Arbitrage trading is a tactic used by investors and traders to profit from price differences between various securities or markets. This trading method is quite popular because it gives traders the chance to buy at a low cost and sell at a high cost with the greatest degree of accuracy.
If you are an experienced trader, you must be familiar with arbitrage trading; but, if you are a beginner, your first concern will be: What exactly is arbitrage trading?
This blog’s main goal is to address all of your questions about arbitrage trading and how it operates in India.
Are you ecstatic? Let’s begin by examining the definition and meaning of arbitrage trading.
Enroll now in our multi-asset trading course and gain expertise in investments
Table of Contents
What is Meant by Arbitrage Trading?
Arbitrage trading refers to the practice of taking advantage of pricing differences or inefficiencies in the financial market to increase profits with little to no risk. It centres on the simultaneous purchase and sale of securities or assets in different markets in order to take advantage of price discrepancies.
It is important to talk about the underlying idea behind arbitrage trading after defining what it means.
The fundamental tenet of arbitrage trading is that there should be no price discrepancies for the same asset in a functioning market. However, there are brief variations in price due to a number of reasons such as supply and demand mismatches, transaction costs, or information asymmetry.
In order to make money, arbitrage traders look for opportunities to buy an item at a lower price in one market and sell it for a greater price in another. However, arbitrage trading entails a high volume of trading and speedy deal executions.
As a result, in order to engage in effective arbitrage trading, traders need to have enough capital, adequate mechanisms for executing trades and reliable market data.
How Does Arbitrage Trading Work?
Using different markets’ or other relevant assets’ price inefficiencies or differences, arbitrage trading makes a profit. The process is relatively straightforward and mainly concentrates on capturing profits from price variations between markets.
A trader who engages in arbitrage often buys a cheap asset from one market and sells it to another market for a relatively higher price. Identification of market discrepancies is the initial step, in which a trader searches several markets for price variations. The trader must move quickly to execute trades after identifying prospective possibilities.
Here, profit is mostly obtained from pricing differentiations rather than market movements. Arbitrage trading requires a thorough understanding of the market, access to a variety of markets, and the flexibility to adjust to shifting market conditions. For successfully navigating the complexity of arbitrage trading, proper execution and risk management are also crucial.
Example
Aman is an arbitrage trader. He is searching for opportunities to make profits through arbitrage trading. On the NSE and the BSE, the identical stock, ABC, is traded. A stock’s price on the NSE is Rs. 600 whereas it trades for Rs. 580 on the BSE.
Aman can purchase the stock on the BSE for Rs.580 and sell it on the NSE for Rs 600, earning Rs. 20 on each share of the transaction. Aman has access to both marketplaces. As the same stock is traded on both exchanges, there are advantageous possibilities to engage in arbitrage trading.
How Does Arbitrage Trading Work in India?
This type of trading in India follows the same rules as in any other market and aims to generate profits by taking advantage of price differences between other markets.
However, there are a few unique factors that must be taken into account while this type of trading in the India, including the following:
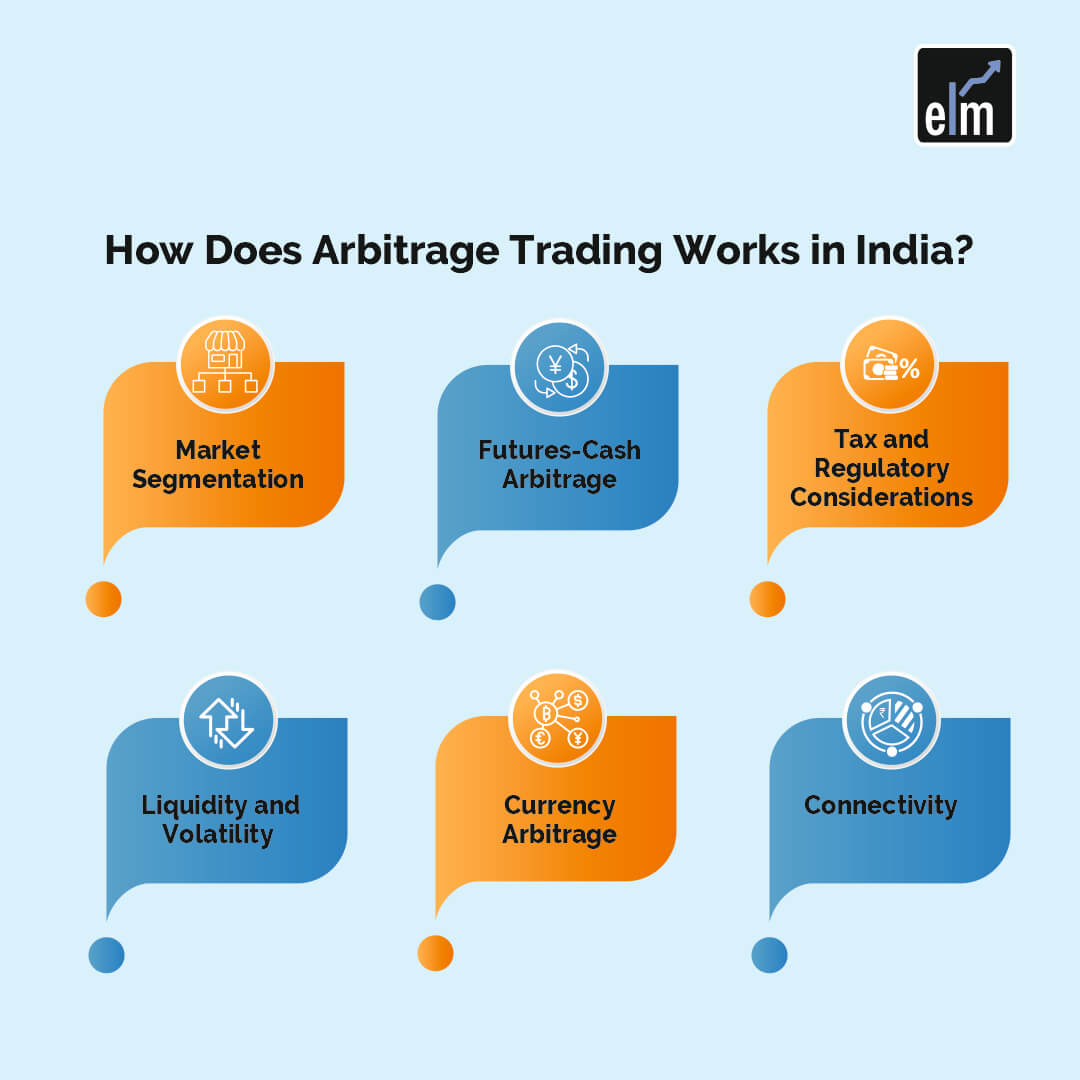
1. Currency Arbitrage
Given that India uses various currencies, traders who engage in foreign exchange or futures currency trading operations may additionally want to think about prospects for currency arbitrage.
2. Futures-Cash Arbitrage
There are numerous chances for arbitrage between the futures and cash markets. In order to secure the price difference, traders can buy and sell equities in the cash market while also taking opposing positions in futures contracts.
3. Market Segmentation
Indian markets are typically divided into different exchanges, such as BSE and NSE, as well as a number of other derivative markets. Price differences between these platforms provide arbitrage traders with numerous opportunities to make money.
4. Tax and Regulatory Considerations
Arbitrage traders in India must take into account the effects of taxation and a number of regulatory restrictions. They must abide by the rules against market manipulation, insider trading, exchange rules, and applicable securities. For accurate profit calculation, knowledge of tax and capital gain legislation is also crucial.
5. Liquidity and Volatility
Understanding liquidity and volatility of Indian markets is crucial as these are among the most worrying effects on arbitrage trading. High liquidity facilitates transaction execution and maximises profit. Volatility frequently adds additional risks since it can cause prices to shift quickly and transaction costs to rise when the market is under stress.
6. Connectivity
One of the most important aspects of this trading is technology. In India, this is not an exception. To detect and profit from price differences, traders need high-speed connectivity, a variety of algorithmic trading systems, and data feeds. Therefore, having access to cutting-edge tools and trustworthy trading platforms is crucial for optimising arbitrage trading.
Types of Arbitrage Trading
The following are the several types of arbitrage trading practised in India:
- Spatial arbitrage is the practice of profiting from price disparities between multiple markets or geographical areas.
- Temporal arbitrage includes price abuses that occur over time.
- Merger Arbitrage: When a company undergoes a corporate event, such as an acquisition or merger, merger arbitrage secures profit from pricing differences.
- Dividend Arbitrage: In this strategy, price differences in equities that pay dividends are taken advantage of.
- Risk-free interest rate arbitrage includes taking advantage of interest rate disparities between markets or nations.
- Statistical arbitrage makes use of numerous quantitative models and statistical research to find mispriced assets in a certain market or sector.
Advantages
Below are the benefits
- Potential profit without risk
- Exploiting inefficient pricing
- Diversity of holdings
- Provision for making fast money
- Protection from market volatility
- Using market-neutral tactics
Disadvantages
Below are the disadvantages of arbitrage trading
- Difficulties with the timing of executions
- Transaction costs
- Opportunity gaps exist.
- Regulations and compliance-related risk
- Problems with market liquidity
Learn more about trading strategies through our course on trading
Bottomline
Briefly said arbitrage is a very effective approach that enables traders to profit from price differences. It provides traders with a number of benefits, but one must also be aware of any hazards connected to a given trading technique. It must be remembered that developing the best market knowledge possible, having the ability to act quickly, and exercising the greatest discipline are all requirements for success in arbitrage trading.
| Unlock profitable trades! Join our Candlestick Pattern Trading Webinar for automated strategies |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is arbitrage trading legal?
Most nations, including the United States and the United Kingdom, permit this type of trading. By ensuring that pricing differences don’t persist for long periods of time, the practice is said to help market efficiency.
What is an example of arbitrage trading?
Aman is an arbitrage trader. He is searching for arbitrage possibilities and techniques to make rapid profits. On the NSE and the BSE, the identical stock, ABC, is traded. A stock’s price on the NSE is Rs. 348 whereas it trades for Rs. 346 on the BSE. Aman can purchase the stock on the BSE for Rs. 346 and sell it on the NSE for Rs. 348, earning Rs. 2 on each share of the transaction. Aman has access to both marketplaces. There are advantageous possibilities to engage in this trading due to the difference in pricing in both markets.
Is arbitrage legal in India?
Yes, as long as you are taking delivery of shares, arbitrage trading is permitted in India. Such operations are encouraged by SEBI since they help maintain uniform securities prices across all exchanges.
Does arbitrage trading still work?
Risk arbitrage is still available to the majority of retail traders notwithstanding the drawbacks of pure arbitrage. Although engaging in this kind of arbitrage involves some risk, it is typically referred to as “playing the odds.