Exchange Traded Funds, investing in the stock market, are a popular way to grow our wealth on a long-term basis. One of the reasons why the stock market is so popular is because of the financial products it offers.
One of these is mutual funds. A mutual fund is a basket of securities that are professionally managed by an expert.
These funds are of different types, usually catering to various risk appetites. In this article, we will talk about one of these types – the ETFs.
What are Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)?
Exchange Traded Funds are a basket of securities that usually track the behaviour of a stock market index.
Unlike other mutual funds, Exchange Traded Funds are traded on the stock market like company shares.
While most mutual funds are created to outperform a benchmark, ETFs are created to track an underlying factor.
The fund manager simply invests in the stocks which are present in a market index to imitate its performance.
In India, an ETF can be tracking the SENSEX, Nifty50, Bank Nifty, etc.
How Can We Invest in Exchange Traded Funds?
There are two ways to invest in Exchange Traded Funds –
- On the telephone, through placing a detailed order with your broker.
- Online, through trading terminals. These are available as websites and mobile apps as well.
Just like for any security, you need to open a trading and demat account with all KYC compliances fulfilled. When you trade ETFs in the stock market, you essentially purchase units of the funds.
An important point to remember here – unlike a normal fund, you cannot purchase a fraction of an ETF unit. ETFs, like shares, are traded at a market price that changes in real time.
However, fund houses provide indicative NAVs to help investors make better decisions. This NAV is different from the market price, which will depend on the supply and demand for the fund.
Since ETFs are traded like shares, every trade will entail brokerage, commission and tax charges as well.
Exchange Traded Funds Types
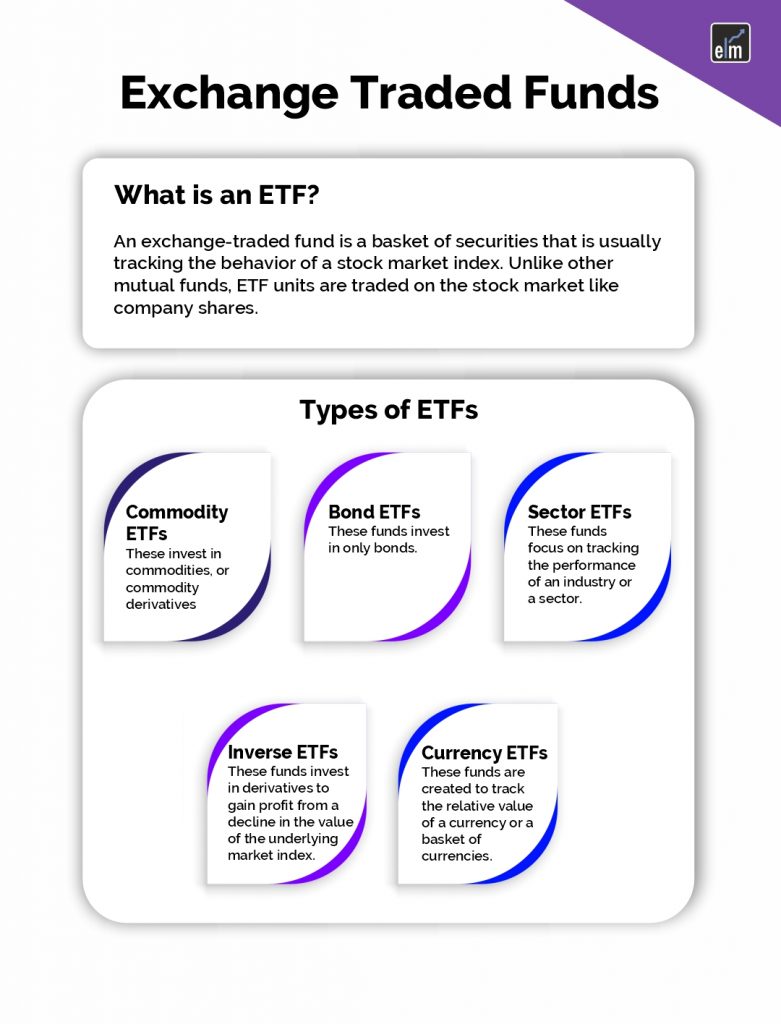
Apart from market indices, ETFs can be created to track the performance of many other economic events.
Some of the popular ETF types include –
- Commodity ETFs – These invest in commodities or commodity derivatives market
- Bond ETFs – These funds invest in only bonds.
- Sector or Industry ETFs – These funds focus on tracking the performance of an industry or a sector.
- Inverse ETFs – These funds invest in derivatives to gain profit from a decline in the value of the underlying market index.
- Currency ETFs – These funds are created to track the relative value of a currency or a basket of currencies.
Advantages of Exchange Traded Funds
ETFs offer a variety of advantages which are –
1. Diversification
As mentioned before, there are many types of ETFs that focus on various securities.
Through investing in an ETF, an investor can diversify their portfolio with multiple securities in one go.
2. Lower costs
ETFs are generally known to have lower expense ratios.
Therefore, instead of investing in various companies, you can choose industry/sector ETFs and benefit from their growth.
3. Arbitrage
Since ETFs actually depend on an underlying factor, they can be used to generate profits from price fluctuations.
Investors can shuffle between index funds and derivatives to quickly gain from a rise or decline in value.
4. Convenience
Unlike other mutual funds, ETFs are freely available to trade on the stock market.
Moreover, they are listed on recognized stock exchanges.
This means that they are as transparent as possible when it comes to their pricing or trading mechanism.
Exchange Traded Funds Disadvantages
One should not overlook the following drawbacks before investing in ETFs –
1. Volatility:
The fact that ETFs depend on an underlying factor can be a disadvantage on the volatility front.
This is because different ETFs are tracking different things – from a stock index, to the crude oil industry.
Therefore, before investing in any ETF, you will have to study the movement of the underlying factor.
For example, if you want to invest in commodity ETFs, you have to understand the various factors affecting commodities.
2. Portfolio Risks
Despite reducing risk with diversification, ETFs bring various risks to your portfolio on a whole.
For example, if you invest in the ETF of an international index, you are bringing political risk.
If you are investing in bond ETFs, you are bringing credit risk to your portfolio.
Bottomline
ETFs are a unique method of growing your wealth. However, the right research and patience is required to ensure that the pros of your investment outweigh the cons. Also, before you invest, you must learn about the other types of mutual funds, compare them and then make your decision.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)?
Similar to individual stocks, an ETF is a kind of investment vehicle that trades on stock markets. It usually invests in stocks, bonds, and commodities with the goal of tracking an index’s performance.
2. How do ETFs work?
ETFs work by pooling money from investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of assets. These assets are then divided into shares, which are traded on stock exchanges throughout the trading day. The price of an ETF share fluctuates based on supply and demand in the market.
3. Are ETFs suitable for all investors?
A diverse variety of investors, including those seeking low-cost investing options and diversified exposure to multiple asset classes, may find success with exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Before purchasing ETFs, investors should take their time horizon, risk tolerance, and investment objectives into account.






Thank you for writing this blog on ETF you have helped a lot in understanding the various concepts of ETF for a budding investor like me. Looking forward to reading more blogs from you.
Investmentz in ETF can be a great investment option.
Hi,
We really appreciated that you liked our blog! Thank you for your feedback!
Keep Reading!