We hope that by now, you are familiar with the Basics of the Call Option from both the buyer’s and seller’s perspectives.
A call option is an option contract in which the buyer has the right to buy a specified quantity of the underlying stock at a predetermined price without any obligation.
If you are now familiar with the call option, then understanding ‘Put Options’ is quite easy.
The view on put options from the buyer’s perspective is that the markets should be bearish, as opposed to the bullish view of a call option buyer.
Let us discuss the basics of the put option and then we will drive the put option premium and trading
Table of Contents
What is a Put Option?
A put option is an option contract that gives the buyer the right, but no obligation to sell the underlying asset at a specific price also known as the strike price.
Put options can be traded on many underlying assets like stocks, currencies, and also commodities.
They help us to protect our trades against the decline in the price of the above assets below a specific price.
Each put contract comprises 100 shares of the underlying security. The trader does not have to own the underlying asset for purchasing or selling puts.
The put buyer has the right, but not the obligation, to sell the asset at a particular price within a specified period. Whereas the seller has the obligation to buy the asset at the strike price if the option owner exercises their put option.
What does it mean by Buying Put Options?
Put buying is one of the simplest ways to trade put options.
When the options trader has a bearish view of a particular stock, then he can purchase put options to profit from a decline in the asset price.
To earn profits, the price of the asset must move below the strike price of the put options before the expiration date for this strategy.
Example:
Suppose the stock is trading at Rs.4900, and the put option contract with a strike price of Rs.70 expires in a month’s time.
You expect the stock’s price to drop sharply in the coming weeks after their earnings report.
The payoff diagram of the examples will look as below:
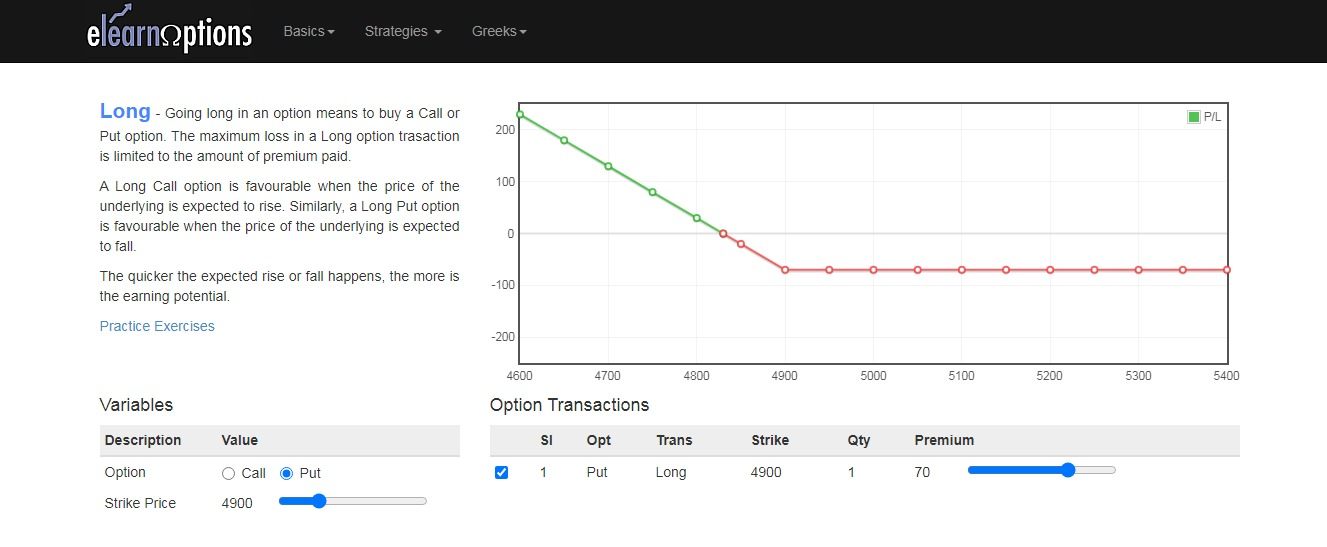
If the prices fall as expected, then we can earn unlimited profits.
But if our trade does not go according to our expectations, our loss will be limited to the premium price that we paid.
What does it mean by Selling Put Options?
Put sellers sell options with the expectation to lose value for benefiting from the premiums received for the option.
Once puts have been sold to a buyer, then the seller has the obligation to buy the underlying asset at the strike price if the option is exercised.
The stock price must increase above the strike in order to make a profit.
If the underlying stock’s price falls below the strike price before the expiration date, then the buyer makes a profit on the sale.
The buyer has the right to sell the puts, while the seller has the obligation and buy the puts at the specified strike price.
However, if the puts above the strike price, the buyer stands to make a loss.
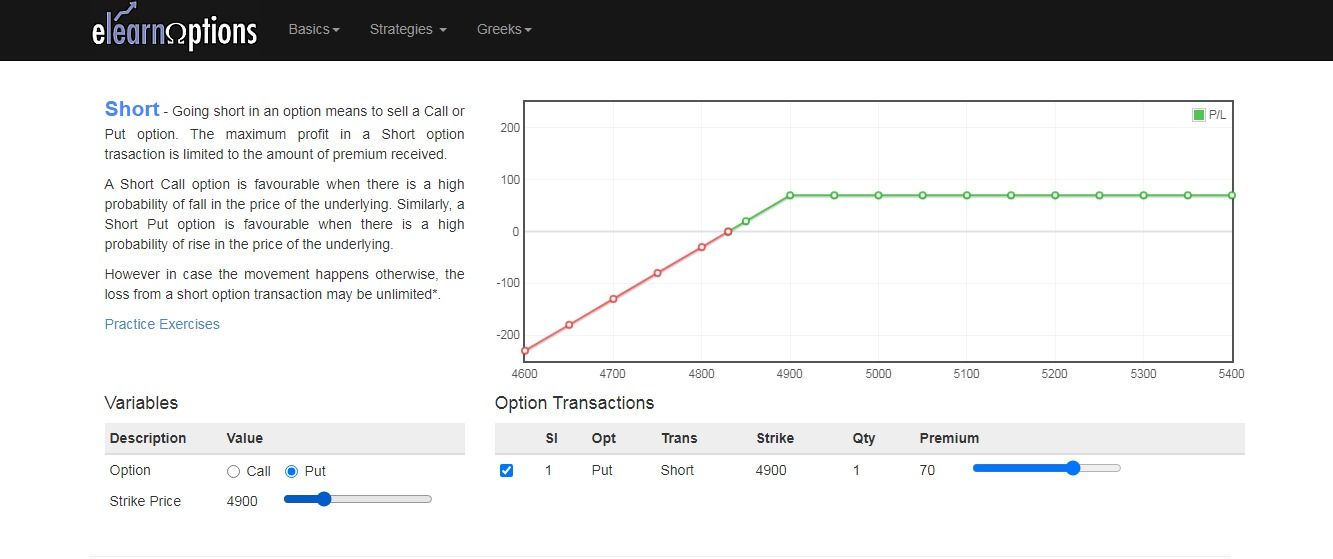
From the above diagram, we can see that the profit is limited to the premium, whereas if the prices move against our expectations, we may suffer unlimited losses.
Put Option Formula
If you want to calculate the value of the put option, then we will need 2 parameters:
• The exercise price
• The current market price of the underlying asset
If the option is exercised, then we can find out the value of the put option by the below formula:
Value= Exercise Price-Market Price of the Underlying Asset
If the option is not exercised, then it has no value.
Put Option Premium
To calculate the put option premium, you will need the following:
• Intrinsic Value
• Time Value
To calculate the intrinsic value, you require the current market price of the underlying stock and the strike price.
The difference between these two is known as the intrinsic price.
The time value depends on how far is the expiration date from the current date. Also, the higher the volatility, the higher is the time value.
Put Option Trading
A put option can be used for speculation, income generation, and tax management:
1. Speculation:
Put options are extensively used by traders when they expect a fall in the prices of the underlying stock
2. Income generation:
Traders can just sell the put option on shares instead of holding the securities.
3. Tax management:
Traders can eliminate paying huge taxes on the capital gain on the stocks by just paying the taxes on the put option.
Learn more about option selling through our option course at elearnmarkets.
Unlock the secrets of Put Options – Learn options trading India with our comprehensive course. Empower your financial journey now!
Bottomline
In summary, put options give investors a versatile tool for controlling risk and making money when the price of underlying assets declines, but they also come with a lot of variables to think about, including time, volatility, and risk management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a put option?
A put option is a financial instrument in which the holder is granted the right, but not the responsibility, to sell a predetermined amount of the underlying asset within a given time frame at a predetermined price.
How do put options work?
Put options grant the buyer the right, either before or on the expiration date, to sell the underlying asset at the strike price, independent of the asset’s existing market value. Put option writers are required to purchase the underlying asset in the event that the buyer exercises the option.
What is the purpose of buying put options?
Put options are purchased by investors as a hedge against possible negative risk in their portfolios or as a way to bet on an asset’s price drop.
You can also use option scans to filter out stocks for trading the next day by using the StockEdge web version.