- What is Factor Investing?
- Assessing Your Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
- Identifying Suitable Factor Investing Strategies
- Matching Factors to Investment Goals And Risk Profile
- Implementing Factor Investing Strategies
- Benefits of Adopting a Factor Investing Approach
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Targeting particular qualities or traits (factors) of stocks that have historically outperformed the overall market is known as factor investing. Value, size, momentum, quality, and low volatility are common criteria.
It adjusts to different market cycles, increases portfolio diversity, and may even boost risk-adjusted returns. Empirical data backs up this approach, which also fits investor objectives and risk tolerance.
With the help of factor investing techniques, investors can profit from the risk premiums linked to particular variables. This provides a diversified portfolio construction method supported by research that has the potential to beat market indices in the long run.
Let us understand factor investing in detail.
What is Factor Investing?
A method of investing known as “factor investing” selects investments according to a number of criteria that can assist in boosting returns, broadening the investment portfolio’s diversity, and controlling overall risk.
Although professionals have been using factor investing for a while, investors have only just begun to take notice of it.
This investing approach makes use of two major kinds of factors:
- These encompass more general risks associated with many asset classes, such as rates of inflation, economic development, liquidity, etc.
- These comprise hazards particular to the class of assets, such as volatility, momentum, value, etc.
Said another way, factor investing harnesses the strength of reliable return generators.
Before you implement any investment strategies, it is important to assess your goals and risk tolerance as below-
Assessing Your Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
Firstly, it is important to clarify investment objectives and identify risk tolerance levels-
1. Clarifying Investment Objectives
- Establish both short- and long-term financial objectives: Establish clear goals, like supporting your schooling, buying a house, or saving for retirement.
- Think about your time horizon: Determine how long you want to take to reach your financial goals—longer than 10 years, for example, or less than 1 to 5 years.
- Determine your liquidity requirements: Assess the degree of liquidity needed to cover unforeseen costs or take advantage of investment possibilities, as well as the accessibility requirements for your investment money.
- Consider the preference for risk: Recognize how much you are willing to give up in the quest for greater returns on your assets.
2. Identifying Risk Tolerance Levels
- Evaluate your level of comfort with market volatility: Assess your level of comfort with the possibility of brief variations in the value of your investments.
- Take financial resilience into consideration: To determine your capacity to withstand investment losses, assess your financial status, taking into account your debt load, savings amount, and consistency of income.
- Recognize psychological aspects: Understand how emotions can affect financial decisions and how they react to market volatility.
- Utilize risk-tolerance surveys: If you want to measure your risk tolerance level in an unbiased manner, think about using the risk tolerance evaluations offered by investment platforms or financial advisors.
Identifying Suitable Factor Investing Strategies
Let us know how you can identify suitable factor strategies for trading-
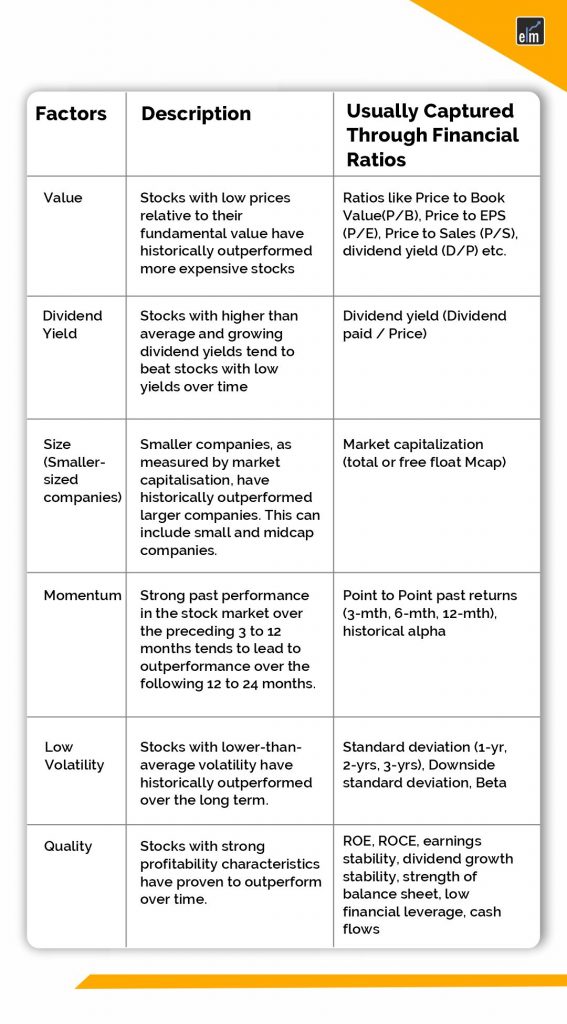
Targeting particular features or qualities of assets that have historically impacted their returns is known as factor investing. Among these are:
- Value: Undervalued stocks in relation to their fundamentals, such as a low price-to-book or price-to-earnings ratio.
- Size: Smaller companies’ stocks, which traditionally have returned more than those of larger companies.
- Momentum: In the short to medium term, stocks that have performed well recently typically continue to do so.
- Qualitative firms have low debt levels, steady earnings, and solid fundamentals.
- Low Volatility: Stocks that fluctuate less in value than the market as a whole.
Matching Factors to Investment Goals And Risk Profile
While adhering to your risk tolerance, choose the elements that will most likely assist you in reaching your investing objectives.
For example, you might take momentum or small-cap exposure into account if your objective is long-term capital appreciation and you have a larger risk tolerance. On the other hand, quality and dividend characteristics may be more appropriate if stability and income production are your top priorities.
Implementing Factor Investing Strategies
You can implement these Factor Investing Strategies by buying stocks or investing in the mutual funds based on each factor as shown below-
1. Value
Mutual funds that invest predominantly in stocks or other securities that are deemed inexpensive in relation to their inherent value are known as value mutual funds. Finding businesses whose stock prices are undervalued in relation to key value indicators like earnings, book value, or cash flow is the main goal of these funds.
Some of the popular Value Mutual Funds in India are-
- Aditya Birla Sun Life Pure Value Fund
- Nippon India Value Fund
- ICICI Prudential Value Discovery Fund
2. Size of the Company
The market capitalization of the businesses that a specific fund invests in is referred to here. Due to their varying investing mandates, different funds tend to concentrate on particular firm sizes:
- Invest in the biggest and most well-known businesses on the market with large-cap funds such as ICICI Prudential Bluechip Fund, SBI Bluechip Fund and so on
- Invest in medium-sized companies with greater growth potential than large-caps, albeit at a higher risk, through mid-cap funds such as Quant Mid Cap Fund, SBI Magnum Mid Cap Fund and so on.
- Small-cap funds: Invest in smaller businesses that carry the most risk and have the potential for rapid growth such as Quant Small Cap Fund, Nippon India Small Cap Fund, SBI Small Cap Fund and so on.
- Diversification is provided by multi-cap funds, which invest across all market capitalizations.
3. Momentum
In India, momentum mutual funds seek to profit from the momentum or trend-following characteristics displayed by particular equities or securities. These funds often allocate their investments to equities that have demonstrated robust price performance in the recent past and are anticipated to sustain their upward trend over the short to medium term.
Examples- ICICI Prudential Nifty 200 Momentum 30 Index Fund, Franklin India Prima Fund
4. Volatility
Mutual funds that seek to control the amount of risk or volatility in their portfolios are referred to as volatility-targeting funds, managed volatility funds, or volatility mutual funds. Compared to standard equity funds, these funds often employ a variety of tactics and procedures to reduce volatility and aim to give investors more steady returns.
Examples- UTI Nifty Low Volatility Index Fund, Kotak Nifty 50 Low Volatility 30 ETF:
5. Dividend Yield
In India, mutual funds that invest largely in stocks that pay dividends or other securities that generate income are known as dividend mutual funds. These funds hope to give investors consistent returns in the form of dividends and with the possibility of long-term capital growth.
Examples- HDFC Equity Dividend Fund, ICICI Prudential Dividend Yield Equity Fund
Benefits of Adopting a Factor Investing Approach
Factor investing presents various potential advantages when contrasted with conventional, passive investing methods.
Increased Profits
It seeks to surpass the market by snatching up particular return premiums linked to various aspects.
Certain characteristics, such as quality and value, have historically outperformed the market average in terms of long-term returns.
Reduced Risk
It spreads out returns from various sources, which may lessen portfolio volatility when compared to market-cap or single-asset strategies.
During market downturns, some elements, such as low volatility, assist reduce portfolio fluctuations.
Being transparent
This strategy provides a precise and unambiguous investing plan founded on predetermined criteria, simplifying the understanding of portfolio holdings and reasoning.
Enables continuous assessment and possible modifications according to shifting market circumstances or investment objectives.
Adaptability and Personalization
This strategy permits the customization of a portfolio to meet particular requirements and risk tolerances through the selection and creative combination of desired components.
Also, easily combines with different asset classes and investing strategies to provide a more thorough approach to portfolio management.
Conclusion
Prior to putting factor investing ideas into practice, familiarize yourself with concepts like as value, size, and momentum. Evaluate your risk tolerance and investing objectives. Choose variables that support your goals and build a diversified investment portfolio. For individualized advice and optimization, consider speaking with a financial professional. Regularly monitor performance and rebalance as necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is factor investing?
Targeting particular traits or variables, such as value, size, momentum, and quality, that are thought to influence asset returns over time is known as factor investing.
2. How does factor investing differ from traditional investing?
While traditional investing frequently depends on larger market patterns or fundamental research of particular securities, factor investing focuses on systematic factors driving asset returns.
3. What are some common factors in factor investing?
A few common factors are quality (financial health), momentum (recent price patterns), size (market capitalization), value (undervalued assets), and volatility (risk).