Bullish options strategies are strategies that several traders use when they anticipate an increase in asset price.
In order to select the best options strategy, it is critical to determine how much the underlying price will rise and the timeframe over which the rally will occur.
Buying call options in simple strategies gain an advantage in a rising market. Still, if a trader fails to cover their position for any unexpected and significant price fall, it increases many risks for a trader.
Furthermore, acquiring while the market is somewhat bullish is not a wise policy. Rather than buying a call, traders should consider a bull call spread strategy.
In today’s blog, we will discuss 7 best bullish options strategies that traders can use if they have a bullish outlook on a stock or index:
Bullish Options Strategies
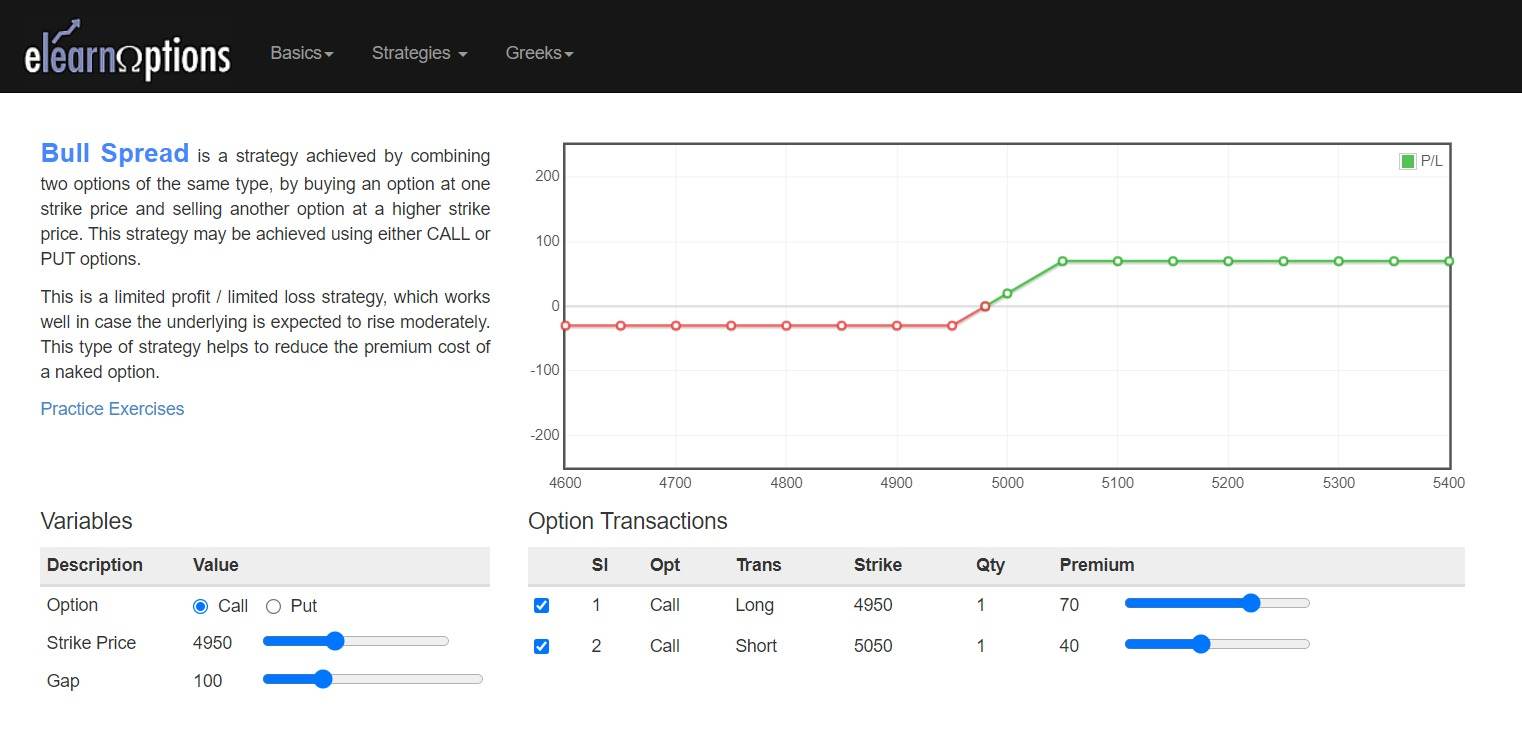
1. Bull Call Spread
A bull call spread comprises one long call at a lower strike price and one short call at a higher strike price. Both options have the same underlying stock and expiration date. A bull call spread is set up for a net debit (or net cost) and profits as the price of the underlying stock rises.
If the stock price rises above the strike price of the short call, profit is limited, and potential loss is limited if the stock price falls below the strike price of the long call (lower strike).
The potential profit is limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the spread’s net cost (including commissions). The maximum risk is equal to the spread cost plus commissions. If the position is held to expiration and both calls expire worthlessly, a loss of this amount is realised.
Below is the payoff diagram of this strategy:
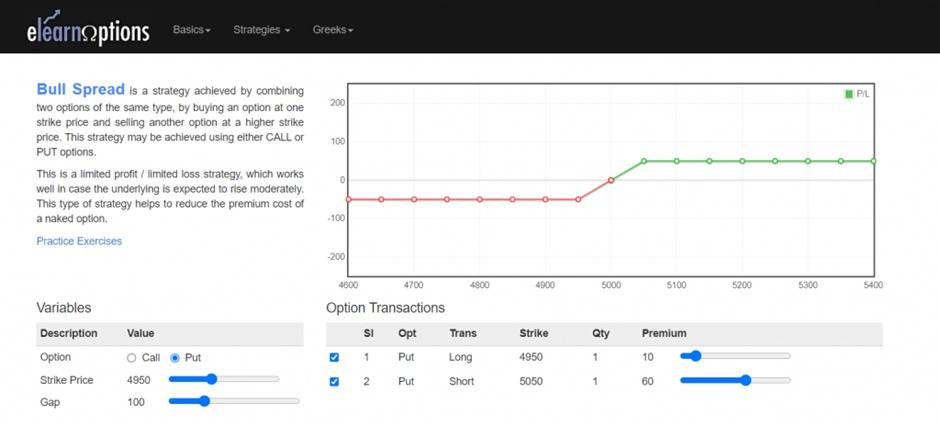
2. Bull Put Spread
A bull put spread involves writing or short selling a put option while concurrently purchasing another put option with the same expiration date but a lower strike price (on the same underlying asset).
The bull put spread is one of the four basic forms of vertical spreads, with the bull call spread, bear call spread, and bear put spread being the others.
The premium obtained for the short put leg of a bull put spread is always greater than the premium received for the long put, implying that receiving an upfront payment or credit is required to begin this strategy.
Potential profit is limited to the net premium received less commissions, and this profit is realized if the stock price is at or above the strike price of the short put (higher strike) at expiration and both puts expire worthlessly. The maximum risk equals the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received, including commissions.
Below is the payoff diagram of this strategy:
3. Call Ratio Back Spread
A call ratio backspread is an options spreading strategy used by bullish investors to limit losses while expecting the underlying security or stock to rise significantly. The strategy combines buying a larger number of call options with selling a smaller number of calls at a different strike but with the same expiration date.
While the downside is protected, gains can be substantial if the underlying security rises significantly due to the ratio feature.
The maximum potential loss occurs if the underlying stock price is at the higher strike price of the two calls purchased when the options expire. However, because the strategy involves the purchase of two call options, the potential profit from a rise in the underlying stock price is theoretically unlimited.
Below is the payoff diagram of this strategy:
4. Synthetic Call
Investors and traders that utilise the synthetic long call strategy buy a stock because they have an optimistic outlook. But what if the stock price falls instead? As an investor, you wish you had some protection from a price decline.
Thus, purchase a Put on the stock. As a result, you have the option to sell the shares at the strike price. The strike price can be somewhat above (ATM strike price) or below the price you paid for the shares (OTM strike price).
Losses are limited to Stock price + Put Premium-Put Strike price. The Profit potential is unlimited when this strategy is implemented.
You can also read our blog on 12 Common Option Trading Strategies Every Trader Should Know
Below is the payoff diagram of this strategy:
5. Bull Butterfly Spread
A long butterfly options trading strategy consists of purchasing one call option at a lower strike price, selling two calls at a higher strike price, and then purchasing one call at an even higher strike price. The strike prices are equally spaced apart, and all calls have the same expiration date.
This butterfly options strategy limits the risk to the net debit paid. The maximum profit potential can be obtained if the stock price is equal to the strike price of the short calls (centre strike) at expiration. This profit is equal to the difference between the lowest and middle strike prices less the net cost of the position, including commissions.
You can practice more such strategies in ElearnOptions
6. Bull Condor Spread
Long Iron Condor Options Strategy involves selling a lower strike put, buying a lower-middle strike put, purchasing a higher middle strike call, and then selling a higher strike call.
One should note that each option traded under this strategy should belong to the same underlying and have the same expiration. Usually, the lower strike and lower-middle strike puts are OTM puts, whereas the higher middle strike and the higher strike calls are OTM calls.
The maximum loss is limited to the extent of the net premium paid. The profit equals to lower-middle strike price-lower strike price-net premium paid.
7. Bull Call Ladder Spread
The bull call ladder spread is an options trading strategy designed to profit from increased security prices. It is similar to the bull call spread in that it is best used when you expect a security’s price to rise but not dramatically.
The main reason for using the bull call ladder spread rather than the more straightforward bull call is that it involves an additional transaction, which reduces the initial cost of implementing the strategy.
Bull Call Ladder is a Net debit strategy where we will have limited profit; Maximum profit will be if the market stays in between higher and middle strike price i.e., the difference between Middle strike and lower Strike Call less net initial outflow.
Maximum Loss is unlimited if the stock moves above the breakeven point.
You can also join our course on CERTIFICATION IN ONLINE OPTIONS STRATEGIES
Bottomline
We hope you found this blog informative and use it to its maximum potential in the practical world. Also, show some love by sharing this blog with your family and friends and helping us in our mission of spreading financial literacy.
Happy Investing!
You can also visit web.stockedge.com, a unique platform that is 100% focused on research and analytics.