Have you noticed that the Indian Stock Market has become too volatile in recent days?
We can also see below that India VIX, volatility indicator, has increased from the levels of 10 to 20 recently-
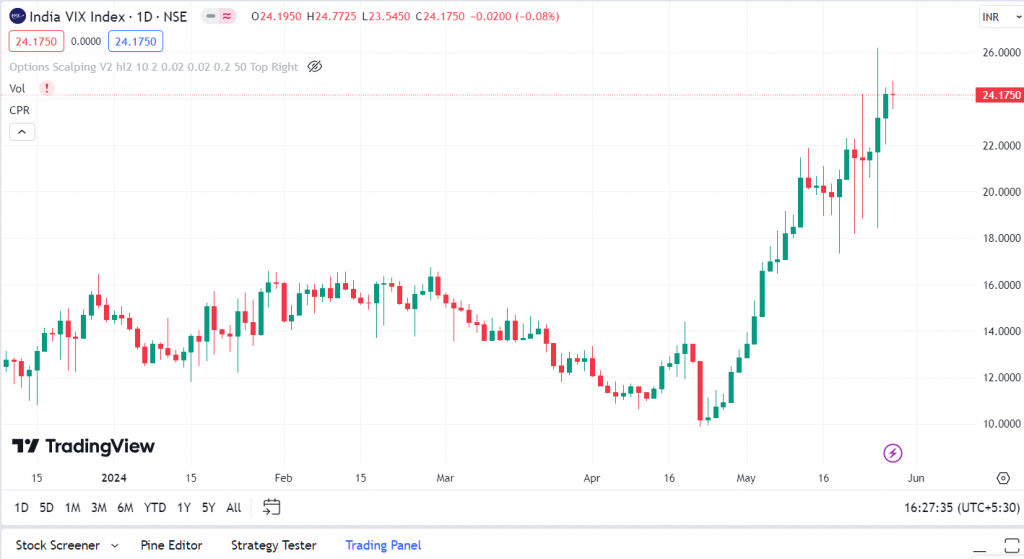
With increasing geopolitical tensions and big events such as the ongoing elections, traders are opting for volatility strategies to make profits in the market.
But before you adopt volatility strategies, you need to understand what is meant by volatility in the stock market.
So, in today’s blog, let us discuss what we mean by volatility in the stock market and an options-based approach to volatility trading.
Table of Contents
What is meant by Volatility in the Stock Market?
In simple language, volatility is a measure of the speed at which the value of assets or market indices fluctuates.
Typically, variance or standard deviation is used to quantify volatility. A high standard deviation number indicates that prices are dispersed over a large range.
On the other hand, a low standard deviation number suggests that prices are tightly distributed within a small range.
The prices move in huge swings when the volatility in the stock market rises. This volatility can be gauged by India Vix.
The India VIX, or India Volatility Index, is a key indicator for Indian stock markets. It can be thought of as a mood meter.
A high VIX suggests investors anticipate significant price swings, signalling a nervous market. Conversely, a low VIX indicates calmness and less dramatic price movements.
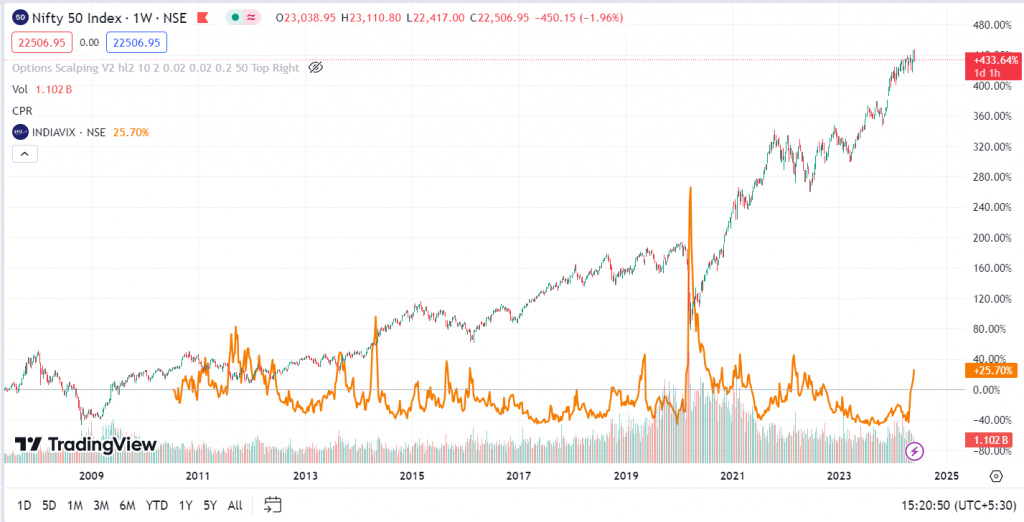
From the above chart, we can see that the India Vix rises when the Nifty 50 goes down.
Why Volatility Matters to Traders and Investors?
Trading tactics such as day trading, options contracts, and short selling allow traders to profit from market movements in both directions (up and down).
More frequent price swings are presented by volatility, which traders can utilize to tactically enter and exit positions.
Volatility raises the possibility of losses even as it presents opportunity. If a trade is not managed carefully, rapid price swings can quickly turn a winning trade into a losing one.
To traverse volatile markets, traders require well-defined trading strategies and good risk management abilities.
Stock values might see notable declines during times of extreme volatility. Smart investors may see these declines as opportunities to purchase high-quality equities at a discount. In the long run, this “buying low” tactic may prove advantageous.
Now that we have understood what volatility is in the stock market let us understand why we should choose options trading for capturing the volatile moves in the market:
Why Use Options for Volatility Trading?
The predicted future volatility of the underlying asset determines the price of an option.
Even if the price of an option is determined by various factors, investors anticipate different degrees of volatility.
Options traders can profit from trading volatility, but doing so-calls for a certain set of tactics.
Here are some Options Trading Strategies for Volatility Trading:
What are Options Trading Strategies for Volatility Trading?
Here are 4 Options Trading Strategies for Volatility Trading:
1. Long Straddle
Purchasing both a call and a put option on the same underlying asset, with the same strike price and expiration date, is known as a long straddle in the world of options trading. With this approach, a trader can benefit from large price swings in either direction without having to forecast an upward or downward trend in the market.
When to use this Strategy?
When a trader anticipates a big price movement in the underlying asset but is unsure of the direction of that movement, they usually use a long straddle. The following circumstances could call for a long straddle:
- Earnings Announcements: There can be a lot of volatility when companies release their earnings.
- Economic Data Releases: Announcements from central banks or significant reports on the economy.
- Political Events: Elections, advances in geopolitics, or adjustments to laws.
- Changes in Market mood: Expectation of abrupt shifts in investor mood.
Example
Suppose Nifty 50 is currently trading at 22,720, and you expect a big move due to upcoming elections. You decide to implement a Long Straddle by buying a call option and a put option, both with a strike price of 22,750.
Total Premium Paid: Rs. 22,666
Breakeven Points: 23,656 (upward movement) and 21,844. (downward movement).
For the Long Straddle to be profitable, the stock’s price must move above 23,656 or below 21,844 before the options expire.
The loss is limited to the amount of premium paid, i.e.-Rs. 22,666.The profit is unlimited.
2. Long Strangle
Buying a call and a put option with the same expiration date but different strike prices is known as a long strangle.
The put option’s strike price is usually lower than the current market price of the underlying asset, and the call option’s strike price is usually higher.
The trader can profit from large price fluctuations in either direction with this positioning.
When to use this Strategy?
When a trader anticipates a significant move in the price of the underlying asset but is unsure of the direction of the move, the long strangle strategy works well.
This might be the result of impending financial reports, noteworthy economic pronouncements, or geopolitical developments that could spark a great deal of market volatility.
Example
Suppose Nifty 50 is currently trading at 22,720, and you expect volatility in the index due to an upcoming election. You decide to implement a Long Straddle by buying a call option of 22,750 and a put option with a strike price of 22,700.
Total Premium Paid: Rs. 22,009
Breakeven Points: 23,630 (upward movement) and 21,820. (downward movement).
For the Long Strangle to be profitable, the stock’s price must move above 23,630 or below 21,820 before the options expire.
The loss is limited to the amount of premium paid, i.e.-Rs. 22,009. The profit is unlimited.
3. Iron Condor
The Iron Condor involves 4 legs-
- Sell a lower strike put (out-of-the-money)
- Buy an even lower strike put (further out-of-the-money)
- Sell a higher strike call (out-of-the-money)
- Buy an even higher strike call (further out-of-the-money)
It is basically a combination of a bull put spread and a bear call spread.
When to use this Strategy?
The Iron Condor works best when you anticipate that the underlying asset will trade in a narrow range and not move significantly either way.
It works well at times when there is little chance of significant price fluctuations, and the markets are stable.
Example
Suppose the Nifty 50 is trading at 22,720 levels. We will set up the Iron Condor in the following way-
Total Premium Paid: Rs. 42,434
Breakeven Points: 24,191 (upward movement) and 22,659. (downward movement).
For the Iron Condor to be profitable, the stock’s price must move above 24,191 or below 22,659 before the options expire.
The loss is limited to Rs. 6,455, and the profit is limited to Rs. 9,795.
4. Butterfly Spread
A butterfly spread aims to make money off of little changes in the underlying asset’s price. To create a position with minimum risk and profit, it entails combining three strike prices with both bull and bear spreads.
Butterfly Spreads can be called butterfly spreads or put butterfly spreads. In this blog, we will discuss an example of a call butterfly spread.
It involves:
- Buy one in-the-money call option (lower strike price).
- Sell two at-the-money call options (middle strike price).
- Buy one out-of-the-money call option (higher strike price).
When to use this strategy?
- When you expect minimal volatility in the underlying asset—that is, a price that stays mostly stable and near the middle strike price—you should use a butterfly spread.
- Perfect for traders looking for a low-risk, defined-reward strategy. When the price of the underlying asset is at the middle strike price at expiration, the maximum profit is realized.
Example
Suppose the Nifty 50 is trading at 22,720 levels. We will set up the Butterfly Spread in the following way-
Total Premium Paid: Rs. 22,934
Breakeven Points: 22,842 (upward movement) and 22,658. (downward movement).
For the Butterfly Spread to be profitable, the stock’s price must move above 22,842 or below 22,658 before the options expire.
The loss is limited to Rs. 178, and the profit is limited to Rs. 2,322
You can also practice these options strategies using Elearnoptions
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you trade volatility with options?
The purpose of the strangle options strategy is to profit from volatility. Buying a call and a put for the same underlying stock and expiration date but with different exercise prices for each option is known as a long strangle.
What option strategy is best for high volatility?
Option premiums are more desirable to sell and less appealing to buy as they are more expensive. These tactics consist of strangles, straddles and butterfly spread.
Conclusion
Thes strategies are used by traders to capitalize on stocks or index which exhibit high volatility. Most of these options strategies involve limited losses hence the downside is protected. These options strategies should only be used by expert options traders who know how to do options trading.