Since trends are made up of numerous price swings, momentum is crucial in determining the strength of a trend. As a result, it’s crucial to recognise when a trend is slowing down and making trading divergences.
Although a decline in momentum does not always indicate a trend reversal, it does indicate that something is shifting, and the trend may consolidate or reverse.
The magnitude and direction of the price are referred to as price momentum. Trading professionals can better understand price momentum by comparing price swings.
Divergence trading can sometimes be intimidating for beginners. Not only do you need to understand the main categories, but they do not always indicate the expected result.
Making a trading decision based solely on divergences is never a wise one. Although strong, these patterns should only be used as a confirmation tool. What, however, are divergences?
Here, we’ll examine how to assess price momentum and demonstrate what trading this pattern in momentum can reveal about a trend’s direction.
What are Trading Divergences?
Simply put, divergences occur when a price moves in one direction while another indicator—typically an oscillating indicator—moves in a different direction.
In essence, you have a divergence if you observe the price rising and setting new higher highs while the oscillator is setting new lower lows. Here are some illustrations of the four most common types:
Types
Below are different types of trading divergences:
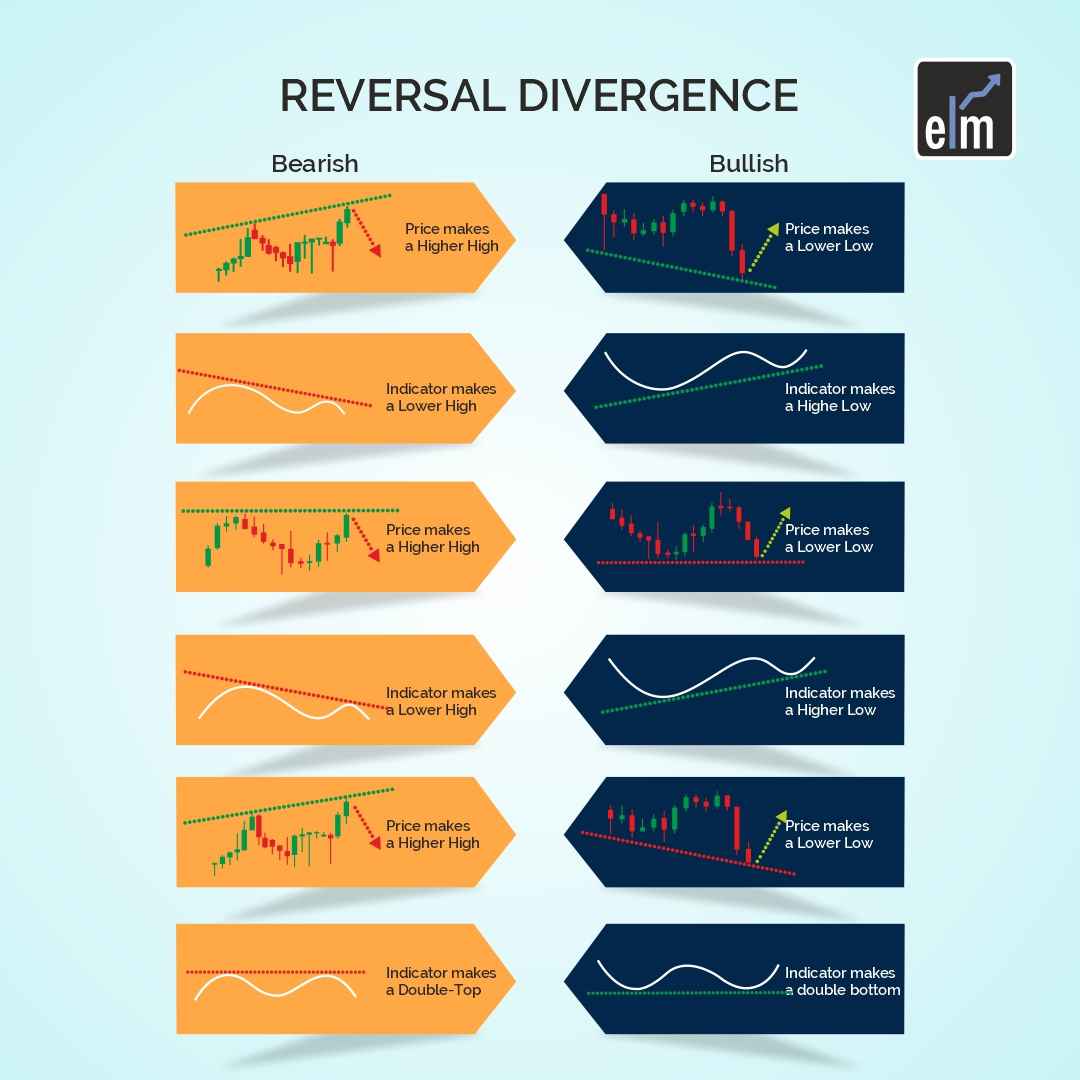
1. Bullish
A bullish divergence is the first thing we will notice. For this example, the oscillator will be the Relative Strength Index.
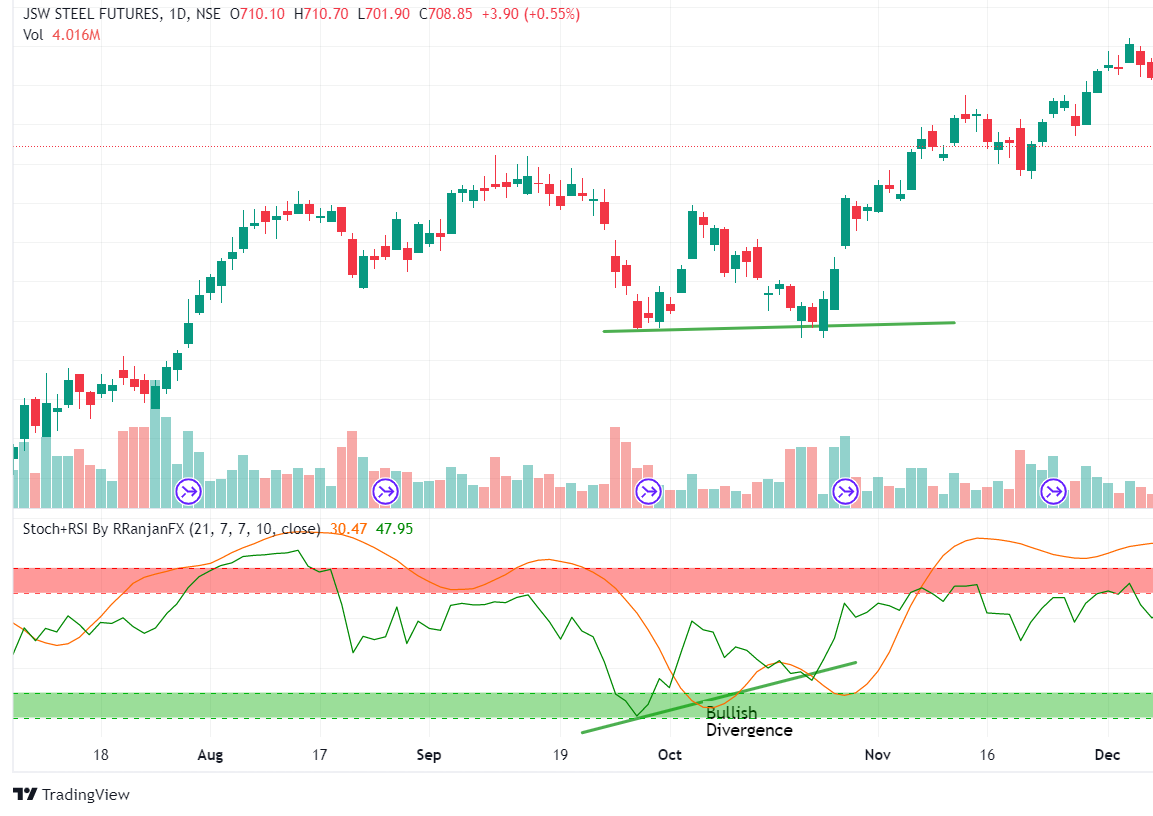
You’ll notice that there are recurring, similar patterns that are associated with divergences when you trade with them. Near the end of a downtrend is where you’ll typically find this in a typical bullish one.
According to this theory, there is a good chance that the price will reverse. Observe how the RSI has made higher lows while prices have made lower lows. Price behaved in the opposite way, testing a swing high and then the previous swing low before continuing to rise, which resulted in another, more pronounced regular bullish divergence.
2. Bearish
Let’s now look at a typical bearish divergence.
In essence, a trade with divergences that are bearish will indicate movement to the downside. Similar to how we see it from a regular bullish pattern near the end of a downtrend, we see it from a regular bearish pattern at the end of an uptrend.
The price has made a higher high (on this chart, it made a significant leap), but on the RSI oscillator, we have lower highs, which is the divergence that we observe. According to the theory, there is a good chance that the price will reverse to the downside.
As can be seen, trade with this pattern on the bearish bias led to a decline in prices and the beginning of a downward trend.
Hidden
The following are examples of hidden divergences.
These patterns merely indicate a divergence within a trend. These are signs that the trend will continue, whereas regular divergences indicate a reversal of trending price action in a trade.
3. Bullish Hidden
Take note of how we are in an uptrend in this instance of a hidden bullish pattern. In addition, we keep making higher lows while the RSI oscillator keeps making lower lows.
There is a high likelihood that the price will stay in the uptrend in a trade with hidden bullish divergence signals. Keep an eye out for the higher low that was formed at the arrow’s point because price action with candlestick patterns can confirm the continuation of the trend.
The bottom of this pattern looks like a tweezer. And as we can see, the price did rise further.
4. Bearish Hidden
Usually, the RSI oscillator has made higher highs while prices have continued to decline and have formed lower highs. This phenomenon is referred to as a hidden bearish divergence.
According to the theory, there is a good chance that the downward trend will continue. Once more, a hidden bearish pattern indicates that the downward trend is still in place.
We created this head and shoulders pattern solely to demonstrate how Price responded to the emergence of this well-known pattern and how the lower high failed to push past the right shoulder. That served as yet another confirmatory indicator of trend persistence.
How to Trade with Divergences?
We used the RSI oscillator in the aforementioned four examples. It is most likely the most typical oscillator type used to find these patterns. However, there are many oscillators, and each has advantages over the others: Stochastics, RSI, Chaikin Money Flow, Awesome Oscillator, Ultimate Oscillator, etc.
There are simply a lot of oscillators available for use. The RSI and Stochastics oscillators are the most widely used oscillators.
Dive into short-term momentum strategies with our course inspired by ‘The Ultimate Guide to Trading Divergences.’ Unlock trading success now!
Trading Example with RSI Stochastics
The Stochastic RSI is basically an indicator of an indicator. Where Stochastics measure the momentum of price and RSI measures the strength of the price movement, Stochastic RSI measures the momentum of the RSI.
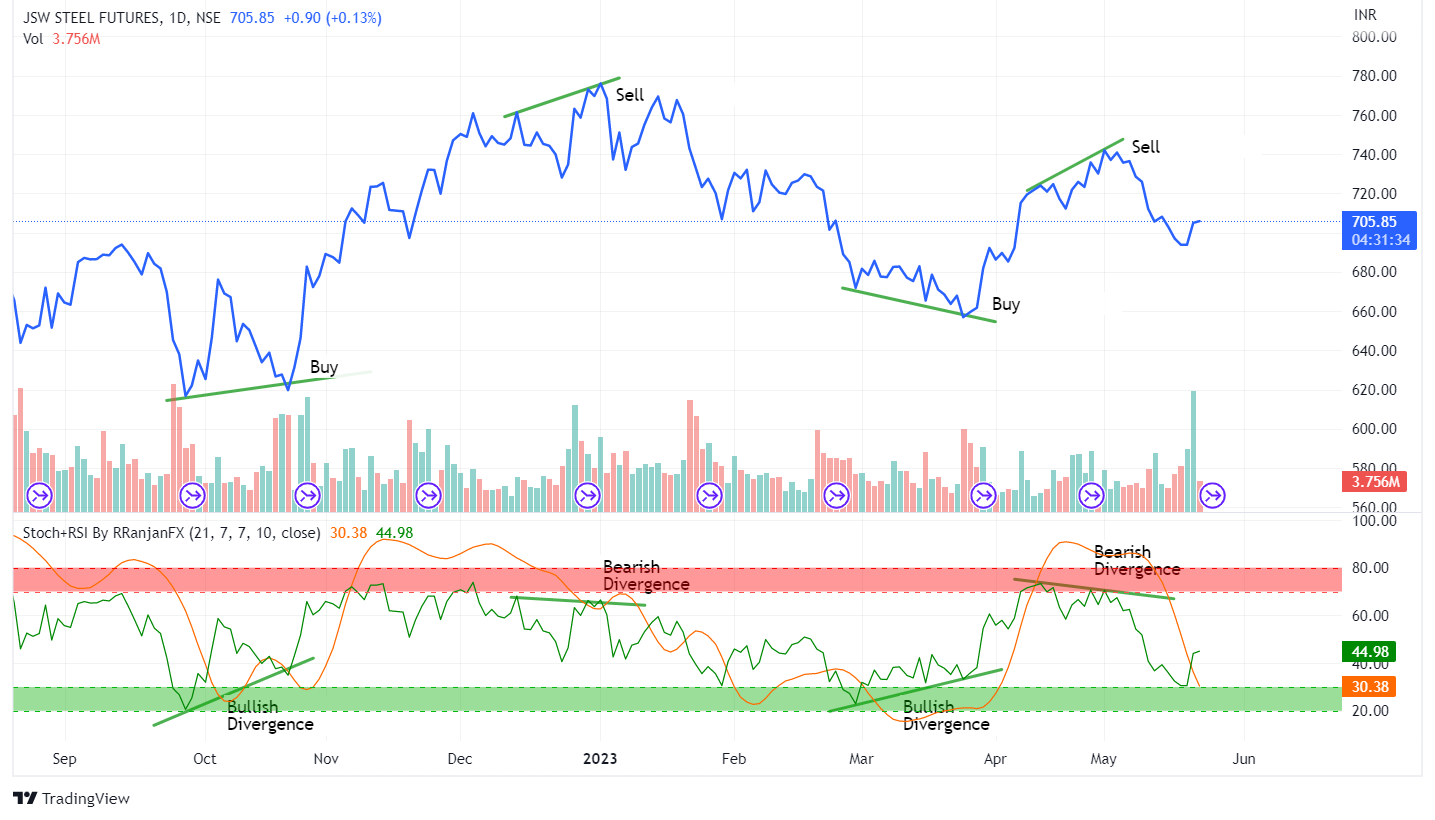
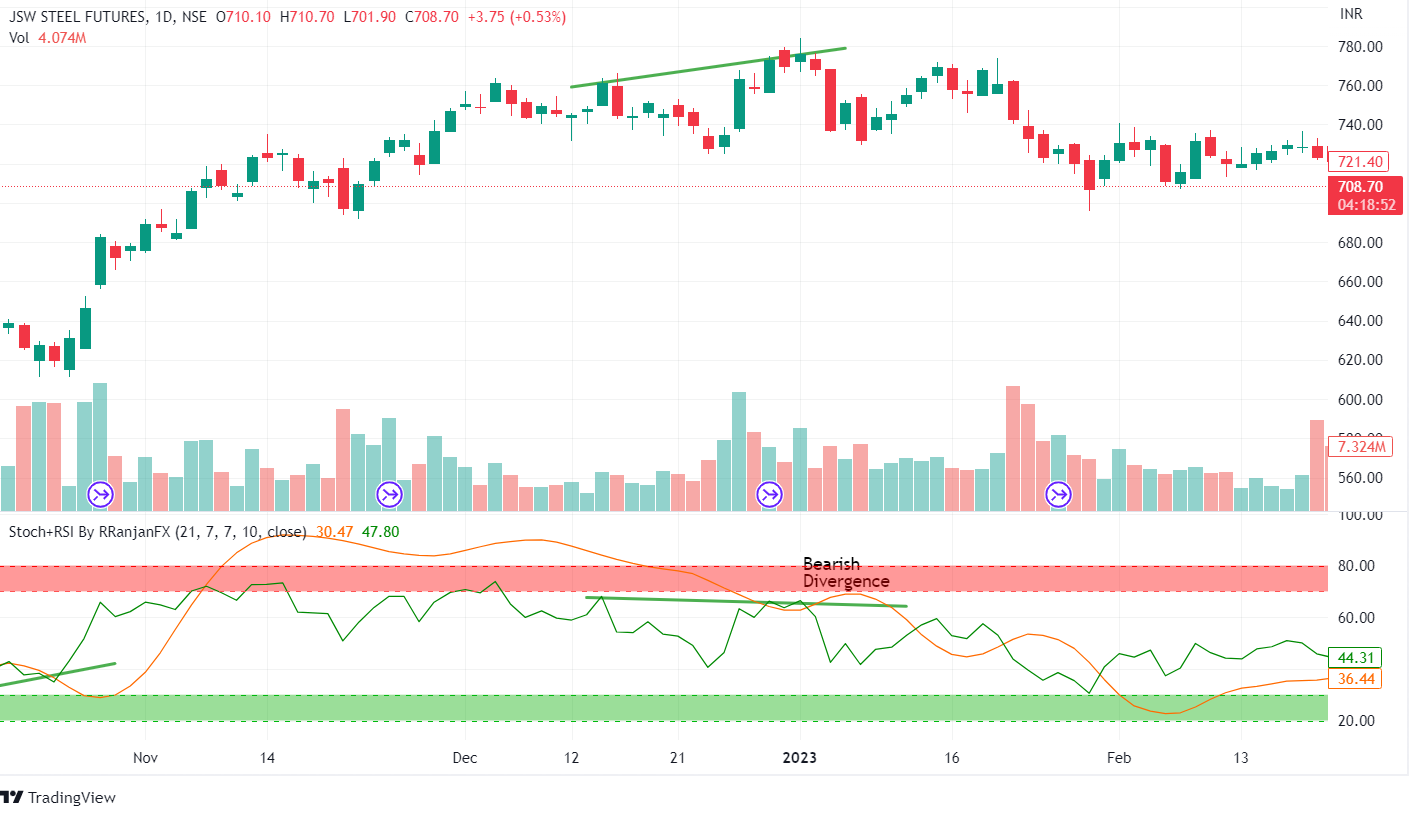
This is what is known as a typical bearish divergence. With the stochastic RSI, you would have seen that much more clearly than you would have with the RSI or stochastics.
As we can see from the above daily chart of JSW Steel, one can easily trade by analyzing bullish and bearish patterns.
Bottomline
Investors should confirm a trend reversal using a variety of indicators and analysis methods before acting solely on divergence, as is the case with all forms of technical analysis. These must be utilised in conjunction with another method of risk control or analysis because they won’t always be present during price reversals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is trade divergence?
Divergence occurs when an asset’s price moves against other data or in the opposite direction of a technical indicator, like an oscillator. This signals a possible weakening of the existing price trend and, in certain situations, the possibility of a price change in that direction.
What is an example of divergence in trading?
The simplest definition of divergence is when the price of the currency pair you are tracking deviates from the charts’ technical indicators. For instance, the indicator is reaching a lower high while the price on the chart you are viewing has just reached a new higher high.