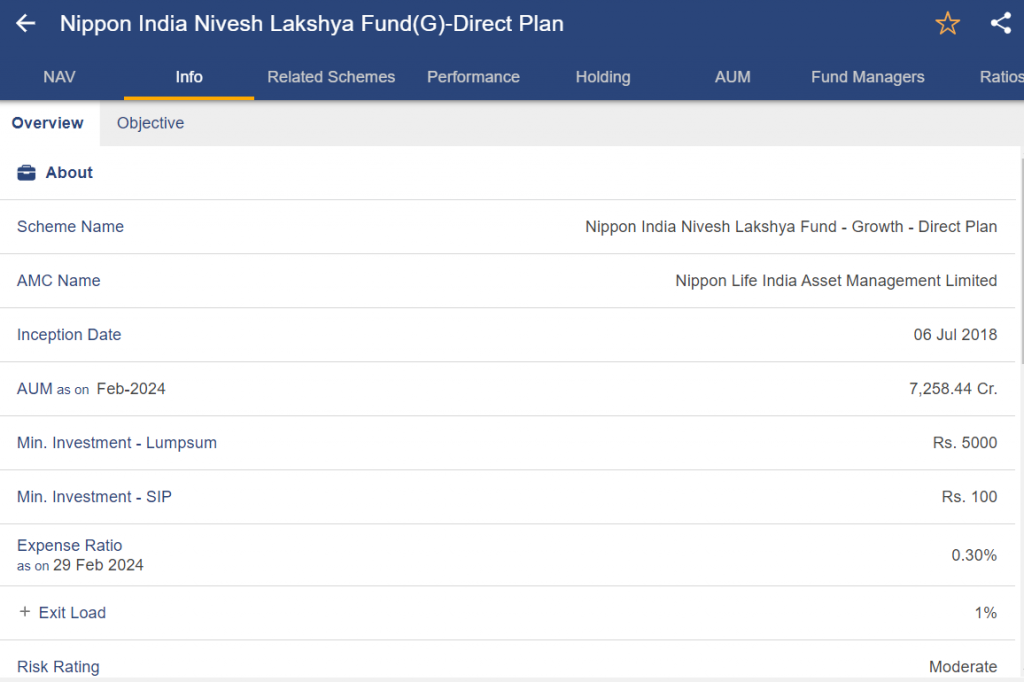
Nippon India Nivesh Lakshya Fund
- Type: Invests in a variety of debt instruments with a target maturity date; this type of debt fund is goal-oriented.
- Investment purpose: To reach a particular investment target by a target maturity date, the purpose is to produce income and capital appreciation. (Select the plan whose target date is closest to your own investing objective.)
- Appropriate for: Investors having a defined investing horizon and a long-term financial goal (such as retirement).
2. Through Exchange Traded Funds
GSec (Government Security) Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) can be a convenient and potentially lower-cost way to invest in the Indian government bond market.
Some ETFs invest in long-term GSecs (perhaps better returns, with increased interest rate risk), while others concentrate on short-term GSecs (reduced volatility, potentially lower returns).
Short-Term: A shorter maturity GSec bond or ETF (such as the Bharat Bond ETF – April 2023) would be appropriate if you need your money returned in less than three years. These may have lower returns but also less volatility.
Long-Term: You may want to think about somewhat longer maturity GSecs or ETFs (such as the ICICI Prudential Nifty 5 Year Benchmark G-Sec ETF) if your ambitions are longer than five years. These could be more volatile, but they could also yield larger rewards.
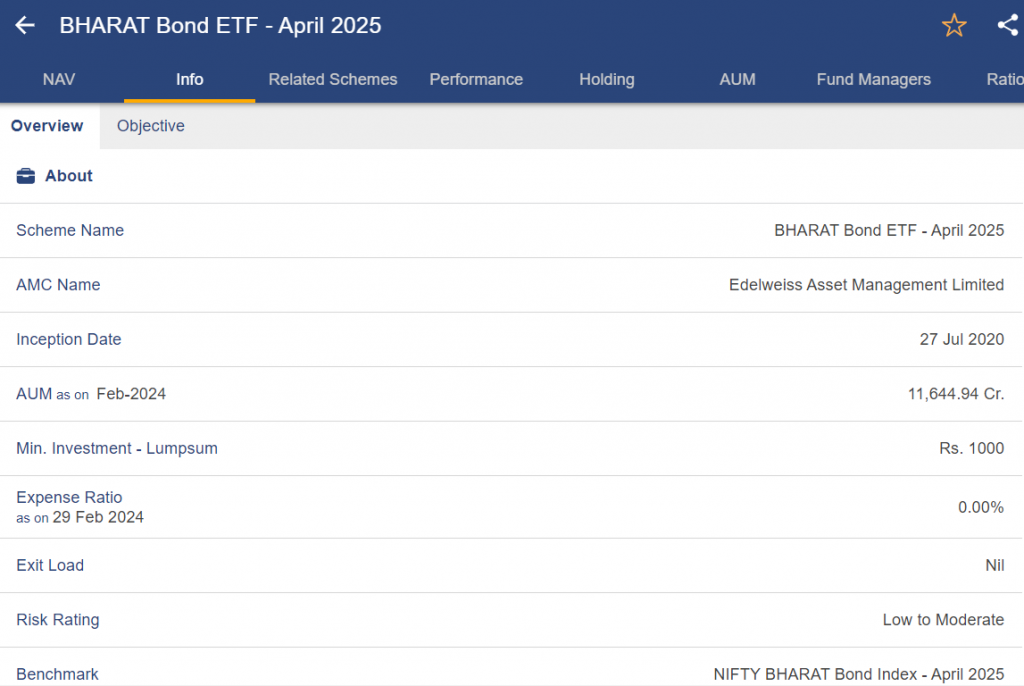
1. Bharat Bond ETF
Every Bharat Bond ETF has a maturity date, and there are multiple of them. The Bharat Bond ETF-2025 is the most well-liked one at the moment. This ETF offers a very short maturity time by investing in government bonds with maturities in April 2025. Investors that are risk-averse or have a shorter investment horizon may benefit from shorter maturities, which are typically associated with reduced volatility.4
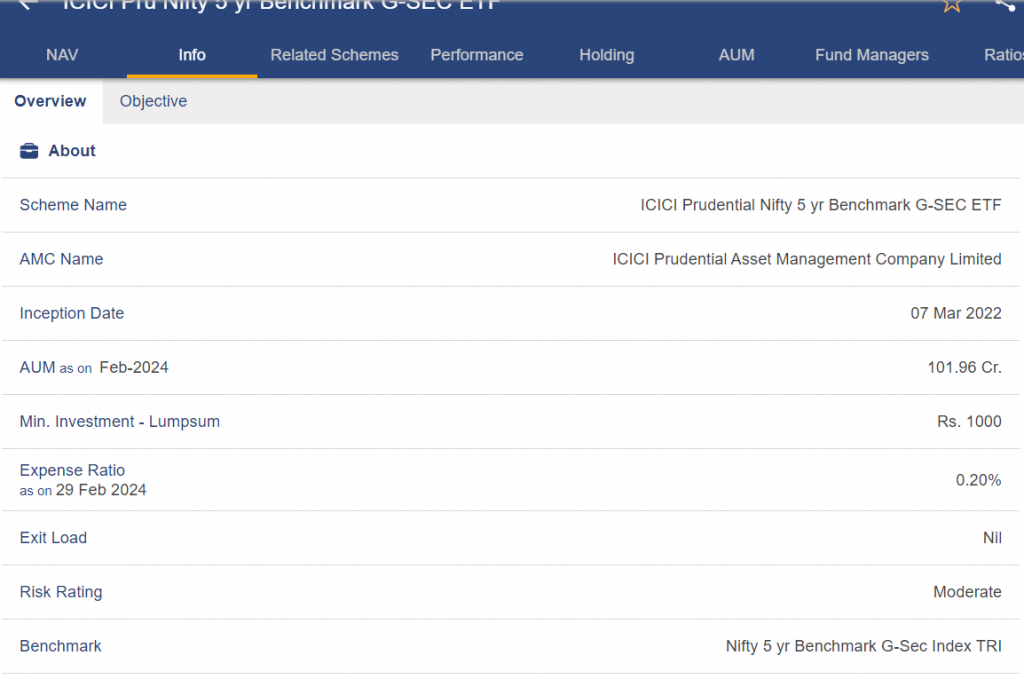
2. ICICI Prudential Nifty 5-Year Benchmark G-Sec ETF
This exchange-traded fund (ETF) invests in a basket of government bonds with a maturity of about five years, tracking the Nifty 5 yr Benchmark G-Sec Index. Compared to the Bharat Bond ETF – April 2023, this has a little bit greater exposure to interest rate changes, but it also has the potential for bigger gains.
Conclusion
Sovereign government bond investments provide portfolio diversification, stability, and income. Even with minimal risk, investors should take inflation and changes in interest rates into account. Government bonds continue to be an essential part of well-rounded investing strategies, whether they are acquired directly, by trading on the secondary market, or through investment funds.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are government sovereign bonds?
Government sovereign bonds are debt instruments, secured by the full faith and credit of the issuing government, that are issued by national governments in their own currency to raise money for a variety of uses.
2. How do government sovereign bonds work?
By buying government bonds, investors lend money to the government for a set amount of time. They are compensated with regular interest payments in the form of coupons and the repayment of the principal amount upon maturity.
3. What are the benefits of investing in government sovereign bonds?
Inflation protection, consistency, safety, and diversity are all provided by government bonds. Because governments are creditworthy, they are seen as low-risk investments.
For more Market Updates, Visit StockEdge