More people in India are realising how important it is to invest their money to make it grow over time. With so many options available, investing has become a way to build financial security and take advantage of the country’s growing economy. Two popular options for investment are IPOs and unlisted shares, but they work in different ways.
An IPO, or Initial Public Offering, is when a company offers its shares to the public for the first time, allowing people to buy and sell those shares on the stock market. On the other hand, unlisted shares belong to companies that are not yet listed on the stock exchange. These shares are bought privately, often at an earlier stage in the company’s growth.
In this blog, we’ll break down the advantages and disadvantages of investing in IPOs versus unlisted shares. Let’s dive in and see how these options compare.
Advantages of Initial Public Offering (IPOs)
Here’s a breakdown of the benefits of investing in an IPO:
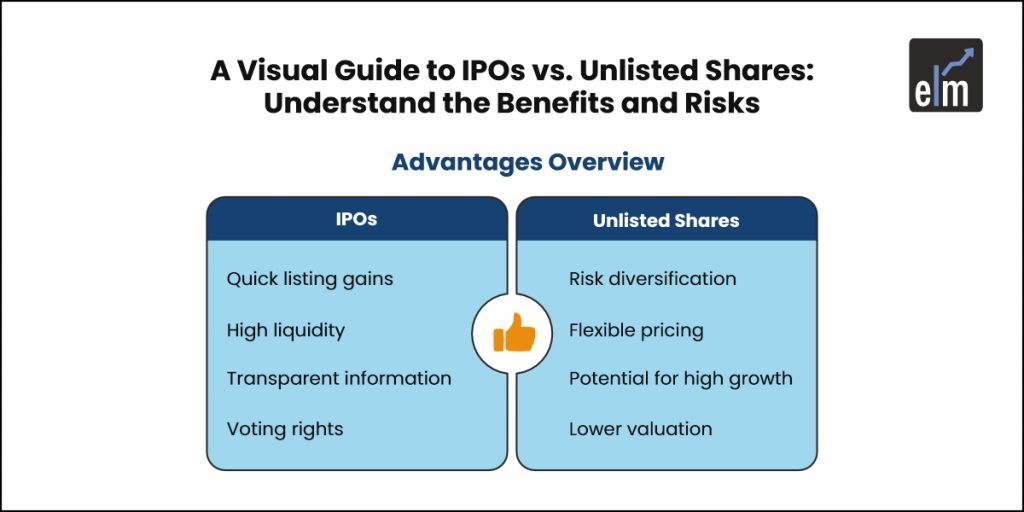
1. Listing Gains
One advantage of IPO investments is the potential for listing gains. This happens when the stock price on the day the IPO lists is higher than the initial investment price. Investors can sell the stock at a profit right from the start if the market demand for it is strong.
2. Liquidity
Once a company goes public, its shares can be bought and sold in the open market. This gives investors the flexibility to buy or sell whenever they want, creating liquidity. Investors don’t have to wait long periods to sell, making IPO investments more accessible.
3. Opportunities for Small Investors
The market regulator, SEBI, has introduced rules to ensure small investors have a fair chance to participate in IPOs. In the secondary market, it’s sometimes harder for these investors to buy shares due to high demand. IPOs open up more opportunities for them to enter the stock market early.
4. Transparency and Information
IPOs are regulated to ensure investors have a clear picture of the company. In the company’s IPO prospectus, investors can review detailed information like financial performance, growth plans, risks, and future goals. This level of transparency allows investors to make informed choices based on what’s most suitable for them.
5. Long-Term Accountability
After buying IPO shares, investors become part of the company as shareholders. Companies are motivated to meet their goals and reach profit targets to satisfy investors. As shareholders, investors can see the company’s progress, and stock prices tend to reflect this performance over time.
6. Financial Efficiency
SEBI’s IPO application system has been set up so funds are only deducted from investors’ accounts once shares are allotted. Until then, the money remains in the account, continuing to earn interest. In contrast, with secondary market purchases, funds are debited immediately, regardless of allocation.
7. Voting Rights and Influence
When you invest in an IPO, you gain voting rights, allowing you to participate in company decisions. For example, if the company proposes an expansion at an annual meeting, shareholders can vote to support or oppose the plan. This level of ownership provides a way for investors to have a say in the company’s direction.
8. Potentially Low Entry Price
Companies often price IPO shares at a discounted rate, making it more affordable for early investors. This means investors can buy in at a lower price, which may be harder to achieve once the stock gains popularity and its price rises after the IPO.
Disadvantages of Investing in an IPO
Investing in an IPO also comes with some disadvantages such as:
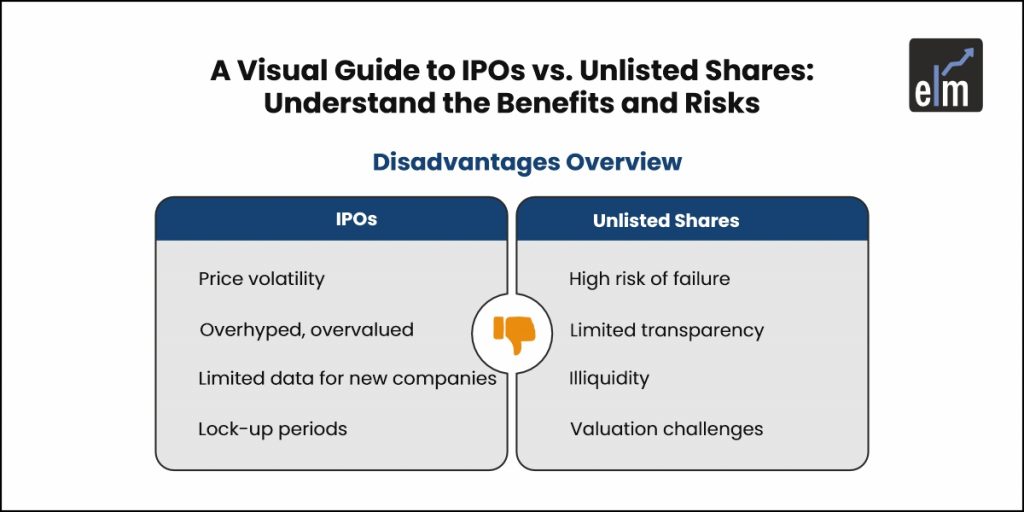
1. Price Volatility
IPO stocks can be very unpredictable. Prices often go up and down quickly in the beginning, which can make it difficult to know the right time to buy or sell. This unpredictability can lead to sudden losses for new investors who are expecting steady growth.
2. Lack of Track Record
Many companies going public are still building their business, so they don’t have the long history or financial stability of well-established companies. This lack of proven performance makes it harder to evaluate if the company is a solid long-term investment.
3. Hype and Overvaluation
IPO stocks can be surrounded by hype, which sometimes inflates the initial share price. When there’s a lot of buzz, companies may get overvalued at first, which means the stock could lose value once the excitement dies down.
4. Limited Information
Since IPOs involve newer companies, there’s often limited public information available. Investors might not have the same access to detailed financial data as they would with long-established public companies, making it harder to make informed decisions.
5. Possible Lock-Up Periods
For some IPOs, there are lock-up periods that prevent early investors or company insiders from selling their shares for a set time after the IPO. Once the lock-up period ends, a large number of shares might hit the market, which could drive down the stock price.
6. Competition for Shares
Retail investors often find it challenging to get access to IPO shares at the offering price. Large institutional investors typically get priority, leaving retail investors to buy at a higher price once trading begins.
Advantages of Investing in Unlisted Shares
Investing in unlisted shares comes with several advantages that can help you achieve significant profits over time.
1. Spreading Out Risk
Unlisted shares are a great option for those looking to spread their investment risks. They work differently from shares listed on the stock exchange and offer a unique set of opportunities, but it also requires understanding of the key considerations to invest in them. By adding pre-ipo or unlisted shares to your portfolio, especially alongside IPO or listed shares, you get access to a new way of managing risk while potentially earning equal or better returns. Additionally, there’s always a chance that these shares could become listed in the future, which could lead to significant gains.
2. Flexible Pricing
One major benefit of unlisted shares is that their prices are often negotiable. This is because there are fewer buyers and sellers in this space, which reduces competition. Fewer people trading these shares means that you have the chance to agree on a price that works for you, making it easier to find a good deal compared to shares on the open market.
3. Lower Valuation
Unlisted shares are often undervalued because they aren’t as actively traded as listed shares. Since only a small number of investors are interested in buying them, especially for the long term, their prices can remain low. For those with experience in investing, this can be a golden opportunity to purchase these shares early before their value increases. Over time, as the company grows and gains recognition, the value of these shares may rise significantly.
4. Opportunity for High Growth
Unlisted shares are typically issued by smaller companies that are still in the early stages of their growth journey. These companies might not yet be ready to go public but have strong potential for expansion. By investing in unlisted shares and holding onto them over time, you can benefit from the company’s growth. When these companies eventually list on the stock exchange, the value of their shares can rise sharply, offering you substantial returns.
5. Potential for Big Profits
Investing in unlisted shares can be a great way to secure strong returns on your investment. If the company you invest in becomes publicly traded, its share prices could see a significant jump. This means that by purchasing unlisted shares at a lower price, you have the chance to enjoy impressive profits when the company grows and its shares are in higher demand.
Disadvantages of Investing in Unlisted Shares
Investing in unlisted shares can be rewarding, but it comes with challenges that require careful thought and preparation. Understanding these risks is important before making any decisions.
1. Higher Risk of Failure
Investing in unlisted shares, especially in startups or early-stage companies, comes with a high level of risk. Many startups don’t survive long enough to become profitable, which means investors can lose their money. While some companies, like Facebook or SpaceX, have achieved great success, not all investments follow the same path.
2. Limited Information and Transparency
Unlisted companies often don’t provide as much information about their operations or management as publicly listed ones. This lack of transparency makes it harder for investors to properly evaluate these businesses.
3. Illiquidity
One of the biggest challenges with unlisted shares is that there isn’t a public market to sell them easily. Finding buyers can take time, and this lack of liquidity can be frustrating for investors. However, this illiquidity might also help some investors avoid impulsive decisions driven by market trends or panic, which could prevent hasty mistakes.
4. Difficulty in Valuing Shares
Unlisted shares are often priced lower than listed ones because they are harder to sell and carry more risk. This lower valuation reflects the uncertainty and lack of accessibility that come with these investments. Accurately determining the value of unlisted shares can also be challenging due to the absence of regular market pricing.
5. Limited Access for Small Investors
Most unlisted shares are not available to average investors. These opportunities are often reserved for institutional investors or individuals with significant wealth, making it harder for regular investors to participate.
Closing Thoughts
Both IPOs and unlisted shares offer unique opportunities, but they also come with their own risks. Choosing between them depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. Understanding how these options align with your strategy can help you make better decisions and grow your portfolio over time.