What is an income statement?
An income statement is a part of financial statement of a company which emphasizes on showcasing the profit or loss of the company over a period of time. The other popular name to prepare income statement of a company is Profit and Loss Account or better known as Statement of Profit and Loss as per the Revised Schedule VI of the Companies Act, 2013.
Major highlights of Income Statement
- Revenues and other income are to be shown separately
- The expenses are to be classified by nature instead of function based classification earlier.
- Now, separate presentation of extraordinary and exceptional items is required.
- Separate disclosure of profit before tax, tax expense and profit after tax from discontinuing operations.
- Disclosure of Basic and Diluted EPS is required to shown on the face.
Income Statement Format
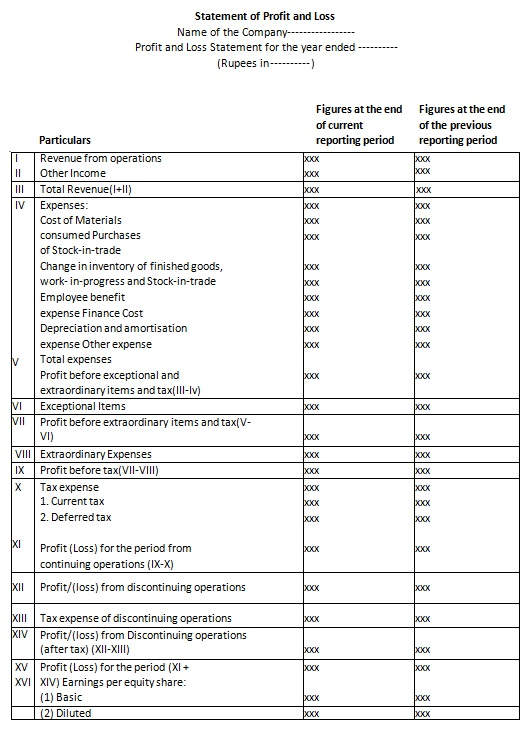
Income Statement Components
Statement of Profit and Loss comprises of the following main components-
Revenue: Revenue is the money received from the day-to-day operations of the company. It can be from two different operations- core and non-core. The income from core operations is shown as ‘revenue from operations’ and the income from non-core operations is shown as ‘other income’.
For example, in case of a manufacturer of steel, revenue from supplying steel to various companies is the core operation and will be shown under ‘revenue from operations’ and if the company is receiving any interest on its bank deposit, that will be shown under ‘other income’.
Cost of Sales: Cost of sales is the expense incurred by a firm for its direct expenses like labor, cost of raw material and manufacturing overheads. The subdivision of this cost can be different for different people.
Also Read: How to better analyse a company
For example, for a manufacturer, cost of sales is the cost of its raw material, labor and direct manufacturing overheads incurred in the production of goods. But the same cost for a retailer or for wholesaler would be the purchase cost of its merchandise while for service-oriented businesses, this cost can be the cost of rendering services.
Distribution Cost: This cost includes the cost of delivering goods from the place of manufacturing/business to the consumer’s place.
Administrative Expenses: Administrative expenses include the expenses that are not directly related to the functioning of the organization. These expenses are generally related to the management and support functions within an organization. Examples of administrative expenses include –
- Finance cost
- Depreciation and amortization
- Legal and professional charge
- Other expenses
Other expenses: This subhead includes all the other costs that are not included under any head mentioned above.
Tax Expense: The tax expense for the year typically includes the following two elements-
- Current tax: This is the tax expense that is due for the current year
- Deferred tax: Deferred tax arises due to difference in the income recognition between the tax laws and the company’s accounting methods.
Purpose of the Profit and Loss Account
The primary purpose of Statement of Profit and Loss is to showcase how much profit or loss a company has generated during the year. However, apart from this, there are various other purposes that the P&L account serves –
Comparative Study – Apart from knowing the profit/(loss) during a particular year, it is also important to know the profit/(loss) of the previous years for effective comparison of the revenue generated and for evaluating the growth prospect of the organization.
Evaluating the solvency of the company – A company with consistent losses year on year can be inferred as a company that is going to be insolvent soon. So, one should be very careful with companies that are consistently incurring losses.
Judging the financial strength of the company – A company who is consistently making efforts to increase its profits year by year is one who is financially very strong and is growing consistently.
Forecasting and Preparing budgets – When you know how much you have saved, you can make an estimate of how that money can be used. Similar is the case with companies. When an organization knows how much profit/(loss) it is making, it becomes easier for it to prepare a budget and helps in forecasting.
Example of a Profit and Loss Statement:
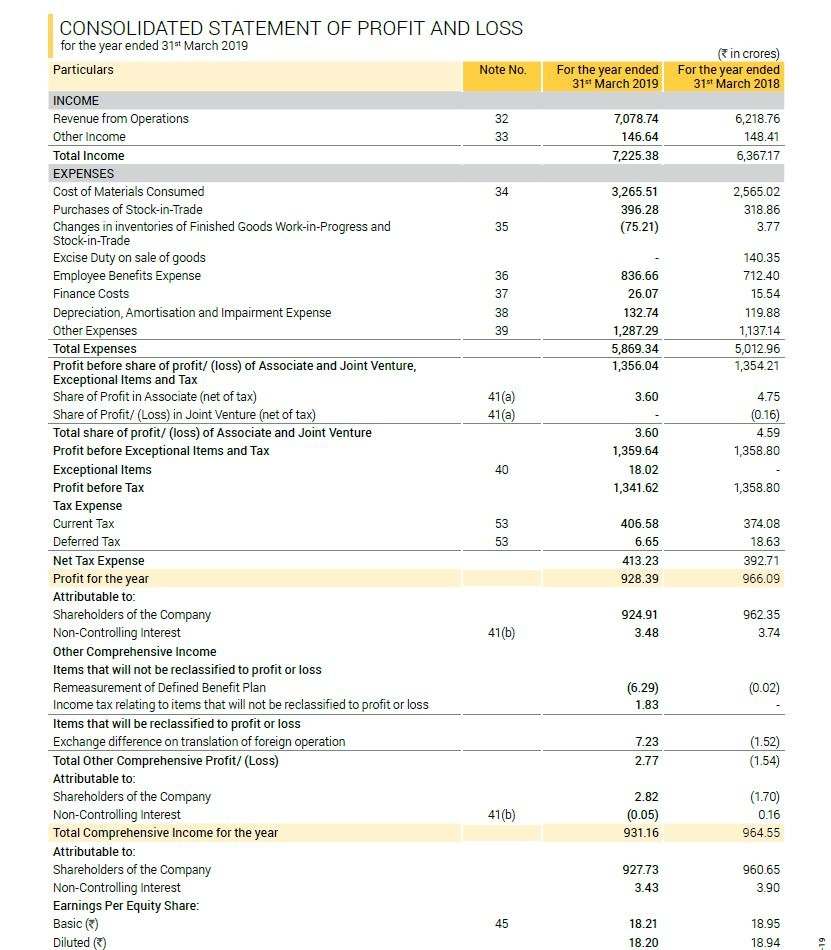
The image above is an excerpt from the annual report of Pidilite Industries Limited. It is a classic example of an Income Statement account filed by companies. Most Income Statements of Indian companies will look similar.
| Pidilite Industries Limited | ||
| PROFORMA OF INCOME STATEMENT: P&L ACC | 2019 | 2018 |
| Particulars | ||
| net sales | 7078.74 | 6218.76 |
| add: operating income | ||
| TOTAL INCOME | ||
| less: increase/decrease in stock in trade & wip | ||
| less: raw material &purchase of traded goods | ||
| less: employees cost | ||
| less: manufacturing & other expenses | ||
| less: power & fuel expenses | ||
| EBITDA/operating profit | 1368.21 | 1341.22 |
| less:depreciation & amortization | 132.74 | 119.88 |
| ebit | 1235.47 | 1221.34 |
| add:other income | 146.64 | 148.41 |
| less:interest | 26.07 | 15.54 |
| PBT | 1356.04 | 1354.21 |
| extraordinary income(losses) | -18.02 | 0 |
| taxes | 413.23 | 392.71 |
| PAT | 924.79 | 961.5 |
Here, the first entry shows the Income.
Under income, we show the amount of money the company could generate from its primary business, Sales.
Total income will include a combination of both sales and operating income. In this case, there is no operating income.
The second entry is the Expenses.
Under this, the cost of materials or the cost of goods sold is the largest expense for a company like Pidilite. This is followed by other expenses such as Employee costs, stock in trade, power costs, etc.
Subtracting the revenue from operations from the cost of goods sold/cost of materials and other operational expenses will get us the EBITDA or operating profit.
Whereas, Subtracting the EBITDA with depreciation and amortization expenses will get us the Gross Profit or the profit before tax value.
Further additions of other income and subtraction of interest and taxes will finally get us the Net Profit or Profit After Tax figure.
Difference between Income Statement and Profit and Loss Account
Many people get confused whether to prepare income statement is the same as Profit and Loss Account. Well, there is essentially no difference between the two. Both are different sides of the same coin. Call it Profit and Loss Account or the Income Statement or the Statement of Profit and Loss, all are same.
However, as per Schedule VI of the Companies Act, 2013, it is better to call it the Statement of Profit and Loss.
Difference between a balance sheet and an income statement
Although there many similarities between the two like both are an essential part of financial statements of a company and many components of Income Statement form part of Balance Sheet, there are still differences between the two.
Learn from Experts: How to Read a Balance Sheet
Represents
While the income statement shows the profitability of a company, balance sheet shows the financial position of the company, i.e. how many assets and liabilities does the company have.
Timing
Where the Income Statement reveals the results of the organization for a particular period of time (usually, one year), balance sheet reveals the status of the assets and liabilities of the firm as of a particular day.
Items reported
The balance sheet depicts the assets, liabilities, equity and loans of the company whereas income statement depicts the revenues and expenses of the company.
Use for management
The balance sheet is used by the management to check the liquidity of the organization and determine whether it is capable of meeting its obligations, whereas income statement is used by the management to analyze the results, find out if there is any deficiency in the organization and do the necessary corrections.
If you are new in the field of finance, then these financial statements like Balance Sheet, Cash Flow Statement, and Income Statement can seem daunting.
Use our Stockedge website to avail various Fundamental and Technical Scans of Financial Markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. When Should Income Statement Be Prepared?
An income statement is prepared at the end of an accounting period to reflect the company’s financial performance over that time. It shows how much revenue was earned and what expenses were incurred, ultimately revealing the net profit or loss.
2. Who Prepare Income Statement?
An income statement is typically prepared by accountants or financial professionals within a company. In larger organizations, it is handled by the accounting or finance department, while in smaller businesses, it may be prepared by the business owner or an external accountant.
3. Why Income Statement is Prepared?
An income statement is prepared to show a company’s financial performance over a specific period. It helps track revenue, expenses, and profit or loss, giving insights into how efficiently the business is operating and where improvements may be needed.
4. Where to Find Income Statement?
You can find an income statement in a company’s annual report, quarterly results, or financial statements section on its official website. For listed companies, it’s also available on stock exchange websites like NSE, BSE, or financial portals like StockEdge.







I being an engineering student, don’t have much idea about financial statements. This write-up helped me to understand the basic concepts of Income Statement.
Thanks Ankit and please keep sharing this kind of articles.
Dear Sir
I don’t undersstand about deferred tax. Could you explain about this.( I am not finance persons)
Deferred tax – Deferred tax arises due to difference in the income recognition between the tax laws and the company’s accounting methods.
Hi Karthik,
Deferred tax refers to the tax effect of temporary differences between accounting income that is calculated by taking into consideration the provisions of Companies Act, 2013 and taxable income that is calculated by taking into consideration the provisions of Income Tax Act,1961.
Thank you for reading!
Keep Reading!
Dear Sir
What you mean profit after tax from discontinuing operations. can you explain the content ?
Hi Karthik,
Profit (or Loss) from Discontinued Operations is a line item on an income statement of a company below Income from Continuing Operations and before Net Income. It represents the after tax gain or loss on sale of a segment of business and the after tax effect of the operations of the discontinued segment for the period.
Thank you for Reading!
Keep Reading!
Loving the info on this internet site, you have done great job on the blog posts.