— 6 mins read—
Many of us have come across the concept of efficient market hypothesis in stock markets, which says market rationally prices in all the available information
But it is not true and there is much evidence that proves that there are a lot of inefficiencies in the market.
The main reason why inefficiencies exist is because of the behaviour of humans.
We act in irrational and unexpected ways and we don’t even accept it.
The study of these human biases is termed “Behavioural Finance”.
What is Behavioural Finance?
Behavioural finance is bound to exist as it is tied up with human psychology of inferring same situations differently.
All humans looking at a similar situation will infer different conclusions, which give rise to either inefficiencies or opportunities.
For eg- When people see a lot of money being made in the markets, then more people jump into it.
And because of this, these people invest after prices have already gone up and thus end up selling when prices are down.
This irrational behaviour causes inefficiencies in the market.
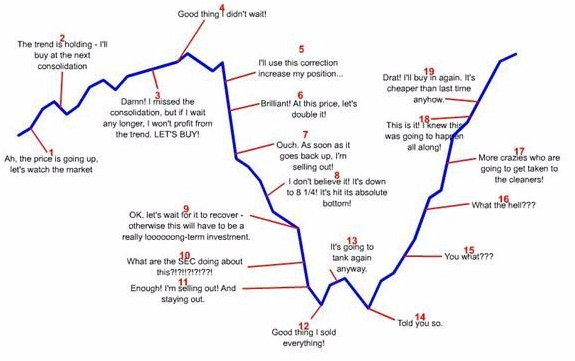
During this situation, intelligent investors are generally on the winning side of the trade.
This is most common in stock markets and is described as “greed” and “fear” behaviour.
Investors become greedy when markets are rising and become fearful when markets are falling.
Importance of Behavioural Finance:
Recent studies show that most investors make trading decisions based on emotions and logic.
These types of investors buy high on speculation and then sell at low in panic thus making a loss.
The main reason for this is that investors sell after the price of the stock has fallen a lot and then buy the stock when the price has increased a lot and they eventually start making losses.
Behavioural finance helps us in understanding this kind of behaviour of the investors.
Understanding Behavioural Finance helps us to avoid emotion-driven speculation leading to losses, and thus help us in devising an appropriate wealth management strategy.
Objectives of Behavioural Finance:
The main objectives of Behavioural Finance are:
To protect the interests of the shareholders when the investment scenario is volatile.
To discuss the issues which are emerging in the financial markets.
For analysing the influence of the biases as there are different personalities in the financial markets.
To examine the different social responsibilities related to this subject.
To make an effort to identify investors’ responsibilities more elaborately.
To examine the contagion effect of various events.
Scope of Behavioural Finance:
The scope of Behavioural Finance is as follow:
To provide an explanation of various corporate activities like the effect of dividends, stock splits etc on the stock.
To help in identifying risks and their hedging strategies
To identify different personalities of investors in the stock market
To enhance the skills of the investment advisors
Assumptions of Behavioural Finance:
There are mainly two ways of overcoming negative behavioural tendencies. These are:
1. Focusing on the process:
There are two approaches to decision making:
Reflexive: Going with your gut for making a decision
Reflective: Making a decision logically
Reflexive decision making leads to making emotional decisions whereas Reflective decision making leads to making logical decisions.
2. Preparing, Planning and Pre- Committing :
Behavioural finance teaches us to invest by preparing, planning and making sure that we pre-commit.
Cognitive Biases:
A cognitive bias is a systematic error in thinking which affects the decisions and judgments that people make.
Most of these biases are related to memory.
The way we remember an event may be biased for a number of reasons and that in turn can lead us to biased thinking and decision-making.
Types of Cognitive Biases:

1. Anchoring Bias
It occurs when investors rely on an initial piece of information to make subsequent judgments.
The initial piece of information acts like an anchor here.
Eg- If an investor considers the 52-week low price of a stock as a reference of a low value, then he might be biased to consider that price as a bargain price, which in reality may not be so.
One way of protecting yourself from anchoring bias is to take a rational view and think independently without thinking much about the reference information.
2. Availability or Recency Bias
This means to assess the likelihood of any future events based on remarkable past events.
Eg- After a recession, investors tend to think that another recession is around the corner. (This is not true most of the time)
3. Social Proof Bias
When people copy the actions of others in an attempt to reflect the correct behaviour in a given situation.
Eg- Investors follow the herd and make decisions. During a bear market, most investors would want to sell, following the herd.
4. Regret Aversion Bias
It is the inaction of an investor because of fear that their decision might be wrong in hindsight.
Regret aversion can cause investors to stay away from the markets that have recently gone down or prefer less risky stocks like blue-chip stocks.
5. Confirmation Bias
It is the tendency to accept information that supports your belief and ignore information that contradicts them.
Eg- Investors with a positive view on some stock is likely to accept any positive news about it and ignore negative news.
6. Over-confidence Bias
It is the tendency to overestimate the quality of your judgment or analysis.
Eg- James Montier mentions in his book- Some 70 per cent of analysts think they are better than their peers at forecasting earnings—yet, the very same analysts had 91 per cent of their recommendations as either buys or holds in February 2008.(sub-prime crisis)
The way out of over-optimism is to stay skeptical and find reasons to reject rather than accept.
7. Hindsight Bias
It is the tendency to feel that the past events seemed more obvious or predictable at present when in fact they could not have been reasonably predicted then.
For eg- Every time after a rally or fall, people tend to point out reasons (like FII data) that seem pretty obvious now, but the same reasons weren’t obvious when they actually happened so as to take any action.
8. Authority Bias
It is the tendency to attach greater accuracy to the opinion of an authority figure and be more influenced by that opinion.
For eg- A prominent figure’s opinion about a particular situation in stock markets may make us biased to believe so, even if they are not entirely correct.
9. Status Quo Bias
It is the tendency to think or act in a particular way even when the actual situation is changing. It is the investor’s resistance to change.
For eg- Investors with a status quo bias will not change his decision to stay put in a stock even when there are clear reasons to do so.
10. Endowment Effect
It is a tendency to assign greater value to things that we already own than things that we do not own.
For eg- If we own a auto indusry stock, it sometimes becomes a tendency to believe that our company will produce superior returns when in reality it may not be so. It also prevents us from researching other opportunities having better return potential.
11. Empathy gap
Sir John Templeton, a legendary investor provides us with a perfect example of empathy gap in action. He was well known for saying “The time of maximum pessimism is the best time to buy, and the time of maximum optimism is the best time to sell.”
Unlock the power of Behavioral Finance in our Advanced Technical Analysis Course online. Elevate your stock price strategies today!
Key Takeaways:
Behavioural finance offers no investment miracles, but perhaps it can help investors to be watchful of their behaviour and, in turn, avoid mistakes that will decrease their invested wealth.
People often tend to think that they are wise and hence need not re-check their portfolio.
They are often stuck in their investment due to biasness.
People often take instant decisions and later regret.
Thus there’s a proverb that people “should not marry stocks”.
Finance geeks always look for good sources of knowledge. You can check out one such source in our research analyst course online and enhance your skills.