Trading multiples is a valuation technique used to value a company by comparing the company’s financial valuation metrics to those of its peers
Typically, the multiples are a ratio of some valuation metric (such as market capitalization, enterprise value) to some financial performance metric (such as sales, EBITDA, earnings)etc.
The basic idea behind this valuation technique is that companies with similar characteristics should trade at similar multiples, all other things being equal.
We will go step by step to understand the same.
In the end, you would get a clear idea on how to use trading multiples for valuing a company.
Suppose that you are valuing companies in paper and paper products industry
Step 1 – Identify Comparable Companies
To find out comparable and similar companies, the parameter below needs to be obtained.
Business mix:– Under business mix, you would see three things- products and services offered by the companies. The geographical location of those companies and types of customer they serve.
Size:- Under the size, you can choose any or all three of determinants- revenue of these companies, total asset under management and EBITDA margins of the company.
We have selected companies which are in the same industry. Market capitalization ranges around 1100 to 2200 crores.
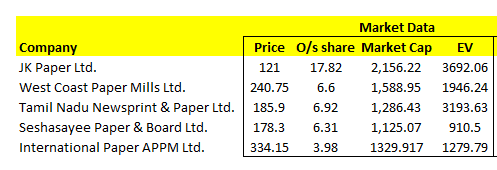
Once you have found the list of companies, it is time to gather their financial information.
Learn in 2 hours – Trading for Living
These are Sales, EBITDA, PAT, Enterprise value, outstanding share and market capitalization figures which you can easily get from Annual report, quarterly reports and brokerage house research reports.
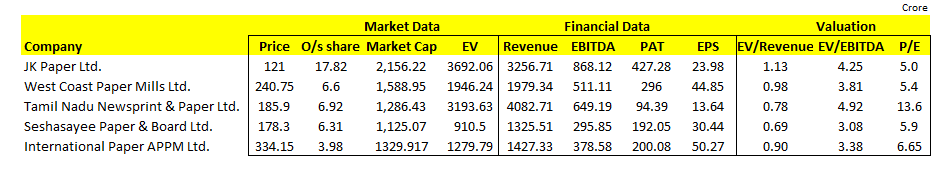
Step 2 – Select Appropriate Multiples for Valuation

These are the most popular multiples which you can use for valuing a company.
EV/EBITDA:
EV = (Market capitalization) + (Value of debt) – (cash and cash equivalents) and EBITDA is earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
This is one of the most common and important trading multiples.
The purpose of using the EV (Enterprise value) is that it not only considers the market capitalization, but it also takes the debt into account.
And on the other hand EBITDA provides a clear picture of the financial performance of a company.
A low EV/EBITDA ratio means that the stock is potentially undervalued while a high EV/EBITDA means a stock is possibly overvalued.
EV/Revenue:
The enterprise values to revenue multiple helps in comparing a company’s revenues to its enterprise value.
It is often use to determine a company’s valuation in the case of potential acquisition.
The lower the multiple, the better it is. A lower EV/Revenue multiple signals a company is undervalued thus investible.
Also Read : What is the right method of selecting stocks?
P/E:
This valuation matrix takes into consideration the current share price in numerator and earnings per share in denominator.
It shows how much investors are willing to pay for each rupee of earning.
For example: If a Company A has a P/E of 10 and company B has a P/E of 20 so to get 1 rupee of profit from a Company A, you need to invest Rs. 10 whereas to get the same 1 rupee of profit from the company B, you would need to put in Rs.20.
Step 3 – Check and Interpret the Result
This is the last step of the whole process. In this step, we will look at various trading multiple of the company and interpret the result.
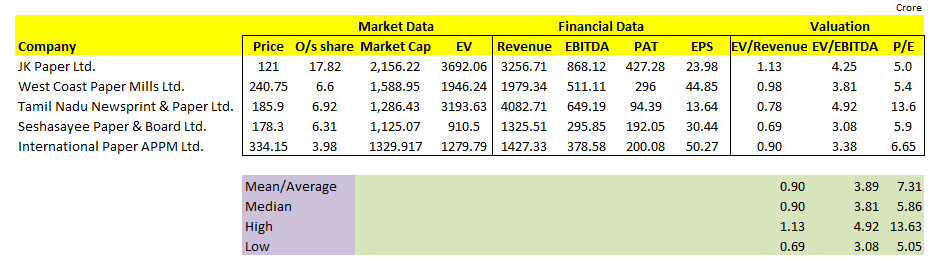
As we note from the above table, the general metric to look at are the simple mean, median, high and Low.
If the company multiples are above the Mean/median, we tend to infer that the company may be overvalued.
On the other hand, if the multiple is below the mean/median, we may infer that the company may be undervalued.
We can infer the following from the table.
Paper and paper product companies are trading at an average of 0.90x EV/Revenue multiple.
Lowest EV/Revenue Multiple is 0.69x and highest is 1.13x.
Paper companies trade at EV/EBITDA Multiple of 3.89x.
Average P/E of these comparable companies are 7.31x.
Seshasayee Paper & Board Ltd. looks undervalued from this analysis.
Advantages of trading multiples:
The main advantages of multiples are that they are relatively easy to use. Easy calculation makes multiples an appealing and user-friendly method.
The information required in trading multiples is easily available and no assumption and forecasting is needed.
Suggested Read : Stock selection criteria
Disadvantages of trading multiples:
This method is based on historic data. It doesn’t include company’s order book, new markets it plans to enter, new products and their potential, etc.
It is not useful when there are no comparable companies. Sometimes it can be difficult to find appropriate comparable companies.
Key Takeaways:
This valuation method is relatively easy to perform, and the data for them is easily available. You can get it from Annual report, Quarterly report, and Research report.
Trading multiples provide a reasonable valuation range, while other valuation methods such as DCF is dependent upon an entire array of assumptions.
These multiples can only be used with companies in the same industry and preferably of a similar size.
In order to get the latest updates on Financial Markets visit Stockedge









Statistics??
Hi Mayur,
Examples are given in the blog itself.
Thanks for reading!
Keep Reading!
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently fast.