Many of us want to invest in instruments which are not very risky and generate good risk-free returns. Here comes the concept of investing in Fixed Maturity Plans (FMPs) funds in order to get a reasonably predictable return with lower tax liability if invested for certain longer period.
Many also want to invest only into government bonds or papers being less risky then Equity for their Financial Planning and Wealth Management.
Thus for each of them we have a solution called Fixed Maturity Plan.
To select which type of fund you should invest in, download Kredent Money App.
What is Fixed Maturity Plans?
All of us are fairly knowledgeable about Fixed Deposits and its returns and the process involved but not many people know about FMPs and its working thus today we will discuss about it in detail.
Fixed Maturity Plan as the name suggests primarily invests in fixed income instruments that have a pre-defined tenure. The pre-defined tenure can range from 30 days to 5 years but the most common tenures are 30 days to 180 days, 370 and 395 days.
It’s an investment option which allows investors to choose their investments on the basis of their time horizon and their cash flow requirements.
These are closed-ended mutual fund schemes with fixed maturities.
Benefits:
- Fixed Maturity Plans invests mainly in commercial papers, corporate bonds, money market securities, government issued securities, non convertible debentures of highly rated companies.
- These plans invest in fixed maturity instruments which allow it to yield a relatively fixed rate of return over the tenure i.e. they have a minimum exposure to interest rate risk.
- These plans invest in highly rated instruments thus minimizing the risk of default. Also the liquidity risk is also minimal in these plans.
- Fixed Maturity Plans acts as a good balance to the investor’s portfolio as they offer a stable return. During times of market volatility these plans acts as a good balance to the overall portfolio.
- These plans invest for fixed maturity allowing the investors to choose maturity period according to their investment horizon and cash flow requirements.
- Fixed Maturity Plans are closed ended funds which are made available only during the initial offer and the redemption can only be made during the maturity. However the investors can sell their funds units in the market if the funds are traded on organised exchanges.
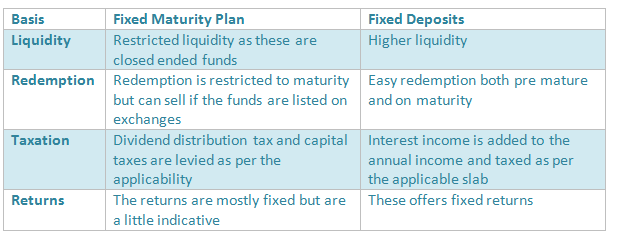
Difference between Fixed Maturity Plan and Fixed Deposits (FDs):
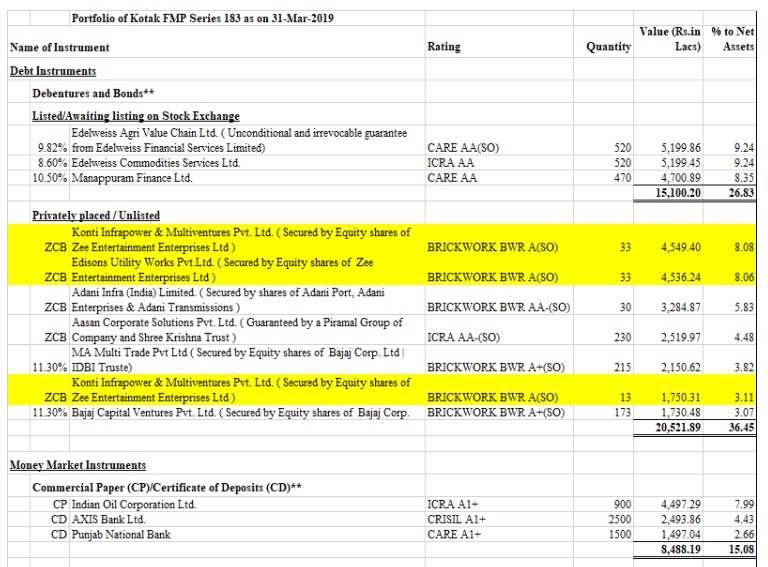
For instance, below is a fund holding of Kotak FMP if we analyse the portfolio, we can infer that the yellow marked instruments of ZEE group were also highly rated by the rating agency but they have been facing issues in the current situation.
So this concludes that although the investment was in highly rated instrument but still default risk cannot be completely ignored.
Limitations:
- Fixed maturity plans can only be redeemed on maturity unless the funds trade on exchanges. Thus has low liquidity.
- Although these have minimal exposure to default risk but the risk of default cannot be completely ignored (which is been seen in some of the current scenario like IL&FS, Zee group etc). Thus returns are not fixed or guaranteed.
- The rates in an FMP are locked as it’s a close ended scheme. Thus even if interest rates rises due to change in monetary policy still the benefit of high interest rates are not passed on.
Fixed Maturity Plan vs other Debt Funds:
Fixed maturity plans are also a type of debt funds but also differ from the other debt funds. Other debt funds are of different types like:
- Dynamic debt funds i.e. the fund in which the fund manager keeps changing the composition according to the interest rate regime.
- Income funds i.e. these funds invest in different maturities by taking interest rate into account.
- Short term and Ultra short term funds which invest in instruments with short term maturities.
- Liquid funds which invests for not more than maturity of 91 days.
- Gilt funds are ones that invest in government securities etc.
Hence there are different debt funds with different focus i.e. the debt funds explained above are specific funds catering to government and short term only. But fixed maturity plans invest in high rated instruments with pre-defined tenure and try to generate returns more than other debt funds. FMP are not specific funds but invests in the instruments which match the criteria.
Who should invest in FMPs?
Fixed Maturity Plans are suitable for investors who can invest money with a lock in period. The investors who want to earn low risk return can invest in these plans as they offer better return than fixed deposit which is fixed and better risk return basis than equity.
FMPs value is reflected by the fund NAV (i.e. total assets minus total liabilities divided by the number of outstanding shares) which is adjusted daily. Hence investor manages himself with the daily fluctuation in the NAV because the interest rate movements in the economy can affect it.
How returns from FMPs will be taxed?
In Fixed Maturity Plan, the taxation depends on the option of its investment- dividend or growth. With the dividend option, the dividend distribution tax (DDT) has to be borne by the investors whereas with the growth option the returns of the plan are treated as capital gains.
In case of capital gain, it is treated as short term if the investments are held for less than 3 years and rest is long term. Unlike all other debt funds, FMP are also taxed on the basis of time horizon of the holding.
Short term capital gains are taxed as per the applicable tax slabs and the long term gains are taxable at 20% with indexation. Although the FMP have similar tax rates with other debt instruments like gilt funds, short term debt funds but they are capable of generating more returns than the others.
How is FMP taxed over FDs?
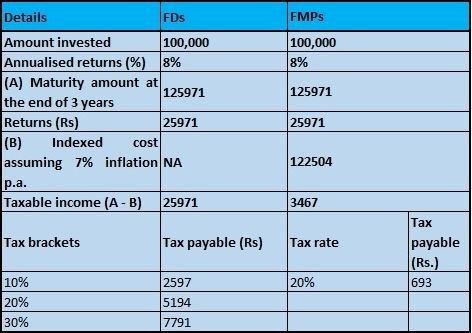
Source: SBI MF
Key takeaways:
- The investor should define his investment tenure before investing in FMP.
- The investor should define his cash flow needs which will help him better understand the FMP he requires.
- The investor should acknowledge the illiquidity of the fund in terms of redemption before maturity or unless the funds are traded on recognised exchanges.
- The investor must be willing to take risk into account in case of default of any instrument (like IL&FS and Zee in current situation).
- The investor must be willing to take risk as compared to fixed deposit because due to the interest rate changes and default of the instruments, FMP can be more risky than fixed deposit.
- The investor should choose in terms of the investment option he needs i.e. dividend or growth.








Hey!
Amazing Post.
Thanks for sharing this amazing post.
Hi Michael,
Thank you for reading!
You can read more Financial Planning blogs here.