The goal of any investor is to increase wealth and maximize profits. But there’s no one right method to accomplish it. The secondary market offers a variety of shares that can be traded and increase your wealth.
The distinction between an equity share and a preference share is often unclear to investors. Selecting between equities and preference shares is one of the most important choices you’ll have to make while investing in the stock market.
Companies can issue two types of securities: preference shares and equity shares. Their ownership rights and the advantages they provide to shareholders, however, are different. Making wise investment decisions as an investor requires knowing the distinction between stock and preference shares.
Let us discuss the differences between equity and preference shares:
Table of Contents
What are Equity Shares?
To raise money, companies sell these shares to the general public. The money thus raised is put toward a start-up’s expansion.
Equity shares are a long-term source of funding for businesses because they are non-redeemable. The corporation retains the share capital throughout, and it is disbursed upon winding up.
The real risk-takers in a corporation are the equity shareholders since they receive the remaining shares during liquidation. Indeed, it is also the source of the distinction between preference and equity shares.
In addition to having the ability to vote, owners of equity shares are also eligible to claim business assets and collect excess.
Some of the features of Equity shares are as follows:
1. Ownership Rights
The genuine proprietors of a firm are its equity stockholders. Investors gain a proportionate ownership position in the company by acquiring equity shares.
2. Voting rights
Equity shares come with voting rights, and their holders are also entitled to receive surplus and claim company assets.
3. Dividend distribution
Dividends, or a percentage of the company’s profits given to shareholders, are payable to equity shareholders. Nonetheless, the company’s board of directors has the last say over dividend payments.
What are the Risks Associated with Equity Shares
Below are some of the risks associated with equity shares:
1. Business and Performance Risk
The financial stability and future business prospects of the company are closely linked to the success of its equity shares. The value of shares can be impacted by bad management choices, recessions, or issues unique to a given industry.
2. Market volatility
Market swings can affect the value of stock shares. Price volatility can be caused by a number of reasons, including investor sentiment, market conditions, and economic considerations.
3. Market Liquidity
A stock’s liquidity may be low, which makes it difficult to purchase or sell shares at the prices you want. This may be especially important for smaller businesses or those whose stock isn’t exchanged as frequently.
What are Preference Shares?
Shareholders who own preference shares are entitled to fixed dividends. Dividends to preferred shareholders are paid out prior to dividends to equity shareholders. Preference shareholders, however, are not granted the ability to vote or take part in the company’s decision-making processes. Preference shares are comparable to debt in terms of priority and capital repayment.
Preference shares are issued by businesses to raise money. A particular kind of preference stock is entitled to dividend arrears. Preferred shareholders are entitled to the company’s assets before common shareholders in the event of bankruptcy. You have the option to convert your preference shares into equity shares at any time.
Some of the features of preference shares are:
1. Fixed dividends
The company’s profits are subject to a priority claim made by preference shareholders. Their payout rate is frequently predetermined, and they get dividends before equity stockholders.
2. Limited voting rights
Preference shareholders typically have either no voting rights or very little voting rights. Generally speaking, common or equity shareholders have the ability to vote.
3. Preference in asset distribution
Preference shareholders have a greater claim on the company’s assets than equity shareholders have in the case of liquidation or bankruptcy. Prior to any payment to equity shareholders, they receive their fair part of the assets.
What are the Types of Preference Shares?
Preference shares come in various types, each with its own set of characteristics and features. The main types of preference shares include:
1. Cumulative Preference Shares
In the event that the business is unable to pay dividends during a specific time frame, the unpaid dividends accrue and need to be settled before any dividends are given to equity shareholders.
2. Non-Cumulative Preference Shares
Unpaid dividends do not accumulate. If the company skips paying dividends in a specific period, shareholders holding non-cumulative preference shares forfeit their right to those dividends.
3. Participating Preference Shares
Participating preference shareholders are entitled to receive fixed dividends as well as a portion of any remaining earnings following the distribution of dividends to other shareholder classes. They could make more money thanks to this functionality.
4. Convertible Preference Shares
After a given amount of time, the shareholder owning these preference shares may choose to convert their holdings into a predetermined number of common shares. This offers the chance to profit from possible capital growth.
5. Redeemable Preference Shares
Companies may choose to redeem or purchase back these shares at the end of a set time frame. This gives the business flexibility and enables it to reimburse shareholders for their initial investment.
Differences Between Equity and Preference Shares
Below are the differences between equity and preference shares:
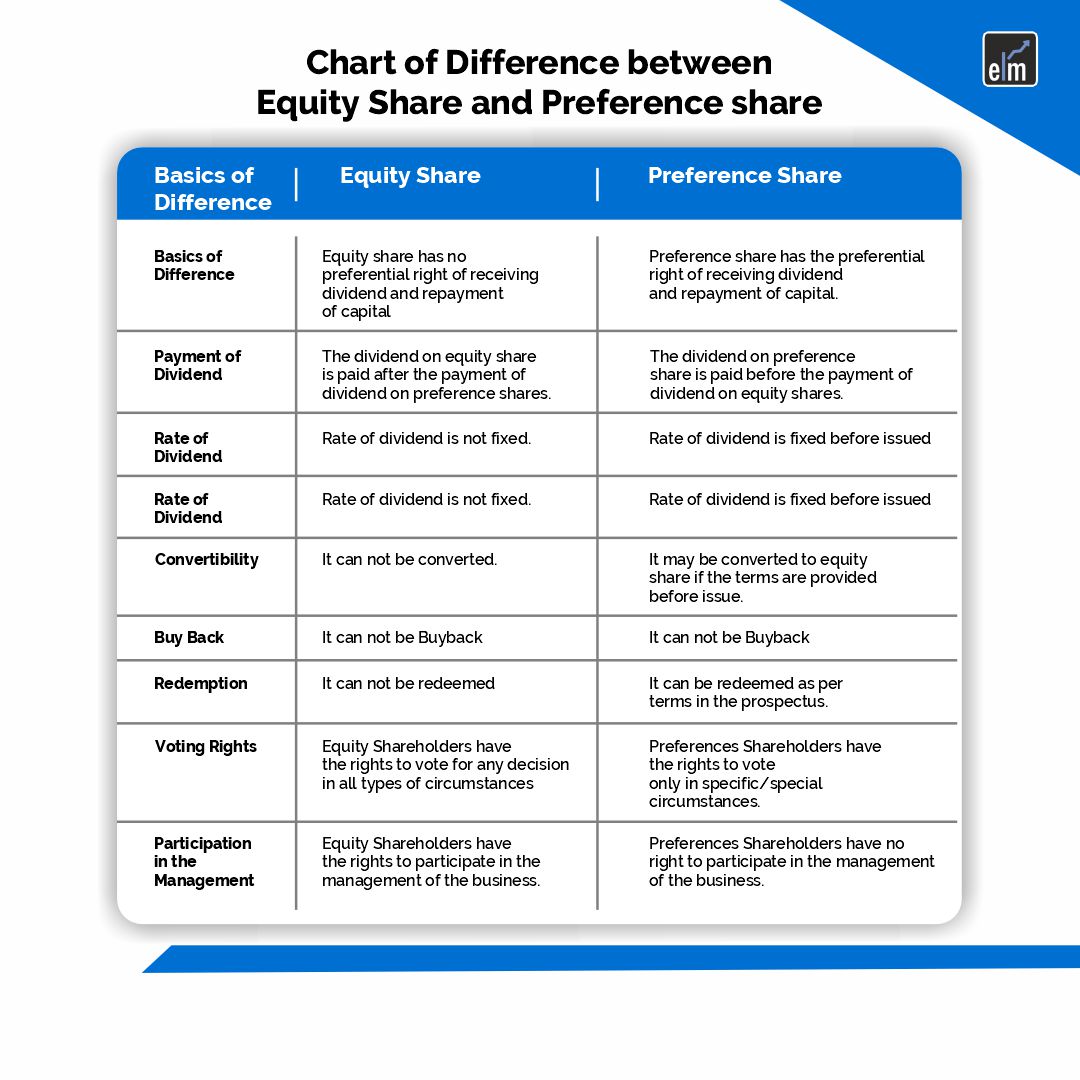
1. Ownership and Voting Rights
Typically, equity shareholders are entitled to vote on corporate issues, which enables them to take part in important choices made at shareholder meetings. Generally, the number of votes is equal to the total number of shares owned.
In general, preference shareholders are not allowed to vote, or their ability to vote may be restricted. The company’s equity shareholders continue to have control.
2. Dividend Distribution
The distribution of dividends on equity shares is left up to the board of directors of the company and is not fixed. Profits are divided among equity stockholders after all other commitments are fulfilled.
Fixed dividends are payable to preference shareholders, and unpaid dividends on cumulative preference shares may accumulate and need to be settled before dividends are disbursed to equity shareholders.
3. Risk and Return Profile
Although equity stockholders may see greater gains, they also carry a greater degree of risk. Their profits are based on how well the business performs as well as how much the share price increases.
Because preference shareholders receive set dividends, they are less risky than equity stockholders. Their returns, however, might not be impacted by the company’s outstanding performance and are restricted to the predetermined rate.
4. Considerations for Investors
Through capital appreciation, equity shareholders may profit from the company’s outstanding success. When all responsibilities are fulfilled, they take part in the excess earnings.
Participating in preference shares gives shareholders an extra revenue stream by allowing them to partake in excess earnings over the predetermined dividend rate.
Bottomline
Both preference stocks and equity stocks have advantages, but they do so in different ways when you compare them. Make careful to choose the best investment option based on your financial objectives and risk tolerance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between preferred stock and equity shares?
Although preferred shares are equity, they are really hybrid assets that fall in between bonds and stocks. They have ratings from the main credit rating agencies and provide more consistent income than ordinary shares.
What is the difference between preference shares and equity debentures?
Preferred shares, or preference shares, are a type of equity instrument that is recognized for bestowing onto their owner’s preferential rights in the case of an underlying company liquidation or dividend payment. A debenture is an asset-free debt security that is issued by a government agency or business.
What is different between equity and shares?
Owners invest capital in the company, which is known as equity, while shares are the portion of equity that is divided. While share relates to the money contributed to the business, it refers to the value of the business overall.
For Stock Market Related Queries, Visit StockEdge