Most people today desire to learn how to trade. People are empowered by this to develop alternative sources of income. Before starting trading in stock markets, one should know the difference between intraday and delivery trading.
There are many different trading platforms, and traders with different interests select them accordingly. Intraday trading is the idea of buying and selling shares on the same day.
Your deal becomes a delivery trade if the position is not squared off on the same day and you anticipate keeping the shares for a longer period of time. Trading tactics change between intraday and delivery trading.
In today’s blog let us discuss delivery vs intraday trading and how your approach should differ for intraday and delivery trades-
| Explore our comprehensive courses on stock market strategies, including in-depth guides on Delivery and Intraday Trading. |
Table of Contents
What is Intraday Trading?
Intraday trading is the practice of buying and selling equities on the same trading day. Instead of being purchased as an investment, stocks are purchased in this scenario in order to profit from changes in stock indexes. The price variations of the shares are consequently monitored in order to make money from stock trading.
An online trading account is created for intraday trading. While trading intraday, it is necessary to make it clear that the orders are for intraday trading. Since the orders are settled before the trading day’s end, it is sometimes referred to as intraday trading.
Traders use real-time charts to closely watch intraday price fluctuations in an effort to profit from fleeting price variations. Short-term traders frequently use intraday charts that are one, five, fifteen, thirty, and sixty minutes long when trading during the market day.
Intraday trading for beginners refers to scalping frequently and using one- and five-minute charts for high-speed trading. For trades with several-hour hold lengths, other intraday trading strategies may use 30- and 60-minute charts. The goal of Intraday Trading Strategies – Scalping is to profit from minute variations in a stock’s price by making a lot of trades per day. Despite perhaps holding their holdings for a longer period of time, intraday traders still take big risks.
Example of Intraday Trading
Let us take an example of intraday trading strategies. Suppose, at 10:15 AM, the share price of Adani Enterprises Ltd was ₹ 2500 per share. The stock price increased to ₹ 2520 per share by 02:15 PM. Mr. X is an intraday trader. He began the day by purchasing 100 shares of Adani Enterprises Ltd. for ₹ 2500 per share.
When the stock price moved up to ₹ 2520, squared off his position by selling all the shares he held of Adani Enterprises Ltd. By doing this, he quickly earned ₹ 2000 in profit or ₹ 20 per share. This example explains to us how intraday trading functions.
Pros & Cons
Let us discuss the advantages of Intraday Trading:
- Intraday trades offer the benefit of margin, which increases position size and has a minimal capital requirement. Another name for it is leverage.
- Due to the leverage involved, intraday traders have the potential to profit even with small initial investments.
- In intraday trading, short selling is used. Simply put, this involves opening a position when a trader anticipates a decline in share prices. Therefore, even when the markets are declining, a trader can still turn a profit.
- A trader’s capital investment is seldom held hostage for very long. The time frame for intraday trades is one day, and the trader may withdraw their investment following the trade’s settlement.
Let us discuss the disadvantages of Intraday Trading:
- Because intraday trades are closed in a single day, a trader does not have enough time to ride the entire wave. Sometimes, prices may not change at all, making it impossible for the trader to profit from that transaction.
- In keeping with the aforementioned argument, due to the shorter time frame, a trader may not be able to wait for the price to turn around and may instead be forced to terminate the position at the end of the day, even if they lost money on the deal.
- Leverage is used in intraday trading, and if it is not used carefully, it could lead to huge losses.
What is a Delivery in the Stock Market?
One of the most popular trading strategies on the stock market is delivery trading. Delivery trading requires a stronger goal of investing than just looking for trading opportunities, in contrast to intraday trading. The investors’ intention is to keep their stock holdings for a longer period of time, which explains this.
There are no time restrictions in place throughout this process for selling stocks. It is regarded as a delivery trade as long as the stocks are delivered to the related Demat accounts.
Since your stocks will be kept in a Demat account, you cannot conduct delivery trades without one.
Example of a Delivery Trade
To further understand how Delivery Trading functions, let’s look at an example. Consider Mr. Y, a long-term stock market investor, identifying ABC Ltd. as an undervalued stock. They therefore believe that the stock’s price will increase in the future.
On August 30, 2023, he paid 200 for 10,000 shares of the corporation. Now, he waits to change or exit his trade until the stock price reaches a certain numerical target or a set deadline. In the ensuing four months, the stock’s price rose to 335 rupees. As soon as his goal is achieved and his trade is a success, Mr. Y sells his firm shares.
Pros & Cons
Let us discuss the advantages of Delivery trading:
- You are not required to sell your investments at a specific time and can keep them for extended periods of time.
- You receive all the extra advantages that come with holding shares, including dividends, incentives, and voting rights.-
- Your investments are hardly affected by market volatility, and delivery traders typically weather these stages.
- You do not have to spend all of your time researching and keeping track of your investments.
Let us discuss the disadvantages of Delivery trading:
- To take the position, you must pay the entire share price.
- Your invested money is permanently locked up.
- In delivery trading, short selling is not advantageous.
Delivery Vs Intraday Trading
Now, let us discuss Delivery vs. intraday Trading-
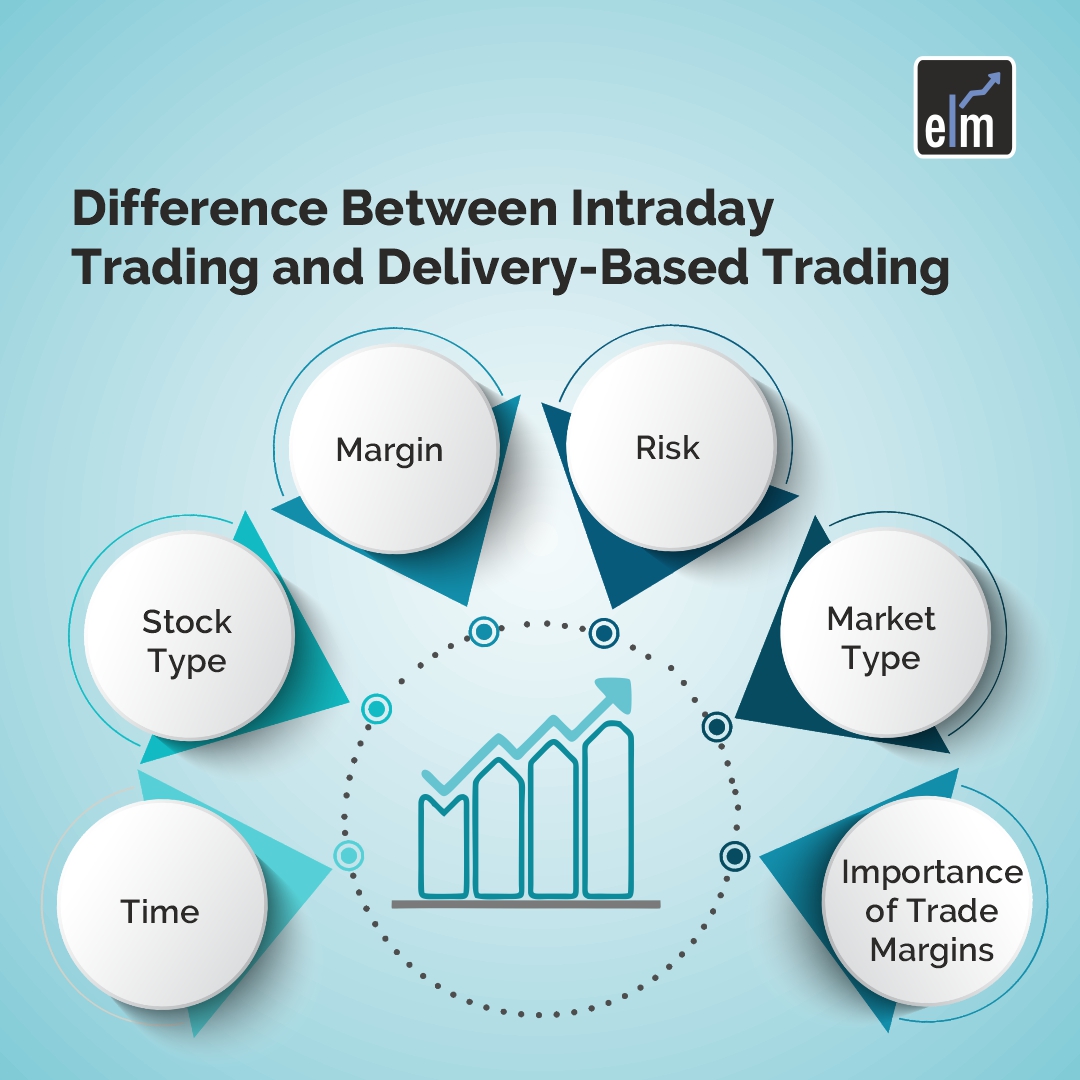
1. Time
The intraday market has a time limit. The trader must buy and sell on the same day. If the broker loses concentration, they might be charged with selling automatically. Contrarily, there is no time limit on delivery deals. They can be sold at any time, depending on the investor’s time frame for investing.
2. Stock Type
Stocks can be divided into two categories: liquid and illiquid. Intraday traders frequently favour liquid shares since their volume is much higher than that of illiquid ones. Due to the high volume, you can buy and sell these shares whenever you choose.
However, delivery traders might choose to participate in both liquid and illiquid equities. As an illustration, some investors invest in penny stocks in the anticipation that the price will increase and they will profit.
3. Margin
Brokers commonly offer intraday traders huge leverage or margin. Using the leverage option, they can buy more shares than their account balance permits. For instance, if your account balance is INR 10,000 and the broker gives a 4x margin, you can buy shares for INR 40,000.
The lender might, however, impose a fee for providing the margin option. On the other side, cash is frequently used to pay delivery trades. You can only buy shares if your account has a big enough clean balance to pay for the transaction. However, for transactions involving deliveries, some brokers offer margin services.
4. Risk
Some investors think intraday trading is riskier than delivery trading. Intraday equity trades don’t involve overnight risks, in contrast to delivery trades. Stock prices may be impacted by numerous factors that are in the company’s control or not.
In addition, the stock may decline the next day if any negative news emerges after the market closes. The short-term volatility may not have a large influence on you if you trade long-term deliveries. However, the volatility could work against your financial objectives if you indulge in short-term positional trading.
5. Market Type
Contrary to delivery traders, intraday traders buy and sell stocks on the same day. They can trade in both bullish and bearish markets as a result. In a bull market, they buy early and sell afterwards. In addition, when the market is bearish, they sell sooner and buy later.
Contrarily, delivery traders generally identify opportunities in a bearish market and hold onto them until the stock value increases. When the market is booming, they sell their assets.
Importance of Trade Margins
Whether you can do intraday or delivery trading, trading margins play an important role.
These margins can be used to boost intraday earnings. Loans that brokers provide their clients at a low-interest rate are traded in margins. With a 10x margin, for instance, you can borrow INR 90,000 from your broker at INR 1,000,000 if you invest INR 10,000 in an intraday trade.
Additionally, these margins contribute to a higher potential return on investment. As trading is guaranteed to be paid on the same day, intraday trading offers a larger margin from brokers than delivery-based trading.
How your approach should differ for intraday and delivery trades?
Let us discuss how your approach should differ for intraday and delivery trading:

1. Trading Volumes
The number of times a given company’s shares were sold and bought in a day is known as the trading volume. Larger and more well-known corporations’ stocks trade at bigger volumes. It is best to stick with these equities for intraday trading.
You’ll have access to enough liquidity at all times to sell shares. For long-term trades, on the other hand, you can hold shares with little trading volume and hold onto the stock until the desired price is attained.
2. Price Levels
Setting pricing targets is recommended. Setting target prices is the best course of action because intraday deals are time-sensitive and there may not be many chances to drive prices down. However, longer trades give you the option of extending your investing duration. Targets can be revised and stock can be held for a longer period of time thanks to delivery trades.
3. Investment analysis
Technical indicators that help in predicting anticipated short-term market swings are the foundation of intraday transactions. However, the outcome of this research does not predict the company’s long-term performance.
In contrast, experts advise investing in long-term possibilities when engaging in delivery trading. Fundamental analysis assists in delivering the desired analysis in such cases.
Learn more about trading strategies through our course on trading
Bottomline
Thus, the main difference between intraday and delivery was the above pointers. Many market experts contend that long-term investments outperform day trading in terms of returns.
If you don’t have the time to evaluate your portfolio every day, you could find that investing over the long term is a good option.
Intraday trading is an option for people who have a good background in technical analysis, are adept at seeing patterns on charts, and have a lot of free time.
Be knowledgeable about your options, whether you choose to focus on technicals or fundamentals when it comes to the stock market. If not for making a profit, it helps to prevent losses.
Join our exclusive stock investing webinar where seasoned experts will share invaluable insights, proven strategies, and the latest market trends
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which is better intraday or delivery?
Many market experts contend that long-term investments outperform day trading in terms of returns. For investors who lack the time to regularly check their portfolios, long-term investing or delivery may be a valuable investment strategy. Some investors think intraday trading is riskier than delivery trading. Intraday equity trades don’t involve overnight risks, in contrast to delivery trades. Stock prices may be impacted by numerous factors that are in the company’s control or not.
In addition, the stock may decline the next day if any negative news emerges after the market closes. The short-term volatility may not have a large influence on you if you trade long-term deliveries. However, the volatility could work against your financial objectives if you indulge in short-term positional trading.
Can I buy in delivery and sell in intraday?
Yes, you are permitted to sell the delivery share on the same day as your purchase order. Regardless of whether you place a buy order for intraday trading (CNC) or a delivery order (MIS), your trade will be treated as intraday trading in this situation rather than delivery trading.
Can we sell delivery shares on the same day?
You can easily sell delivery shares on the same day in the stock market. You can sell your delivery shares when you receive a good price for them without encountering any transactional difficulties. Trading for delivery of shares, however, will be regarded as intraday trading rather than delivery.
Can I convert delivery to intraday?
Only if they are bought the same day as the auto square-off timing may delivery holdings be converted to intraday positions.