The currency pair consists of two currencies. In the case of foreign currency transactions, one will always be sold while the other will be bought and vice versa. For example, Mr A wants to convert X amount of INR (Indian rupees) into USD.
For this, he will need to sell the amount in INR and buy-in USD. On the other hand, if Mr A wants to convert USD into INR, he will sell USD and buy INR.
What is Base & Term Currency?
The above pair denotes the number of units of home currency per unit of foreign currency. For example if the quote is 1 $ = Rs. 67/-, this means that to buy a $, you need Rs. 67. This signifies a DIRECT QUOTE in India-usd inr rate
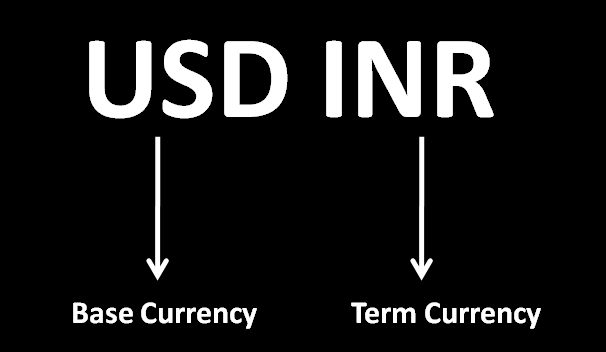
Direct Quote–USD INR Conversion
Based on the above example, always keep in this mind, that in the case of a direct quote, foreign currency transactions are always listed as the base currency and the domestic/ home currency as the term currency.
Indirect Quote–Currency USD to INR
An indirect quote is just the opposite of a direct quote. In this case, the home currency is always listed as the base currency, and the foreign currency transactions are the term currency.
For example, the indirect quote will be INR 1 = USD 0.01503. Hence, it is the value of $ in the Indian rupee.
Note: Direct quote is more common than an indirect quote.
Two-way Quotes

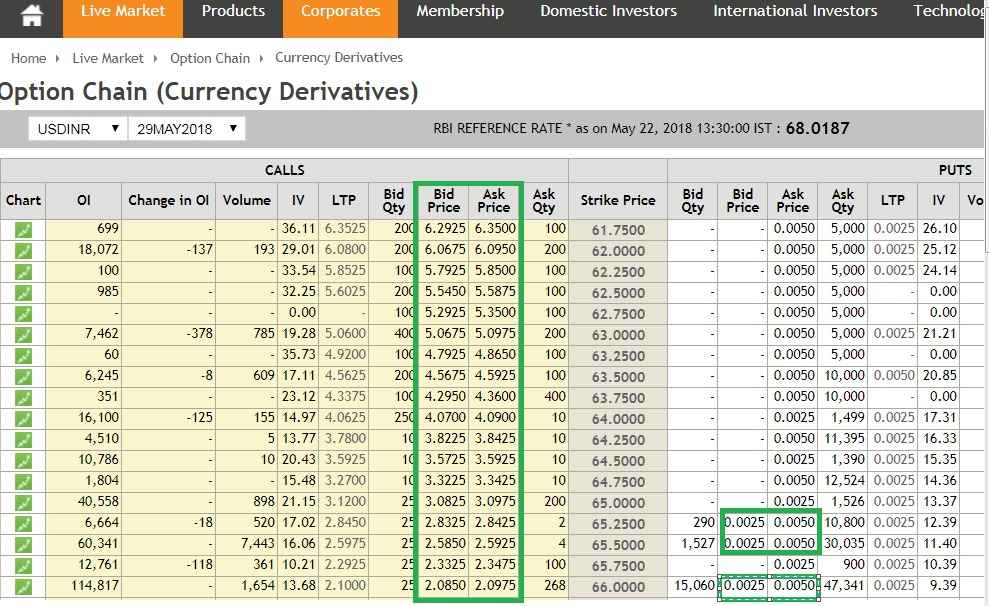
You will always find the quotes coming with two quotes for buy/BID as well sell/ ASK.
In the above figure, you will see that the USD INR rate is 67.5000/67.5025. This means the following:
The market participant bids Rs. 67.5000 to buy USD and ask Rs. 67.5025 for selling USD.
The difference between the BID-ASK rate (67.5025 – 67. 5000 = 0.0025) is called the “Bid-Ask Spread.”
Note: The narrower the bid-ask spread the better is the price quotation as it ensures more liquidity in the market. In case you are getting a wider spread quotation, then either the currencies are not well traded or demand & supply is not very good.
Price Quotation Norms
The prices can be quoted either up to 2 decimal points or 4 decimal points.
For example: In the figure below, you will find that the maximum prices are quoted up to 4 decimal points.
What is Currency Appreciation & Depreciation?
Whenever the currency is traded whether in the Over Counter (OTC) market or Exchange-traded market, the currencies rates fluctuate which causes an appreciation/ depreciation in any one of the currencies from the pair.
Appreciation – When the value of a currency increases, it is called appreciation. This means that when more of a term/ quotation currency can be bought using one unit of the base currency, it is called currency appreciation.
For example, the quote of USD INR moves from Rs. 65.00 to Rs. 65.65, we say that USD has appreciated by INR 0.65, this means now you have to pay more for purchasing 1 unit of the base currency.
Depreciation – When the value of a currency falls, it is called depreciation. This means that when we need less term/ quotation currencies to buy one unit of the base currency, it is called currency depreciation.
For example, the quote of USD INR moves from Rs. 65.65 to Rs. 65.00, we say that USD has depreciated by INR 0.65, which means that now you will pay less to buy one unit of the base currency.
You may also read about Gain in Indian Currency to know how you can be benefited from currency appreciation.
Exchange Rate Arithmetic
In this, we will learn how to determine the exchange rates when the direct quote for the transaction is not available.
For example, The quotes are as follows:
USDINR = 66.50/ 51
EURUSD = 1.1400/ 10
Find the cross rate for EURINR
For finding out the cross rate for EUR-INR, you simply need to multiply the rates in the following manner:
= Bid rate* Bid rate/ Ask rate* Ask rate
= 66.50 * 1.14/ 66.51*1.141
= 75.81/ 75.88
Bottomline:
Hope we have been able to justify the concept of foreign currency transactions in the most simple manner.
In case of any queries, do not forget to comment below.
Also, follow our blog page to read on related topics.
In order to get the latest updates on Financial Markets visit Stockedge
Happy Learning!!