Key Takeaways:
- A futures contract is a contract between a buyer and a seller in which, the former agrees to buy a specific number of shares or an index from the latter, at a pre-mentioned time in the future for a pre-determined price.
- Every contract is regulated by the stock exchange or the clearinghouse which is an agency that looks after settling trades on the stock exchanges.
- There are differences between options and futures contracts.
- The futures contract can be traded easily.
The Futures contract is an extension of the Forwards Contract.
As discussed in our previous blog, Forwards Contract is a contract where two parties agreed to exchange cash for goods in the future.
The Futures Contract helps in eliminating the risks that are associated with the forward contract.
Let us discuss in details what is mean by futures contracts and how does it eliminates the risks of forward contracts:
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| What are Futures Contracts? |
| Futures Trading Example |
| Analyzing Futures table |
| Futures Trading Vs. Options Trading |
| Advantages of Futures Trading | Limitations of Futures Trading |
What are Futures Contracts?
A futures contract is a contract between a buyer and a seller.
In which, the former agrees to buy a specific number of shares or an index from the latter, at a pre-mentioned time in the future for a pre-determined price.
When the transaction takes place these details are agreed upon.
As futures contracts are standardized in terms of expiry dates and contract sizes, they are traded on exchanges just like we trade stocks.
Every contract is regulated by the stock exchange or the clearinghouse which is an agency that looks after settling trades on the stock exchanges.
Both the buyer and the seller of a futures contract are obligated to fulfill it’s agreed upon at the end of the expiry.
Futures Trading Example:
From the above you must have understood about futures theoretically, now let us understand practically,
For example, if someone wants to buy a September crude oil futures contract.
So they make a futures contract that they will buy 200 barrels of oil from the agreed price as of September expiration whatever the market price at that time.
The seller also agrees to sell those 200 barrels of oil at the agreed price.
Now both the buyer and seller are obligated to buy or sell these 200 barrels of oil unless they trade with other buyers or sellers.
Traders can also buy futures of stock, index funds, foreign currency exchanges, etc.
Analyzing Futures table:
Now you must be wondering where we can check the details of the futures contract.
Let us take an example of Reliance Industries Ltd.
You can log in to the NSE website to see the details of any stocks or index futures contract.
Learn the tricks & techniques of Futures & Options in just 2 hours by Market Experts
Below is the screenshot:
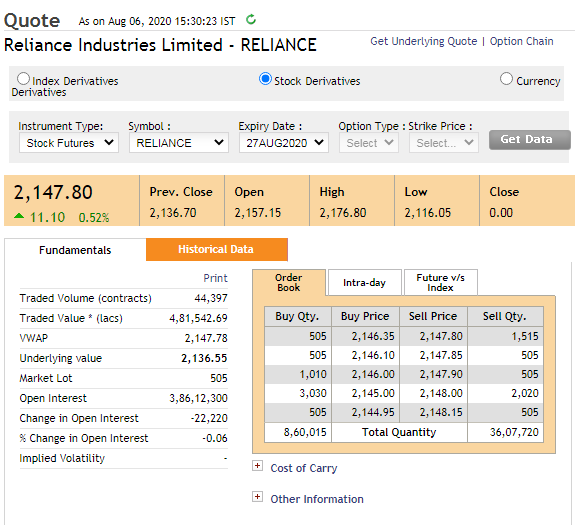
1. Instrument Type :
If the underlying asset is the stock, of the futures contract in which we are entering then we check the details of Stock Futures.
Thus the instrument type is the ‘stock futures’
2. Symbol:
This is the symbol of the stock that is Reliance Industries in this case.
3. Expiry Date :
This is the date on which the contract ends.
As we can see, the RELIANCE futures contract will expire on 27th Aug 2020 that is the last Thursday of the current month.
4. Underlying Value :
This is the price at which the underlying asset is trading in the spot market.
We can see that the current spot price is Rs.2147.80 per share.
5. Market lot (lot size) :
As futures contracts are standardized contracts, lot size is also fixed.
The lot size refers to the minimum number of shares that can be bought or sold if we want to enter into an agreement.
The lot size for RELIANCE futures is 505, meaning a minimum of 505 shares or a multiple of 505 can be traded.
The contract value will be: Lot size x Price of futures
= 505 x Rs.2147.80
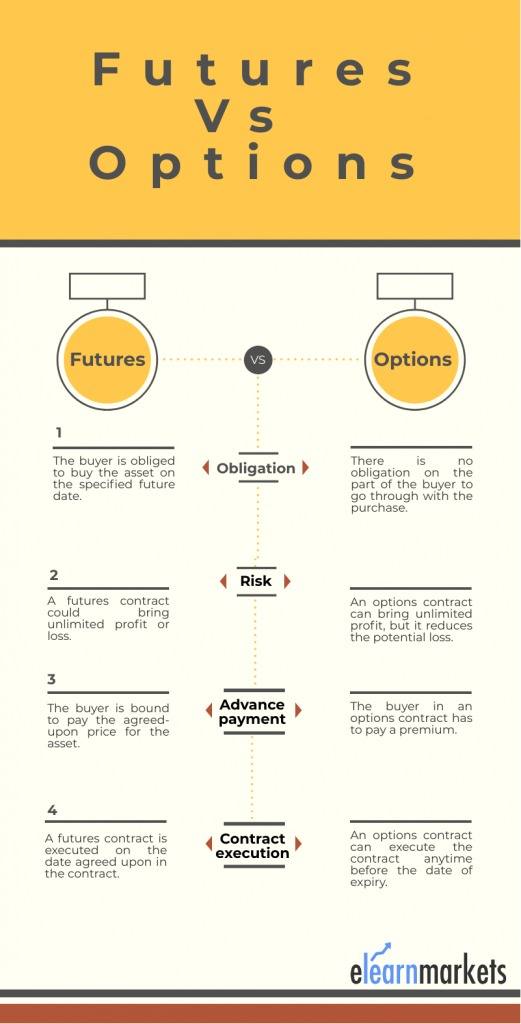
Futures Trading Vs. Options Trading:
Here are the differences between Futures trading and Options trading:
Advantages of Futures Trading:
Here are advantages of trading futures contracts:
1. Standardized Contracts:
In the futures contract, the terms of the contract are standardized and they are not negotiable.
2. Futures Contracts are tradable:
The futures contract can be traded easily.
At any point, if the traders’ views change then they can just transfer the contract to someone else and then get out of the agreement.
3. Futures Market is regulated:
The futures market is highly regulated by the stock exchanges or clearing corporations just like the stock market.
4. Futures Contracts are time-bound:
The futures contracts are time-bound as they end on the expiry date.
5. Cash settled:
The futures contracts are mostly cash-settled and there is no tension of moving the physical asset.
Limitations of Futures Trading:
There are also some limitations of trading the futures contracts.
Investors have a risk of losing more than the initial margin amount as futures use the leverage
You may miss out on favorable price movements when investing in a futures contract of that company.
Hi, to learn more about Futures Trading, please refer to our blog below:
Ready to master Futures Trading? Explore our Future and Option Trading Course now for expert insights and strategies!
You can also learn future and options trading through our courses. Hop in Now!
Happy Learning!!






Great Blog, Keep it up.
Hi,
We really appreciated that you liked our blog!
Thank you for Reading!
Keep Reading!