Key Takeaways
- Bonus shares are free rewards: Companies issue bonus shares to existing shareholders from their profits or reserves, instead of paying cash dividends.
- Improves market liquidity: By increasing the total number of shares, bonus issues make stocks more affordable and easier to trade without changing the company’s total market value.
- Encourages investor trust: Bonus shares signal strong financial health and help attract retail investors while rewarding long-term shareholders.
- Possible downsides: Issuing more shares can dilute Earnings Per Share (EPS) and may lead to a temporary fall in the stock price per share.
- Tax and compliance: Bonus shares have tax implications when sold (capital gains rules apply) and companies must follow regulatory steps during issuance.
The idea of earning bonus shares for their investment excites a lot of people. However, have you ever questioned why businesses offer these bonus shares at no cost? Are they truly free, too?
Many investors may find bonus shares, sometimes referred to as stock bonuses or scrip dividends, to be an exciting facet of the financial world. These shares could be a great addition to your investing portfolio, but before you make an investment, be sure you completely grasp what bonus shares entail.
In today’s blog, let us understand bonus shares meaning, including what they are, why corporations issue them, how they operate, pros and cons:
What are Bonus Shares?
The significance of bonus shares is that they are an extra set of shares that the company has given to current shareholders as a “bonus.” Despite producing money, the corporation is unable to distribute dividends to its stockholders, hence these extra shares have been allocated. Bonus shares, however, are only available if the business has booked significant profits and has a sizable free reserve.
Moreover, dividend distribution is the only use permitted for these reserves or profits. The bonus shares are assigned to shareholders based on their proportionate ownership stake in the business.
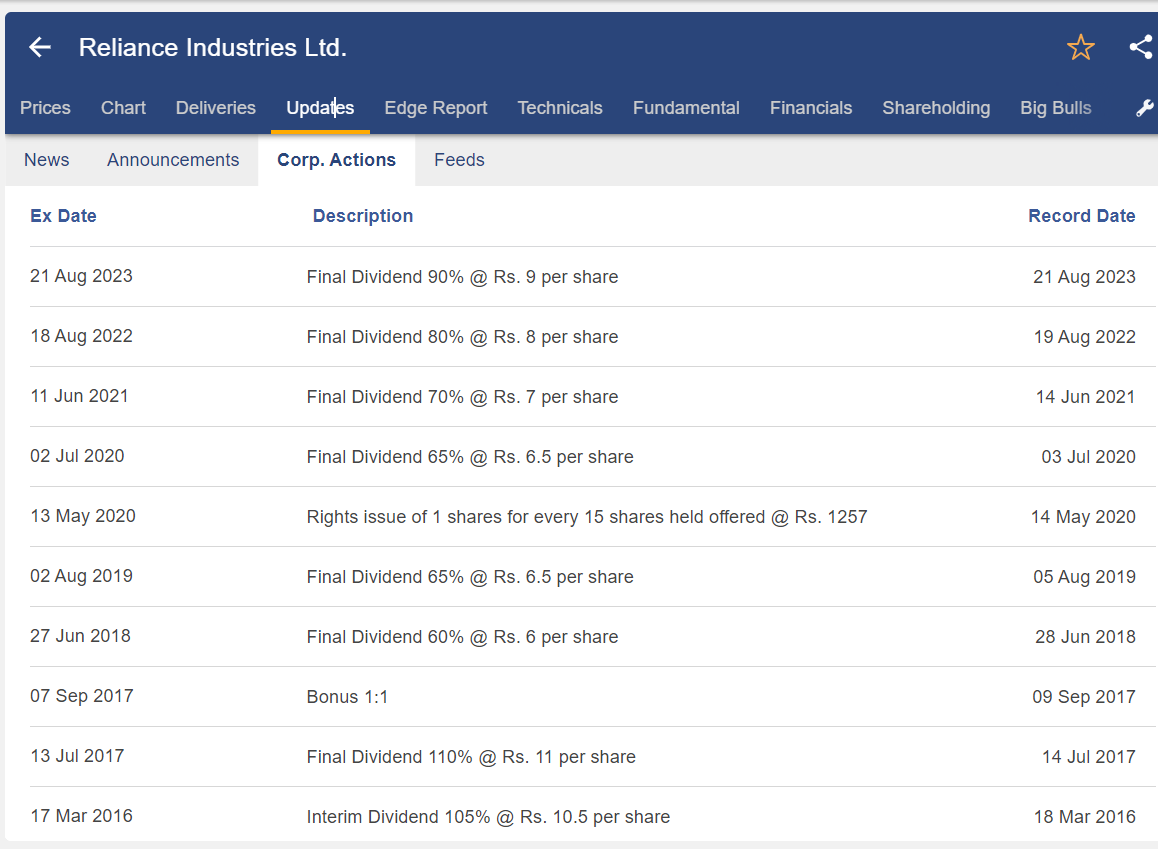
For instance, the shareholder will have twice as many shares as they already do if the corporation announces a one-for-one bonus share. On 7.9.2020, Reliance Industries Ltd. issued a 1:1 bonus. Assume that shareholder A owns 100 shares of Reliance. Following the news of the one-on-one bonus shares, shareholder A will own 200 shares.
But why is it important to issue bonus shares by the company? Let us understand below:
| Register in our Stock Markets for Beginners Course and kickstart your journey to investment knowledge. |
Why is It Important for Companies to Issue?
Bonus shares operate on the fundamental tenet that the total number of shares increases proportionately to the ratio of held shares to outstanding shares.
For example, let’s say Investor A owns 200 shares of a corporation and the company announces a 4:1 bonus, meaning that for every share he receives four more shares gratis. He will receive an additional 800 shares for free, bringing his total holdings to 1000 shares.
Bonus shares are distributed by companies to promote retail involvement and broaden their shareholder base. It is more difficult for new investors to purchase shares in a company when the price per share is high. The price per share decreases as the number of shares increases. But the total capital is still there.
Companies give dividends also to their investors, but how is it different from bonuses? Let us discuss below!
How are They Different from Dividends?
A corporation will pay dividends to its shareholders in proportion to whatever excess or profit it makes. Bonus shares indicate that the business has chosen to provide its shareholders additional shares.
Subsequently, stock represents a portion of the company’s profit, which is distributed as cash. Increasing a company’s share liquidity is the primary purpose of bonus share issuance. It is possible to buy and sell shares on the market without changing the price.
Therefore, the goal of stock dividends is to return money to the company’s shareholders. A ratio will be decided upon for the bonus shares’ distribution to shareholders. The decision to disburse stock dividends to shareholders will then be made.
Why do Companies Issue Bonus Shares?
Bonus shares are usually issued by companies for multiple primary purposes-
First, by decreasing the price per share and increasing liquidity, they promote greater participation from retail investors in their stock.
Secondly, they offer an alternate means of rewarding investors by paying out dividends.
Lastly, they show that the business is well-positioned financially to continue expanding and adding value for shareholders. We’ll go into more detail about these factors when we examine the benefits of issuing bonus shares.
What are the Benefits?
Below are the advantages:
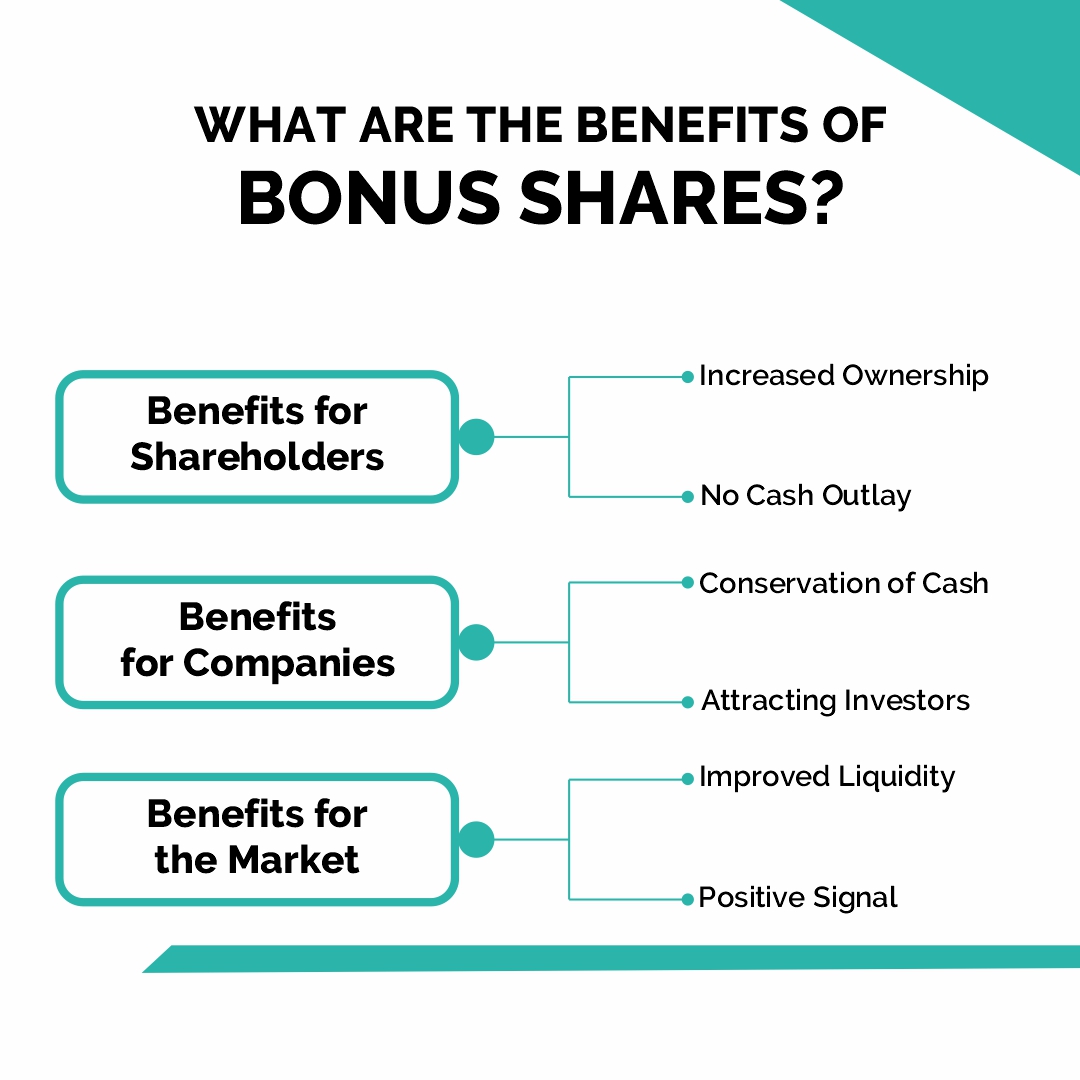
1. Benefits for Shareholders
- Increased Ownership- Bonus shares are seen to be advantageous for the company’s long-term investors who want to increase their investment.
- No Cash Outlay- Bonus shares are issued by the company at no cost to shareholders; this increases the number of outstanding shares held by investors in the company and improves stock liquidity.
2. Benefits for Companies
- Conservation of Cash- Companies that issue bonus shares to their shareholders gain from being able to avoid situations in which they would otherwise find it difficult or undesirable to pay their shareholders cash dividends.
- Attracting Investors– Because bonus shares have been invested in the company, which in turn provides capital to the investor, they aid in fostering investor faith in the business and operations of the company.
3. Benefits for the Market
- Improved Liquidity- With the issuance of bonus shares in the market, the companies have more free-floating shares.
- Positive Signal- These shares are distributed to strengthen the company’s position and reputation in the market, win over current shareholders, and draw in a number of small investors to the stock market.
Now let us discuss the process of issuing bonus shares by the companies:
What is the Process of the Issue?
1. Decision to Issue Bonus Shares
Calling a board meeting is the first action that has to be done. Per Section 173(3) of the Act, notice must be given at least seven days before the board meeting. The next step is for the corporation to schedule the board meeting and set the agenda.
2. Approval by Shareholders
All directors, shareholders, auditors, and other eligible members must receive notice of the general meeting to approve the issuance of bonus shares, with a minimum of 21 clear days to do so.
3. Record Date and Ex-Date
In the board meeting, the company also has to decide the record date as well as the ex-date for the issue of these shares. The deadline set by the business to qualify for bonus shares is known as the record date. The corporation will award bonus shares to all shareholders who have shares in their Demat account on the record date.
One day prior to the record date is the ex-date. In this case, in order to qualify for these shares, an investor must purchase shares at least one day prior to the ex-date.
4. Allocation
If the shares are held in physical form, the corporation must produce share certificates within two months of the date of allotment; otherwise, the depository must be notified as soon as the shares are allotted.
Tax Implications
Capital gains tax is due if a shareholder holds bonus shares for an extended period of time and treats them like investments. However, the earnings can be recognized as business income if the shareholder is involved in the business of trading shares.
These shares are not subject to any additional taxes because the full selling price is considered a capital gain. These shares are subject to tax implications dependent on the holding period, just as ordinary equity shares.
Risks and Considerations
Below are some risks:

1. Dilution of Earnings per Share (EPS)
The issuance of additional shares to current owners without a commensurate increase in cash is known as the “bonus issue.” As a result, we must restate the EPS for the prior year and modify the number of common shares prior to the event.
2. Impact on Stock Prices
In contrast to a cash dividend payment, the additional shares are distributed at a discount to the company’s stock price, which means that owners do not receive an instant financial boost. For illustration, let’s say an investor purchases 100 shares of XZY Ltd. stock at a price of Rs.10 apiece. The company offers a one-for-one bonus program.
The investor currently owns 200 shares following the bonus issue (100 original shares plus 100 bonus shares). The extra bonus shares that were added to the existing supply have made them worth Rs. 5 apiece (10 ÷ 2), therefore the investor will not be receiving any money right now.
3. Market Perception
Shareholders accumulate shares when they are offered regularly. This lowers the price of shares. It might not sit well with certain stockholders.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Also, the companies need to file many regulatory compliances in the process of issuing these shares to the investors.
Conclusion
A corporation that issues these shares to its stockholders does so by distributing extra shares to them from earnings or existing reserves. The market capitalization of a company does not increase with a bonus issue since the price of the stock adjusts proportionately to the additional shares issued. Businesses typically use bonus offerings to draw in ordinary investors, offer a dividend substitute, and/or present a stable financial image.
| Explore our effective ways to make mone in stock markets webinar to diverse strategies and seize opportunities for making money in the stock markets. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the meaning of 1 5 bonus shares?
This indicates that for every five shares owned by the corporation, one bonus share was awarded.
2. Are bonus shares good or bad?
When a business issues bonus shares from reserves or profit, it shows that it is profitable and strong enough to issue additional equity shares. Bonus shares are also a fantastic method to thank shareholders, particularly in situations where businesses are strapped for cash and are unable to distribute cash dividends.
3. Will bonus shares reduce share price?
Because bonus shares are credited to the account at no cost and the holding average is determined by applying the First In First Out (FIFO) technique, the average price, or buy average price, of a stock is decreased following the credit of bonus shares to the account. Bonus shares have no buy price because they are free.
4. What is the meaning of bonus 1:3?
A shareholder will receive one bonus share for every three shares held if a corporation has set a bonus share ratio of 1:3.