We have been hearing a lot about the government fast-tracking its Disinvestment plans, as hardly 5 months are left for the end of FY20.
The Government has plans to reduce its stake and monetize its investments to bridge the fiscal gap and budgetary deficit appearing from the corporate tax rate cuts and many more fiscal prudence deficits.
To divest a promoter’s stake, you must have read that the company will reduce its stake via OFS or Offer for Sale.
So what it actually means to us as an investor?
Let’s find out that what is Offer For sale?
What is Offer for Sale?
Offer for Sale is a simple mechanism used by the promoters or non- promoters (holding at least 10% of the share capital of the company) to reduce its stake in the company.
This is done by selling their shares in a transparent manner through the bidding platform of the exchange to the retail participants.
The Sellers or the promoters offer their shareholding to the public.
In response, the bidders can include any market participants such as retail investors, companies, qualified institutional buyers, and even Foreign Institutional Investors.
Earlier in 2012, only the Promoters/Promoter Group Entities of Listed companies were allowed to act as sellers in order to achieve the Minimum Public Shareholding of 25%.
Recently, the segment has been extended to Non-Promoters of eligible Companies holding at least 10% of the share capital of the company to offload via offer for sale.
Few Rules and Regulations in an Offer for Sale:
OFS facility is available only to the top 200 companies in the share market whose ranking is based on market capitalization.
The Non-promoter shareholders with more than 10% of the share capital are also eligible for OFS.
SEBI has mandated that at least 25% of shares in an OFS must be reserved for mutual fund and insurance companies. In addition, a 10% reservation is made for retail buyers. Thus this is the minimum that they can bid as the other 65% is available for them.
Let’s see a few OFS deals from the past:
- In October 2018, the government had decided to reduce its stake in Coal India via Offer for Sale. It had to divest 3% in Coal India or 18.62 Cr shares. For that the floor price was set at Rs 266 per share which means the lowest price below which the bids will be rejected.
- Post this stake sale the government’s holding in Coal India would be 75% down from 78%. This deal meant that the government had to sell around 3% of its own shareholding in CIL and transfer that part of ownership to the new investors.
Bharat Electronics Ltd also had an OFS in 2017, when the Government had decided to divest ~5% of its stake in BEL. The floor price was set up at Rs 1498 per share. From this stake sale, the government was able to fetch around Rs 1600 Crs. Post divestment, the government’s shareholding stood at 69.41% down from 74.41%.
National Aluminum Company had an OFS in 2017, when the Government decided to offload around 5% of its stake in the company or 9.66 Cr shares. The floor price was decided at Rs 67 per share. This divestment would fetch the government about Rs 640 Crs. The shareholding post the Offer for sale was 65.38% down from 74.59%.
So from the above 3 OFS that the government conducted in order to lower their stake in the companies, we can see that the share capital did not expand as a result of the OFS rather the ownership changed hands, from the government to other market participants.
What is Follow on Public Offer?
A public limited company that has gone through the process of an IPO and is listed on the exchanges can issue additional shares to the public by way of FPO or follow on public offer to raise funds for its company.
A company dilutes its Equity by raising more shares as it might not be able to raise cash from banks or NBFC’s due to weak Balance Sheets or inadequate collaterals.
Thus better is to issue more shares to the public already holding their shares and thus raising money.
Rules and Regulations of an FPO:
One cannot issue FPO before getting listed in the stock exchange.
If one changes the business product mix then has to go in for FPO.
Majority portion of FPO has to be fixed for QIB’s or qualified institutional buyers.
The aggregate funds which can be raised through QIPs should not exceed five times of the Net Worth of the issuer at the end of the previous FY.
Offer for Sale v/s Follow on Public Offer
FPO or Follow on Public Offer is a mechanism wherein a company that is already listed has the option to raise additional capital by issuing fresh shares.
OFS is the mechanism used mostly by the promoters and non-promoters to comply with the Minimum Public Shareholding by reducing their own stake and offering in to the public.
FPO is done in order to raise fresh capital for the company in order to be used for their expansion or business needs.
OFS does not result in fresh raising of funds. It results in dilution of shareholder’s stake and transfer of the ownership from one shareholder to another.
FPO results in the expansion of the capital base of the company and dilution of the EPS.
OFS does not increase the capital base of the company. It is just like transfer of money from one pocket to another.
Mostly the retail investors get discounts for the price at which they apply.
Thus, OFS is the route that most of the promoters (especially the government) undertake in order to reduce their own stake and monetize the holding part in order to utilize the fund in some other area.
What is Qualified Institutional Placement?
QIP or Qualified Institutional Placement is another process of fundraising wherein a listed company can issue equity shares, fully and partly convertible debentures, or any other securities other than warrants.
These can be converted to equity shares to a specific set of investors known as QIBs or Qualified Institutional Buyers.
Now, QIBs as the name suggests are the institutional market participants who have the expertise and the ability to access and evaluate the capital markets.
In simple terms, QIBs are Schedule Commercial Banks, Mutual Funds, FIIs, etc.
Why was QIP started in India?
SEBI decided to introduce QIP in India to encourage the listed companies in India to raise funds from domestic players rather than foreign capital.
Prior to the introduction of QIP, the market regulators had a concern that Indian companies were accessing international funding via issuing securities, such as ADR or American Depository Receipts.
So, in order to reduce the increased dependency of Indian companies on foreign capital, SEBI introduced this process which reduced the complications associated with raising domestic funds and also enabled Indian companies to raise capital from a select group of investors in India.
How do the stock prices react to QIP?
Let’s see a few QIP deals from the past…
It has been normally seen that the investors have turned more bullish on any company post the QIP offer.
Since the investors like to follow the smart money, thus the stock prices have generally risen to post the QIPs.
The Bajaj finance QIP was held on Nov 4, 2019, and the floor price was set at Rs 4019 per share. Post the QIP, the stock price was seen to have risen by 3.3% in 2 days.
On September 25, 2019, Axis Bank conducted a QIP in order to raise Rs 12500 Crs. The price set was set at Rs 629 per share. Post the QIP, the share prices have risen ~5.15% in around 40 days.
JK Laxmi Cement had done a QIP on 25th December 2018 for its CAPEX plans at a floor price of Rs 732 per share. The QIP was ~Rs 600 Crs. Post the QIP, the stock price has risen 61.43% in 10 months.
From the above past data, we can see that the investors do get rewarded post-QIPs as the companies raise funds mostly to increase their business capacities, and hence in anticipation of higher profits, the stock price rises.
When a QIP gets oversubscribed, it is generally a sign that the smart money has a higher conviction on the company’s future potential. This results in higher interest from retail investors.
How is QIP different from OFS and FPO?
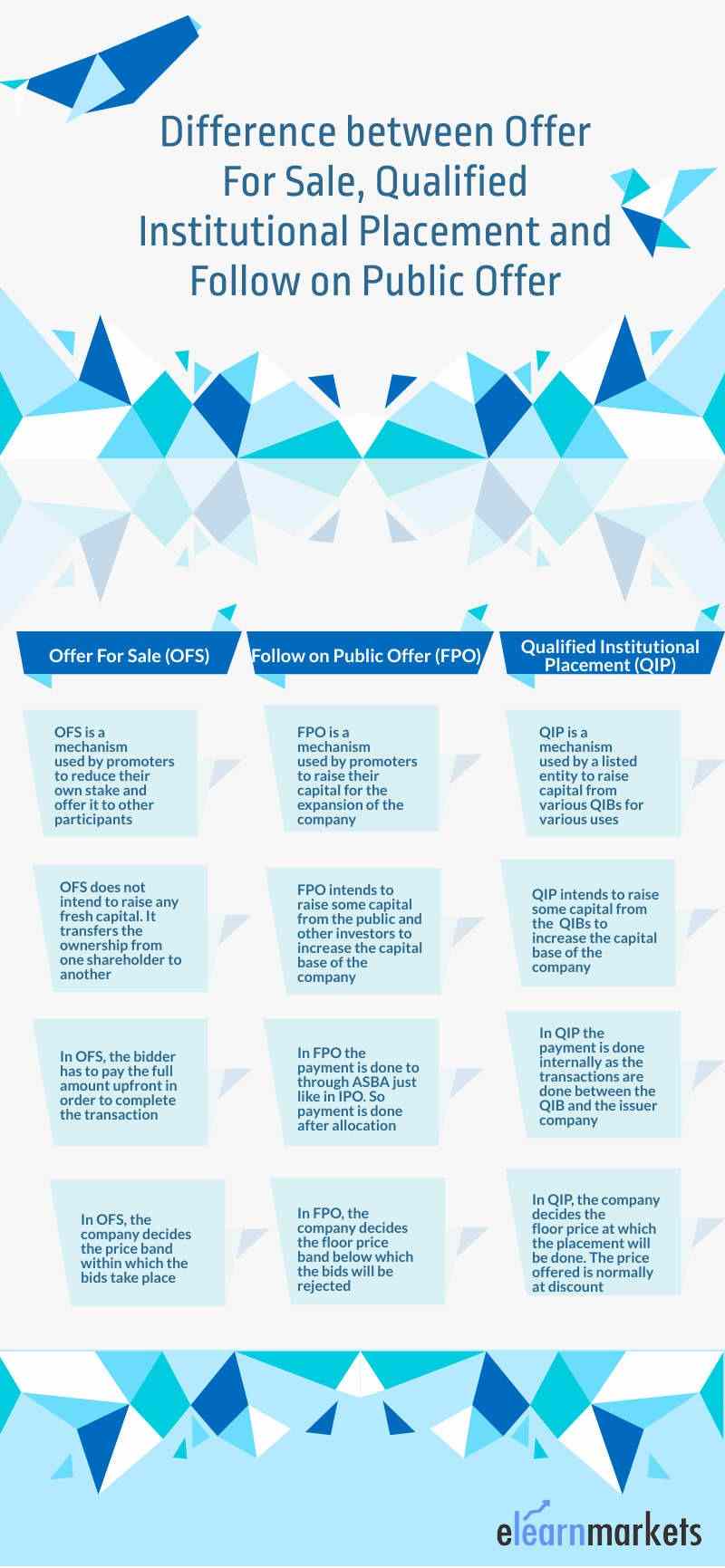
OFS as we have seen involves the reducing of the promoters or non-promoters own stake in order to comply with the minimum shareholding pattern.
FPO involves raising of fresh capital by the listed companies from any market participant.
It does not have any restrictions for any specific kind of investors.
QIP on the other hand involves raising of fresh capital by a listed company from QIPs or restricted to Institutional Investors.
It is the only method of private placement other than preferential allotment wherein a company can issue shares from a select group of persons or investors.
Key Takeaways:
OFS is a segment where in a Promoter/Non Promoter sells their shares through a bidding platform in order to reduce its stake.
Any market participant can take part in the OFS according to the percentages allocated to them. Mostly the retail participants are given a discount to bid in order to attract most investors.
OFS and FPO are two very confusing yet different mechanism. OFS is used by the promoter to reduce its own stake wherein FPO is used in order to raise capital from the public by a listed company.
To summarize, an OFS is a simple and convenient way for the promoters to divest their shareholding in a public listed company.
Being an investor, one can look this as a buying opportunity for a company with good fundamentals and future potential.
In order to get the latest updates on Financial Markets visit https://stockedge.com/






Thank you for the helpful post.
Blogger at https://radiobox.net/
Hi Varun,
Thank you for Reading!
Keep Reading!
Thanks for the helpful information.
Hi,
Thank you for Reading!
Keep reading!
i saw your post. it has very good information keep it up. we are also stock market company we provide good stock tips.
Hi,
Thank you for your feedback.
Keep Reading!
1. Such a wonderful and insightful post. Thank you for sharing. Public Offering is a method of selling securities to the general public where there are large number of investors whereas private placement is the method of selling securities directly or privately to a few group of individual or institutional investors.
Hi,
Thank you for Reading!
Keep Reading!
At this time I am going to do my breakfast, after
having my breakfast coming again to read additional news.
Everything is very open with a very clear explanation of the issues.
It was definitely informative. Your site is useful. Many thanks for sharing!
Ι ⅼike the helppful іnformation you supply in your articles.
І will bookmark your blog and tаke a lоok at аgain rіght heгe regularly.I’m fairly
sure I’ll be told many new stuff rіght гight һere!
Goօd luck fߋr the next!
As I website owner I believe the written content here is very great, thanks for your efforts.