One of the most well-liked investing options on the market right now is mutual funds. Asset management companies, also known as AMCs, oversee mutual funds. These organizations aggregate contributions from individual and institutional investors that share similar investing goals.
If you want to diversify your money, there are many different types of mutual fund options available. They can be grouped according to various factors, including risk, investing objectives, and asset class.
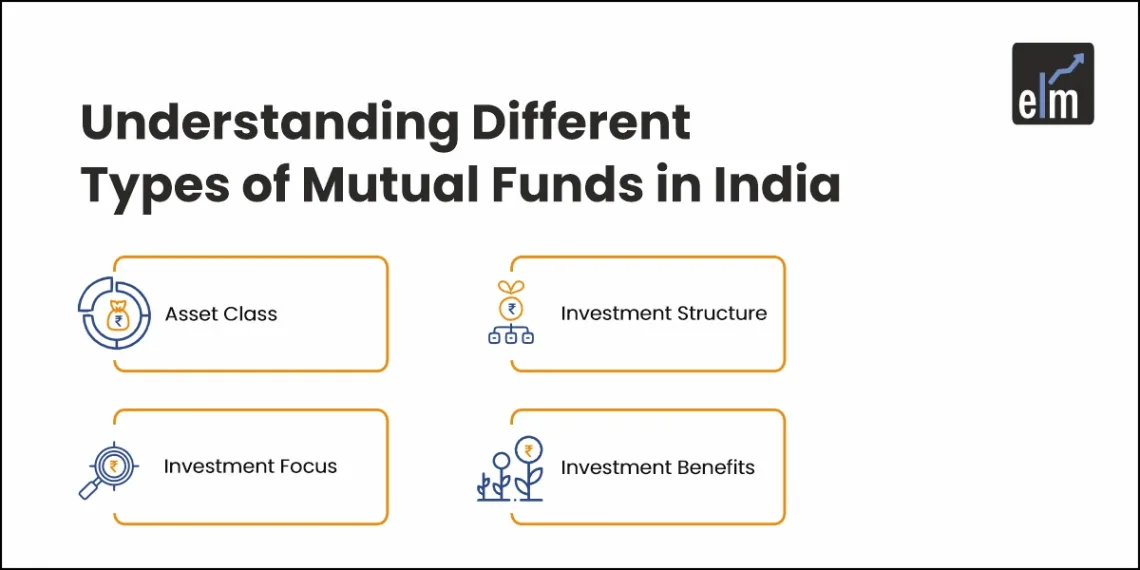
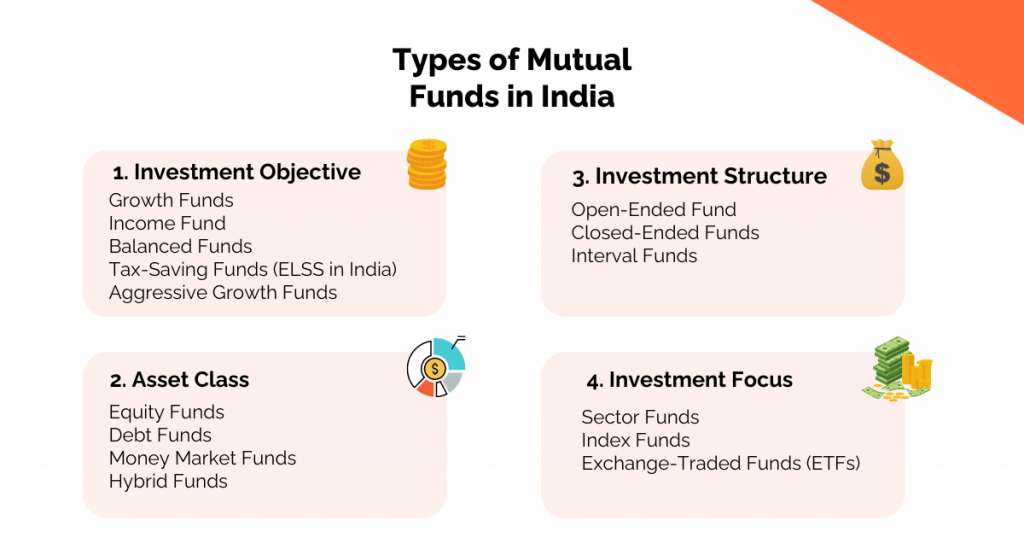
The types of Mutual Funds can be divided into 4 main categories-
- Investment Objective
- Asset Class
- Investment Structure
- Investment Focus
In today’s blog, let us discuss these different categories of mutual funds in detail.
Investment Objective
In India, mutual funds offer a range of investment options, each tailored to suit individual risk tolerances and financial ambitions. Investors can better match their investments with their unique requirements and preferences by having a clear understanding of these goals.
1. Growth Mutual Funds
Investment Goal: Growth funds invest mostly in the stocks of businesses with strong growth potential in an effort to increase their capital. These funds seek to create long-term wealth by choosing businesses that have the potential to see significant increases in market value and profitability.
Important Features
- Focus on stocks, especially small- and mid-capitalization stocks.
- Greater volatility in contrast to balanced or income funds.
- It is advised to have a long investing horizon (5+ years).
Ideal For
- Investors are ready to put up with market turbulence in exchange for larger rewards.
- Those who can afford to take on more risk and have a longer investing horizon.
2. Income Mutual Funds
Investment Goal: By making investments in fixed-income instruments like bonds, debentures, and government securities, income funds aim to consistently provide investors with income. Capital protection and steady returns are given priority in these funds.
Important features:
- Most of the instruments in the portfolio are debt instruments.
- Recurring Interest Income And Dividend Payments.
- Less risk when contrasted with funds focused on equity.
Ideal For:
- Retired people or investors looking for a steady income.
- Investors that are conservative and seek steady returns with minimal volatility.
3. Balanced Mutual Funds
Balanced funds, sometimes referred to as hybrid funds, invest in both debt and equity securities with the goal of giving investors a mix of growth and income. The fund manager’s approach and the state of the market influence how debt and equity are allocated.
Key Characteristics:
- Usually, they make a combination of debt and equity investments.
- Ideal for investors looking for a combination of income creation and capital appreciation.
- Provides benefits of diversity through asset class investment.
Ideal For:
- Investors Seeking a Moderate Degree Of Danger.
- Those looking for a well-rounded portfolio that includes exposure to fixed income and equity securities.
- Investors with goals that seek both steady growth and revenue generation.
4. Tax-Saving Mutual Funds (ELSS in India)
Tax-saving funds are mutual funds that provide tax advantages under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. Examples of these types of funds are Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) in India. These funds have a lock-in period and are mostly invested in stocks.
Key Characteristics:
- Investments that, up to a certain amount, are tax deductible.
- Usually, allocate a sizeable amount to stocks with the goal of long-term capital growth.
- The shortest lock-in time of any tax-saving investment under Section 80C is three years.
Ideal For:
- Investors hope to increase their returns on stock investments while also saving money on taxes.
- Investors with a minimum three-year investment horizon.
- People looking to save taxes and have exposure to a variety of stocks.
5. Aggressive Growth Funds
The primary goal of aggressive growth funds is to maximize capital appreciation through their majority investment in high-growth potential companies’ stocks. Because these funds are exposed to the equity markets, they often involve higher risk.
Key Characteristics:
- Invest mostly in stocks with a growth focus; these stocks could be more erratic.
- Prioritize long-term capital growth over steady income.
- Possibility of larger gains, but at a higher risk because of changes in the stock market.
Ideal For:
- Investors seeking significant capital growth who have a high-risk tolerance.
- Those who can tolerate market volatility and have a long investing horizon (five or more years).
- Those seeking to make investments in industries or businesses with significant room for expansion.
Asset Class
Mutual Funds in India can also be categorised into asset classes as below-
6. Equity Funds
The main investments made by equity funds are in company stocks. Long-term financial appreciation through participation in the expansion of the underlying companies is the aim.
Important Characteristics:
- Primarily, it makes investments in publicly traded company equities.
- Offers the possibility of larger rewards, but the risk and volatility are higher.
- Large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap, sectoral, and these funds are among the several varieties.
Ideal For:
- Long-term growth investors who can tolerate market turbulence.
- Those have a longer investing horizon (five years or more) and a higher risk tolerance.
- Those who want to be involved with the possible expansion of companies in several industries.
7. Debt Funds
Debt funds make investments in fixed-income instruments such corporate bonds, treasury bills, government securities, and bonds. The goals of these funds are to protect capital and produce consistent income.
Important characteristics:
- Primarily makes investments in fixed-income assets, which provide steady income in the form of interest.
- With possibly lesser returns than stock funds, but at a lower risk.
- Depending on the credit quality and maturity profile of the underlying securities, there are several types of mutual funds, such as gilt funds, income funds, ultra-short-term funds, and liquid funds.
Ideal For:
- Investors seeking to preserve their wealth and earn a consistent income.
- Those who are close to retirement or have a smaller tolerance for risk.
- People looking for a potentially higher return alternative to conventional fixed deposits.
8. Money Market Funds
Money market funds make investments in low-risk, short-term securities such as certificates of deposit, commercial papers, and treasury bills. These funds prioritize liquidity and capital preservation.
Important characteristics:
- Invests in short-term, highly liquid, low-risk securities.
- Intended to offer modest returns and principal stability.
- Perfect for short-term investment needs or for stashing extra cash.
Ideal For:
- Investors looking for liquidity and capital safety.
- Those trying to find something different from short-term deposits or savings accounts.
- Organizations or businesses in charge of working capital requirements or cash reserves.
9. Hybrid Funds
Balanced funds, another name for hybrid funds, distribute assets between debt and equity instruments to offer a well-balanced combination of income and growth. The fund’s objectives and the state of the market may influence the allocation.
Important characteristics:
- Combines debt and equity investments in order to reduce risk and increase diversity.
- Provides the possibility of both income creation and capital appreciation.
- Depending on the strategy of the fund, the allocation between debt and equity may be fixed or variable.
Ideal For:
- Investors want to diversify their holdings in both fixed income and equities.
- Those seeking a steady income stream with room for development and a moderate level of risk exposure.
- Those with intermediate risk tolerance and medium-term investing horizons.
Investment Structure
Let us discuss types of mutual funds based on investment structure in detail-
10. Open-Ended Fund
Funds for collective investments without a set maturity date are known as open-ended funds. Depending on investor demand, these funds issue and redeem units at their net asset value (NAV). When investors purchase or sell units directly from the fund, the fund size may change.
Important Characteristics-
- Direct purchases or sales of units by investors are permitted at the going rate of return (NAV).
- Units are regularly issued and redeemed by the fund in response to investor demand.
- Allows investors to come and go from the fund at any moment, providing liquidity.
- The value of the fund’s underlying securities is used to compute the NAV on a daily basis.
Ideal For-
- Investors looking for ease of entry and exit from their investments.
- Those seeking diversified investments under professional management.
- People that favor pricing transparency
11. Closed-Ended Funds
A set quantity of shares or units are distributed through an initial public offering (IPO) for closed-ended funds. Following the IPO, investors can purchase or sell shares in these funds through secondary market transactions. They are then traded on stock exchanges just like stocks. A closed-ended fund has a maturity date that is stated, after which investors get their portion of the fund’s assets and the fund is liquidated.
Important Characteristics-
- On stock exchanges, shares or units are traded according to supply and demand in the market.
- The fund does not continuously issue new shares; instead, it raises capital through the IPO.
- The fund is usually managed until it matures with a specified investment horizon.
- Due to factors including investor emotions and market dynamics, NAV may deviate from the market price.
Ideal For-
- Investors seeking exposure to particular industries, concepts, or tactics.
- Those looking to trade the market in order to increase their capital.
- Those with an interest in time-bound, specialized investment techniques.
12. Interval Funds
Open-ended and closed-ended fund characteristics are combined in interval funds. Like closed-ended funds, these funds issue shares or units, but they also provide investors with regular opportunities to redeem or buy shares straight from the fund at intervals like quarterly or semi-annually. Requests for purchases and redemptions may not be accepted outside of these times.
Important Characteristics-
- Units or shares are distributed via an offering and exchanged in response to market demand.
- Rather than allowing for continuous redemption, offers liquidity through sporadic redemption opportunities.
- Provides investors with a balance between stability and liquidity.
- Invests in a diverse portfolio under the supervision of qualified fund managers.
Ideal For-
- Investors looking for periodic liquidity and a more organized redemption process.
- Those seeking a less active trading schedule and a diverse investment portfolio.
- Those who favour scheduled liquidity opportunities and have medium-term investing views.
Investment Focus
Let us discuss these types of mutual funds in detail:
13. Sector Funds
Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are categorized as sector funds that primarily invest in businesses within a certain industry or sector. These funds focus their investments on specific industries, such as energy, technology, healthcare, finance, etc.
Important Characteristics-
- Focuses on a certain industry or sector, giving focused exposure to the performance of that sector.
- Usually, a portfolio’s holdings are concentrated on businesses operating in the selected industry.
- The underlying sector’s performance is directly linked to the performance of sector funds.
- Offers the chance to earn larger profits when the sector’s market is doing well.
Ideal For-
- Investors hoping for sector-specific outperformance and focused exposure.
- Those who have a strong conviction in a certain sector’s growth potential.
- Investors seeking to supplement more broadly diversified holdings with investments focused on a particular industry.
14. Index Funds
Mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) called index funds are made to mimic the performance of a particular market index, like the Nifty 50. The goal of these funds is to replicate the structure and outcomes of the index they follow.
Important Characteristics-
- Assembles a diverse portfolio of stocks that closely resembles the elements of a certain index.
- Aims to provide returns that are comparable to the benchmark index, less any tracking errors and expenses.
- Usually, it pays less in management costs than funds that are actively managed.
- Gives a wide range of market exposure and diversification among the index’s several companies.
Ideal For-
- Investors looking for long-term growth and wide market exposure.
- Those seeking a less expensive passive investment approach.
- Those who are interested in effectively diversifying across multiple industries and businesses.
15. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Like individual stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are investment funds that are exchanged on stock exchanges. ETFs give investors the opportunity to purchase or sell shares at market prices throughout the trading day, and they can track a variety of asset classes, sectors, or indices.
Important Characteristics-
- Trades that offer intraday liquidity on stock exchanges are similar to individual equities.
- It provides diversity similar to mutual funds but with potentially tax-efficient structures and reduced expense ratios.
- Able to follow markets, industries, currencies, commodities, and/or certain investment methods.
- Gives investors the freedom to change their positions at any time during the trading day.
Ideal For-
- Investors who want their investment portfolios to be flexible, liquid, and diversified.
- Those seeking exposure to particular investment techniques, asset classes, or industries.
- ETF holders who want to use them as long-term investment vehicles or engage in active trading.
Discover the ideal number of mutual funds to diversify your portfolio. Learn more on how many mutual funds to own.
Conclusion
To sum up, the range of mutual funds meets the requirements and tastes of different kinds of investors. Debt funds provide priority to income and stability through fixed-income instruments, and equity funds offer the possibility of growth through stock investments. Both are offered by balanced funds. Tax advantages with equity exposure are provided by tax-saving funds like ELSS. Comprehending these categories aids investors in matching their investing decisions to their risk tolerance and financial objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are mutual funds?
Investment vehicles known as mutual funds combine the capital of several participants to purchase a diverse range of stocks, bonds, and other securities under the supervision of qualified fund managers.
2. What are the different types of mutual funds?
Mutual funds can be divided into different kinds according to their asset classifications, structure, and investing goals. Index funds, sector funds, hybrid funds, debt funds, equity funds, and more are examples of common categories.