Hindi: आप इस लेख को हिंदी में भी पढ़ सकते है|
Steel is a commodity that is used in our day-to-day life. It is used in constructing homes we live in, the cars we drive, the utensils we eat in, etc.
Steel finds usage in various sectors including construction and infrastructure, engineering, automobiles, etc.
It is an important engineering and construction material.
Steel is widely used all around the world because of its strength and it can be recycled over and over again without loss of its property. (Fact: Steel is roughly 1,000 times stronger than iron in its purest form, and it can be recycled without loss of its strength)
Steel is crucial in the development of the infrastructure of any economy.
Before going further, we must know some raw materials used in steel making.
- Iron ore:– Iron ore is the primary raw material used in the manufacture of steel.
- Limestone:– It is used by the steel industry to remove impurities from the iron made in blast furnaces.
- Met coal:- Metallurgical coal or coking coal is a grade of coal that can be used to produce good-quality coke. Coke is an essential fuel and reactant in the blast furnace process for primary steelmaking.
- Coal:– The primary fuel used by iron and steel producers.
- Crude steel:-Steel in the solid state which after melting, is suitable for sale or further processing. (Raw steel)
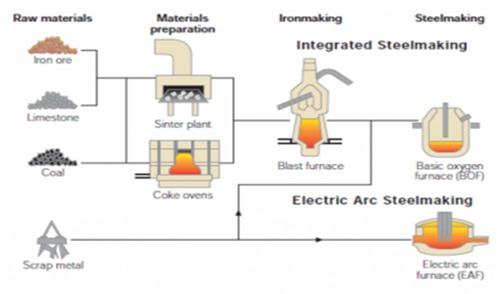
1. Steel Making Process:
There are 3 steps to making steel:
- Iron making
- steel making
- Continuous casting process.
a) Iron making:
This is the first step in making steel. Iron ore, coke, and limestone are melted in a blast furnace. After the melting process, it becomes molten iron also known as hot metal and Pig iron in the industry.
b) Steel making:
Steel is produced via two main routes i.e
- Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF):- In BOF, iron is combined with varying amount of steel scrap (less than 30%), after that oxygen is blown into the vessel causing a rise in temperature to 1700 degree Celsius. The scrap melts, impurities are oxidized and carbon content is reduced, resulting in liquid steel. (For BOF Firms, producing steel requires sourcing a variety of raw material namely iron, coal and limestone. Due to the necessity of raw materials, large-scale steel firms like to vertically integrate its production process backward into coal and iron ore mining too to reduce costs.)
- Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF):- EAF doesn’t involve iron making. This route reuses mainly existing steel (scrap). It uses some direct reduced Iron (DRI) and pig iron for chemical balance. The electric arc operates with an electric charge between two electrodes providing heat for the process. This furnace doesn’t require coke as raw material but depends on electricity. (EAF furnace only requires scrap steel as the major input. As long as scrap steel remains plentiful in the market, these firms have easy and cheap access to the required raw material.)
c) Continuous casting process:-
The last stage of producing steel is the continuous casting process where steel is converted into various steel products:
- Hot Rolled products:- Hot rolled product is widely used as a construction material and pipes in various industries.
- Cold Rolled products:– Cold Rolled products is used in making appliances, barrels and auto frames.
- Coated steel:- Coated steel is used in high end appliances, office equipment and automobiles exteriors.
- Electrical Steel Plates:- Electrical steel plates are used in transformers and motors.
- Wire rods:- Wire rods are used as automobile tire cord, wire for bridges etc.
- Stainless steel:-Nickel and chrome are added to steel to produce stainless steel products which are used in kitchen appliances, medical equipment etc.
2. World crude steel production:
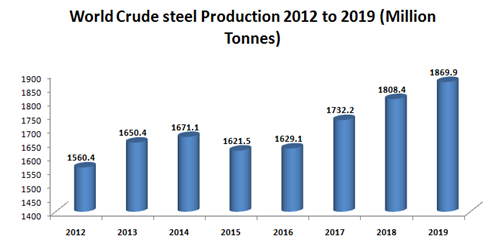
World crude steel production reached 1,869.9 million tonnes (MT) for the year 2019, up by 3.4% compared to 2018. Crude steel production contracted in all regions in 2019 except in Asia and the Middle East.
Asia produced 1,341.6 MT of crude steel in 2019, an increase of 5.7% compared to 2018.
3. Top 10 steel producing countries with market share:
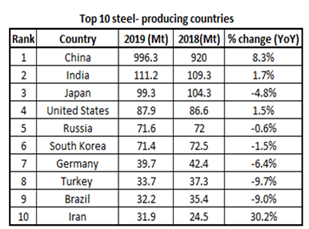
China remained the world’s largest crude steel producer with 996.3 MT up by 8.3% compared to FY2018. The country’s share in the global crude steel production has increased from 50.9% in FY 2018 to 53.3% in FY2019.
India crude steel production for FY2019 was 111.2 MT, up by 1.8% compared to FY 2018.
India ranked second on the global steel map, with the establishment of new state-of-the-art steel mills, continuous modernization and up-gradation of older plants, improving energy efficiency, and backward integration.
4. Indian steel industry:
Indian Steel Industry contributes ~2% to India’s GDP and employs ~5 lakh, people, directly and 20 lakh people indirectly.
Steelmaking requires iron ore, coking coal, and limestone as input ingredients, out of which India is self-sustaining in iron ore and limestone whereas a large part of the coking coal requirement of the domestic steel industry is being met through import.
Because of the shortage of domestic coking coal in quantity as well as quality, pig iron producers/BF operators in India have to significantly depend on imports. Nearly 85% of the coking coal is imported at present.
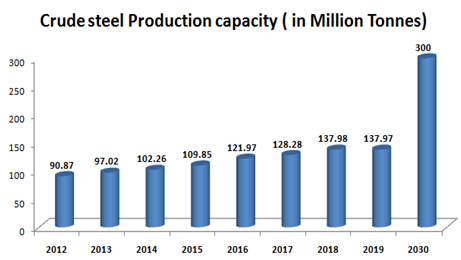
India’s steel production capacity has expanded rapidly over the past few years, growing at a CAGR of 6.1% from 90.87MT in FY2012 to 137.97 MT in FY2019.
5. Route-wise Crude Steel production capacity in FY19. (in Million tonnes):
Currently 47% of production capacity is through BA-BOF, 26% is through EAF and 27% is through IF.
The national steel policy 2017 has envisaged achieving up to 300 MT of production capacity by 2030-31. Out of the total capacity, the BF-BOF route is expected to contribute 65% of capacity, while the remaining 35% is expected to be contributed from EAF and IF route. India would need to invest 10 Lakh crore (US$ 156.08) billion by 2030-31.
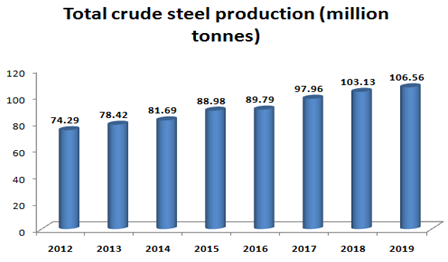
Steel production in India has been growing at a fast pace. The rapid rise in production has resulted in India becoming the 2nd largest producer of crude steel during 2018, from its 3rd largest status in 2017. India surpassed Japan to become the World’s second-largest steel producer.
Total crude steel production in India has increased to a CAGR of 5.3% during FY12-19, with the country’s output reaching 106.56 MTPA in FY2019.
The steel manufacturing output of India is expected to increase to 128.6 MT by 2021, accelerating the country’s share of global steel production from 5.9% in 2019 to 7.7% by 2021.
6. Total Finished steel Production and consumption (In million tonnes):
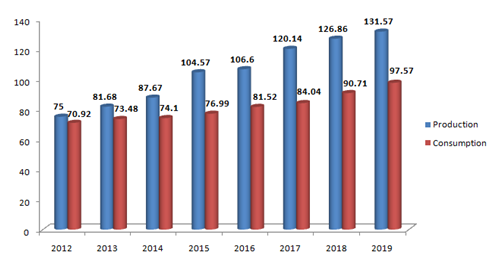
In FY2018-19, production of total finished steel was 131.52 MT, a growth of 3.7% over last year.
India’s finished steel consumption grew at a CAGR of 4.7% during FY12-FY19 to reach 97.57 MT. India is the 3rd largest finished steel consumer in the world after China & USA and is expected to surpass the USA in terms of steel consumption. India’s finished steel consumption is anticipated to increase to 230 MT by FY2030- 31.
Steel is going to witness a huge demand driven by affordable housing (construction in urban and rural areas), expansion of railways network, the opening of the defense sector for private participation, and the growth in the automobile sector Going Forward.
7.Import and Export of Finished steel:
In 2018-19, India exported 6.36 MT of finished steel. During the same period, the country’s finished steel imports reached 7.84 MT.
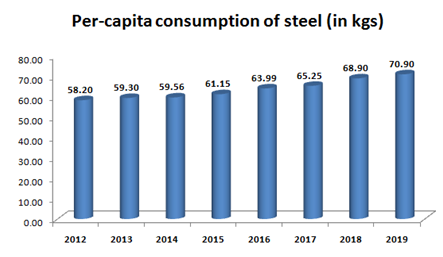
India’s per capita consumption of steel grew at a CAGR of 3% from 58.20 kgs in FY2012 to 70.90 kgs in FY2019. The level of per capita consumption of steel is treated as an important index of the level of social-economic development and living standards of the people in the country.
The National Steel Policy aims to increase per capita steel consumption to 160 kgs by FY2030-31. It is expected that consumption per capita would increase supported by rapid growth in the infrastructure sector, rising expansion projects in railways, airport,s etc.
8. Government Initiatives:
Government initiatives in the Steel industry are as follows:
- The Government approved the National Steel Policy (NSP) 2017 on May 3rd. The NSP is in step with the government’s long term vision to give thrust to the steel sector. National Steel Policy 2017 envisages 300 MT steel-making capacity and 160 kgs per capita steel consumption by 2030-31.
- 100% FDI through the automatic route allowed in the Indian steel sector.
- The government hiked the export duty on iron ore to 30% ad valorem on all varieties of iron ore (except pellets) to ensure supply to domestic steel industry.
- Ministry of Steel has issued necessary direction to the steel companies to frame a strategy for taking up more Research and Development (R&D) projects by spending at least 1% of their sales turnover on R&D to facilitate technological innovations in the steel sector.
- Government introduced Steel Scrap Recycling Policy aimed to reduce import.
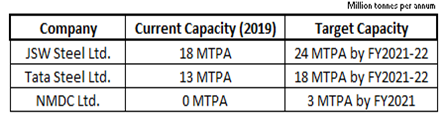
9. Capacity expansion by Companies:
Companies in the steel industry are investing in expanding their capacity for future growth.
Capacity expansion by companies for the next three years:
10. Steel demand Drivers:
The steel industry derives its demand from other important sectors like infrastructure, aviation, engineering, construction, automobile, etc.
- Capital Goods:- The capital goods sector accounts for 11% of steel consumption and is expected to increase 14-15% by FY2025-26 and has the potential to increase in tonnage and market share.
- Automotive Industry:- The Automotive industry accounts for around 10% of demand of steel in India. It is forecasted to grow in size to US$ 260-300 billion by 2026. Demand from the sector for steel is expected to be robust.
- Infrastructure sector:- The Infrastructure sector accounts for 9% of steel consumption and expected to increase 11% by FY2025-26. Because of rising investments in infrastructure, the demand for long steel products would increase in the years ahead.
- Railways:- laying of tracks and construction of foot over bridges, rail coaches, railway stations will also drive the steel demand.
- Airport:-The number of operational airports stood at 103 as on 31st March 2019.. Under union budget 2020, Government is targeting 100 more airports by FY2024. Development of new airports in Tier-II city would sustain consumption growth.
- Oil and Gas:– India’s primary energy consumption of oil and gas is expected to increase to 10 mbpd and 14 bcfd, respectively, by 2040.. Under budget 2020, Government plans for the expansion of National Gas Grid to 27,000 Km from the present 16,200 Km. this would lead to an increase in demand, providing a lucrative opportunity to the steel industry.
Bottomline:
- Easy availability of low-cost labour and presence of abundant iron ore reserves make India competitive in the global Market.
- Companies in the steel industry are undertaking modernisation and expansion of plants to be more cost efficient.
- Growing demand in the construction industry, Infrastructure development, automotive sector, oil and gas sector and rising demand for consumer durables and capital goods will drive the growth of steel industry.






Thanks for sharing benificial information about steel making ,casting process,top 10 steel producting companies in market,import and export of steel.