Investing in stocks? When you decide to invest your money rather than just saving it, you should also keep in mind that there is not just one investment style.
So, do you know your investment style? You probably haven’t given it much thought if you’re like most investors. Nonetheless, learning the fundamentals of the significant investment types is one of the quickest ways to make sense of the thousands of products accessible today.
When it comes to achieving your investment goals, asking the appropriate questions might help you select which road to take.
For example, Are you a risk-taker or a risk-averse person? Do you want to make short-term or long-term gains? Are you considering investing independently, using a Robo-advisor, or hiring an advisor?
This type of analysis might assist you in matching your needs to your investment approach. With that in mind, here are ten styles of investing in stocks, each with its own unique speciality-
Top 10 Styles of Investing in Stocks:
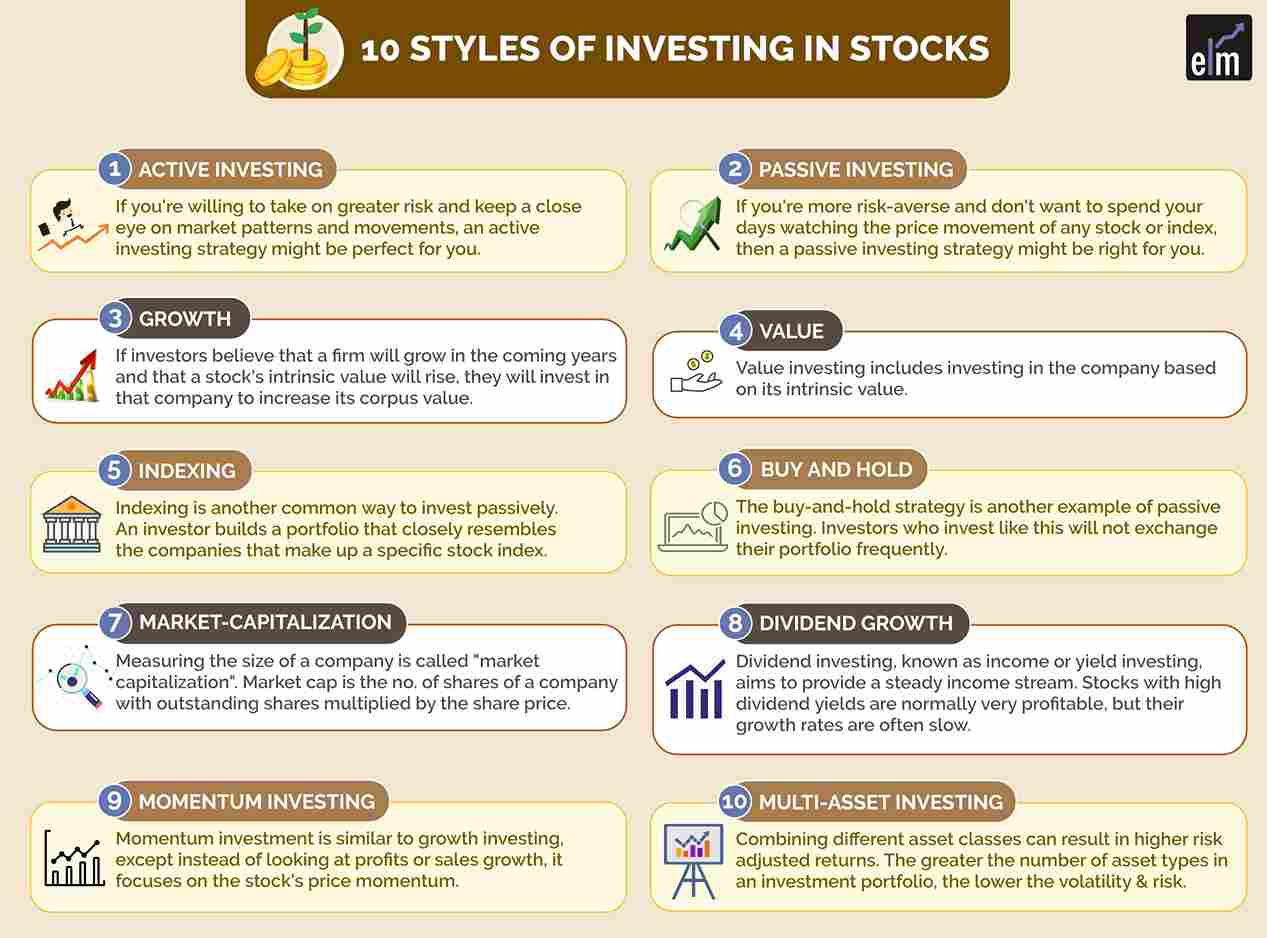
1. Active Investing
If you’re willing to take on greater risk and keep a close eye on market patterns and movements, an active investing strategy might be perfect for you for investing in shares.
Active investment is frequently done by those persons who are more concerned with the present than the future.
This approach involves picking specific stocks and using market timing to outperform the market to make short-term gains.
Active investing frequently comes with significant tax and transaction cost implications because it includes more frequent and short-term buying and selling.
2. Passive Investing
If you’re more risk-averse and don’t want to spend your days watching the price movement of any stock or index, then a passive investing strategy might be right for you.
Passive investors put their money into investments over a long period.
Passive investors build portfolios that track a market-weighted index rather than trying to time the market like active investors.
Because of the diversification, tracking an index frequently results in lower risk and cheaper costs due to low turnover.
Difference between Active and Passive Investing-
- Active investing is a method of investing that involves conducting thorough research and selecting investments with the goal of outperforming the broad market index. Passive investing is a strategy for investing that selects all of the investments that make up the broad market index (selected) with the goal of matching the broad market index (selected index) performance
- For picking investments, active investing uses fundamental/technical analysis. Passive investing entails selecting investments based on the market index’s composition, which is a less hazardous strategy to investing.
- Active investors believe markets are inefficient and are more interested in taking advantage of short-term price changes, whereas passive investors believe markets are efficient and follow a long-term buy-and-hold strategy.
- Due to the high amount of transactions resulting from frequent buying and selling, active investing has significant operating costs and capital gains taxes. Passive investment is more tax efficient and has fewer operating costs because it includes a lesser volume of transactions.
- Shorting, borrowing money for investments, employing derivatives for hedging/speculation, arbitrage, and other methods are all examples of active investing. Passive investing necessitates the adoption of fewer strategies while yet matching benchmark results.
The next decision that investors must make is whether to invest in fast-growing companies or undervalued sector leaders-
3. Growth
If investors believe that a firm will grow in the coming years and that a stock’s intrinsic value will rise, they will invest in that company to increase its corpus value.
Growth investment is another name for this. On the other hand, short-term holding is preferred by investors who feel a company will provide good value in a year or two. Investors’ preferences also influence the holding period.
For instance, how soon do they need money to buy a house, send their children to school, plan for retirement, etc.?
4. Value
Value investing includes investing in the company based on its intrinsic value.
When the market goes through a correction, the value of such undervalued companies will be corrected, and the price will soar up, leaving investors with significant returns when they sell.
Warren Buffet, the world-famous investor, employs this method.
Difference between Growth and Value Investing-
- Finding companies that are predicted to develop faster than the market is known as growth investment, whereas finding companies whose stock prices are lower than their underlying worth is known as value investing.
- Growth stocks often reinvest earnings to expand rather than pay dividends, but value stocks pay out a lot of them.
- Growth stocks have a bigger return potential than value equities, but they are riskier and more volatile.
5. Indexing
Indexing is another common way to invest passively. An investor using this strategy builds a portfolio that closely resembles the companies that make up a specific stock index.
They want their portfolio to match the index in terms of performance.
If you want a simple and low-cost strategy to build a diverse portfolio over time, this type of investment may be a suitable fit.
Because of the decreased turnover, transaction costs and taxes associated with managing these portfolios are extremely minimal.
Indexing is done by investing in index mutual funds or exchange-traded funds, which track the performance of a benchmark index such as the Nifty 50 or Sensex.
ETFs tend to be more tax- and cost-efficient compared to traditional index funds.
6. Buy and Hold
The buy-and-hold strategy is another example of passive investing. An investor who invests in buy-and-hold securities will not exchange their portfolio frequently.
They want to grow in the long run. The concept behind buy and hold is to invest in stock while its price is still low to profit from the stock’s price rising over time.
7. Market-Capitalization
Measuring a company’s size is called “market-capitalization” or “cap”. Market capitalization is the number of shares of a company with outstanding shares multiplied by the share price.
Some investors feel that small-cap companies should be able to deliver better returns because they have greater growth opportunities and are more agile.
However, the potential for greater returns in small caps comes with greater risk. Among other things, smaller firms have fewer resources and often have less diversified business lines.
Share prices can vary much more widely, causing significant gains or large losses. Thus, investors must be comfortable taking on this additional level of risk if they want to tap into a potential for greater returns.
8. Dividend Growth
Dividend investing, also known as income or yield investing, aims to provide a steady income stream. Stocks with high dividend yields are normally very profitable, but their growth rates are often slow.
Your duty as a dividend investor is to select firms with a high yield that will be able to pay dividends in the future.
It would be much better if the corporation could improve its dividend yield.
Dividend investment methods are about more than just making money. For example, a yield portfolio can see significant capital growth if dividends are reinvested.
Dividend-paying companies are often profitable, making them defensive during downturns.
You can also take our course on How to Invest in the Indian Stock Market?
9. Momentum Investing
Momentum investment is similar to growth investing, except instead of looking at profits or sales growth, it focuses on the stock’s price momentum.
According to evidence, the best-performing stocks in a specific era can outperform in succeeding ones.
Price action alone is thus used to make buying and selling decisions, albeit it does help to avoid small and illiquid companies. A simple momentum strategy would invest in 10 to 20 of the best-performing equities and keep them for a year.
All equities are sold at this stage, and the process is repeated. On a monthly or quarterly basis, more complex iterations of the approach will continuously rotate funds into the stock with the highest momentum.
There are ready-made strategies available in StockEdge that helps us filter in stocks both bullish and bearish, as shown below:
Traders can select either momentum, continuation or reversal strategies according to their trading style, as shown below:
After selecting, traders will get a list of stocks fulfilling that criteria.
Read more about Investing in Stocks from ELM School
10. Multi-Asset Investing
Over the long run, stocks usually produce the best results. They are, nonetheless, the most volatile asset class.
Combining different asset classes can result in higher risk-adjusted returns. The greater the number of asset types in an investment portfolio, the lower the volatility and portfolio risk.
Stocks, bonds, cash, commodities, real estate, hedge funds, and private equity funds may all be included in a well-diversified portfolio.
Diversification can be further enhanced by diversifying the stock portfolio among multiple of the above-mentioned trading strategies.
You can also watch our video on Are you an Active or Passive Investor? Find out in this video!!!
Bottomline
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to investing. Your risk tolerance, investment time horizon, age, and objectives determine the one that works best for you.
We hope you found this blog informative and use it to its maximum potential in the practical world. You can also checkout various investing courses on our platform. Also, show some love by sharing this blog with your family and friends and helping us in our mission of spreading financial literacy!
Happy Investing!