In the world of investment management, tactical asset allocation, or TAA, is a dynamic method that provides a proactive means of managing the intricacies of financial markets.
As opposed to Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA), which, over time, sticks to predetermined percentages of asset classes, TAA values flexibility and responsiveness to shifting market conditions.
Fundamentally, TAA is the art of proactively modifying portfolio allocations in response to short- to medium-term market outlooks, economic indicators, and other pertinent factors in order to maximize opportunities and minimize risks.
With this flexible strategy, investors can take advantage of new trends, reduce losses in bear markets, and maximize profits in a variety of market cycles.
In today’s blog, let us discuss what tactical asset allocation is all about.
What is Tactical Asset Allocation?
The investment approach known as tactical asset allocation, or TAA, is dynamically modifying the distribution of assets within a portfolio in reaction to current market conditions as well as other pertinent variables.
While Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA) keeps a constant allocation to different asset classes over an extended period of time, Targeted Asset Allocation (TAA) frequently rebalances the portfolio to take advantage of perceived market inefficiencies or opportunities.
How does Tactical Asset Allocation work?
The process of actively participating in the tactical asset allocation itself and temporarily modifying long-term target weights in order to take advantage of market or financial opportunities is known as tactical asset allocation.
Let’s take an example where data indicates that for the following 18 months, there will be a significant growth in the demand for commodities. To capitalize on the opportunity, an investor could be wise to move additional money into that asset class.
The tactical allocation in the portfolio may then turn into while the strategic allocation will stay the same.
- Cash = 5%
- Bonds = 25%
- Stocks = 55%
- Commodities = 25%
Within an asset class, tactical changes are also possible. Assume that the 30% large-cap and 25% small-cap holdings comprise the 55% strategic allocation of equities. It can be a smart tactical move to temporarily adjust the stock allocation to 50% large-cap and 5% small-cap if the prognosis for small-cap stocks is not promising. This will allow conditions to alter before long.
Tactical changes typically fall between 5% and 10%, although they can fall even lower. It is uncommon in practice to make a tactical adjustment of more than 10% to any asset class. This significant modification would reveal a basic issue with the way the strategic asset allocation was put together.
Rebalancing a portfolio differs from tactical asset allocation. Trades are performed to return the portfolio to the intended strategic asset allocation during the rebalancing process.
For a brief period of time, tactical asset allocation modifies the strategic asset allocation with the goal of returning to the strategic allocation after the transient possibilities pass.
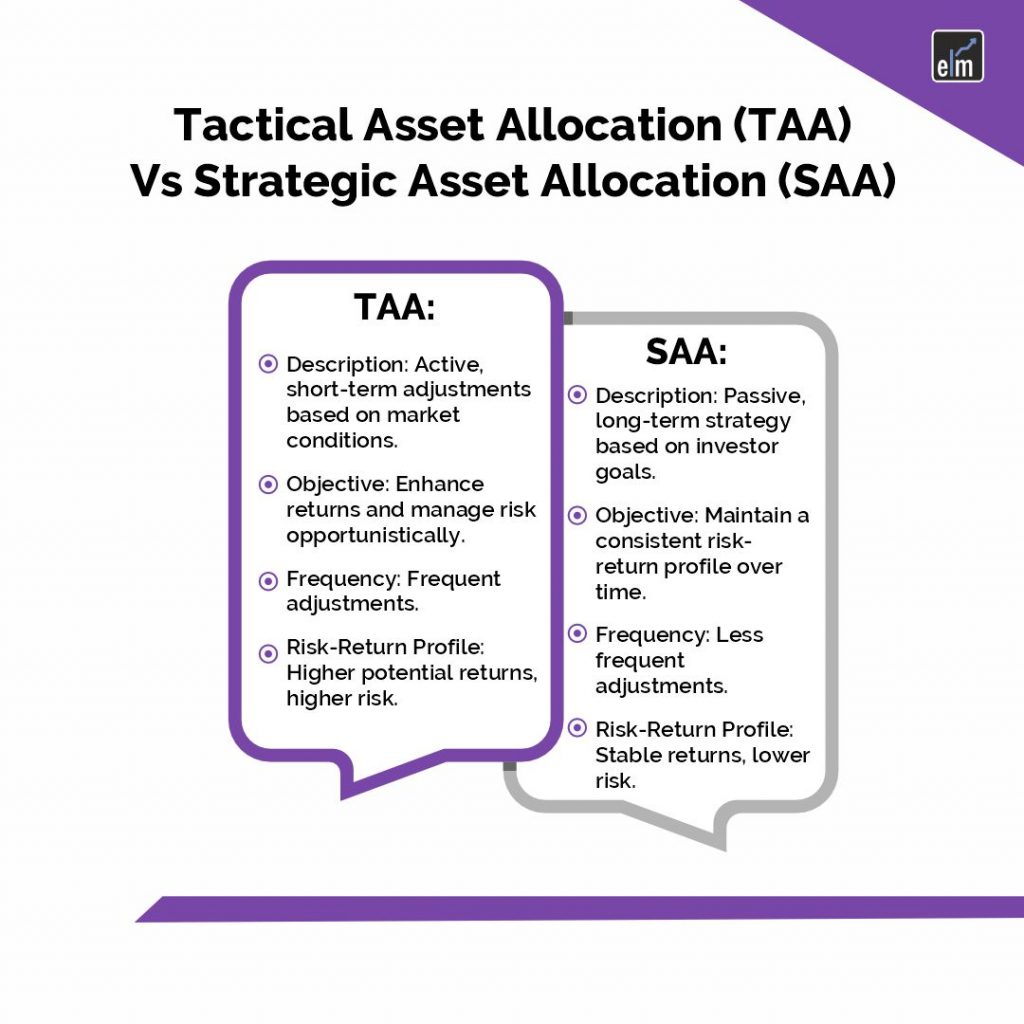
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) vs. Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA)
There are two distinct methods for managing investment portfolios: tactical asset allocation (TAA) and strategic asset allocation (SAA), each with unique goals and traits. The two are contrasted as follows:
1. Goal
The goal of tactical asset allocation, or TAA, is to proactively modify a portfolio’s asset allocation in response to opportunities or hazards that arise in the short- to medium-term market. TAA’s main goal is to increase returns and control risk by taking advantage of perceived mispricings or shifting market conditions.
Conversely, Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA) is a long-term method of managing a portfolio. It entails setting a target asset allocation determined by the investor’s time horizon, risk tolerance, and financial objectives. Building a diversified portfolio that meets investor goals and has a steady risk-return profile over time is the aim of systematic asset allocation (SAA).
2. Regularity of Modifications
TAA: TAA entails regularly modifying the allocation of the portfolio in response to changes in the market, economic indicators, and other immediate considerations. When using TAA, portfolio managers can adjust the allocation every quarter, month, or even more often.
SAA: SAA usually entails fewer modifications over time. Long-term factors are taken into account when establishing the goal asset allocation, and changes are made on a regular basis (e.g., annually or biannually) to bring the portfolio back to its target weights.
3. Risk and Returns
TAA: TAA is more dynamic and opportunistic, seeking to capitalize on transient market trends or inefficiencies. Because of the active nature of portfolio management and the potential for market timing errors, TAA strategies have a higher level of risk even though they may yield larger rewards.
SAA: SAA is all about keeping an asset mix that is strategically chosen to help investors reach their long-term financial goals. Following the established asset allocation targets over time should result in a more stable risk-return profile.
4. Implementation
TAA: To effectively implement TAA methods, market circumstances, economic indicators, and other pertinent aspects must be actively monitored. To promptly modify the portfolio allocation, portfolio managers employ quantitative models, technical analysis, and fundamental research.
SAA: A more passive approach to portfolio management is used to implement SAA. To realign the portfolio with the strategic targets, periodic portfolio modifications are undertaken once the target asset allocation has been established.
Benefits of Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation, or TAA, is an investment approach that investors and portfolio managers use to proactively rebalance their portfolio’s asset mix in response to shifting market circumstances, economic forecasts, and other variables.
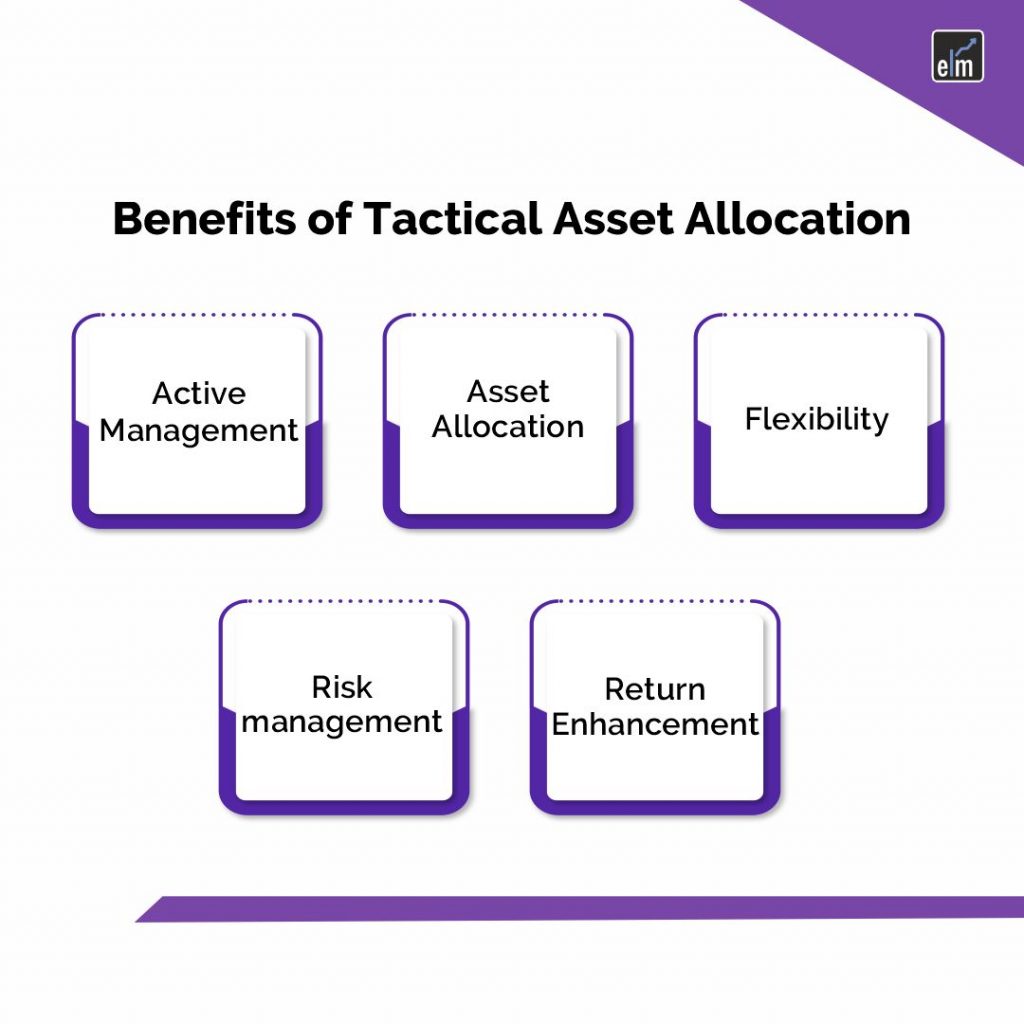
Active Management
TAA entails actively managing a portfolio by modifying the distribution of assets in response to a range of variables, including investor sentiment, market trends, economic indicators, and valuation criteria. Unlike buy-and-hold passive techniques, TAA necessitates continuous decision-making and monitoring.
Asset Allocation
The distribution of investments among various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and cash equivalents, is referred to as asset allocation. The goal of TAA is to dynamically rebalance the allocation across these asset classes in order to reduce risk or take advantage of opportunities.
Flexibility
One of TAA’s primary characteristics is its adaptability. Portfolio managers have the ability to modify their exposure to various asset classes in accordance with their evaluation of the state of the market and their projection of future returns. For instance, they might shift their allocation from equities to bonds if they think bonds offer superior risk-adjusted returns and equities are overpriced.
Risk management
Another application for TAA is in risk management. Investors can actively manage portfolio allocation to minimize downside risk in times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty. For example, in periods of market stress, they might devote a larger portion of their assets to defensive investments like cash or bonds.
Return Enhancement
By seizing short- to medium-term market opportunities, TAA seeks to increase returns in addition to risk management. Investors aim to attain greater returns by investing in asset classes that are anticipated to perform better in the present market conditions, as opposed to using a static asset allocation approach.
Drawbacks of Tactical Asset Allocation
Here are the drawbacks of Tactical Asset Allocation-
- Costlier: Compared to passive index funds, this option may have higher fees because it requires active management.
- Implementation complexity: For successful execution, a high level of proficiency in risk management and market analysis is needed.
- Danger of underperformance: It’s hard to time the market right, and active management doesn’t ensure success.
Conclusion
Tactical asset allocation is a dynamic investment strategy that actively modifies asset allocation in response to shifting market conditions in an effort to maximize returns and minimize risk. It necessitates diligent execution, astute analysis, and proactive portfolio management.
For More Market Updates, Visit StockEdge
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA)?
The goal of the tactical asset allocation (TAA) investing approach is to actively modify a portfolio’s asset allocation in response to shifting market conditions, economic indicators, and other variables.
2. How does TAA differ from Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA)?
TAA is a short- to medium-term strategy that makes changes in response to market opportunities; on the other hand, SAA is a long-term strategy that aims to create a target asset allocation that is in line with investor objectives.
3. What factors influence TAA decisions?
Market movements, economic statistics, valuation metrics, geopolitical developments, and investor emotions are some of the elements that affect TAA decisions.