In this blog we will understand about the risk involved in business through the concept of leverage. This course: NSE Academy Certified Finance for Non-Finance People will help you to learn more about this concept.
Before we understand the above-mentioned topics, we should know about the following formula of computing net income which is as follows and the risks involved therein:
| Particulars | I | II | III |
| Sales (Price * Quantity) | Sales risk | Business risk (Operating margin) | |
| Less: Variable cost | Operating risk | ||
| Contribution | |||
| Less: Fixed cost | |||
| Earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) | |||
| Less: Interest | Financial risk | ||
| Net Income |
Based on the above table, we will understand the risk involved at various stages of computing net income:
Sales risk
Sales is the function of both price and quantity. Price multiplied with quantity will give you the total sales.
So when we talk about the sales risks that a company faces, it primarily comprises of either the price is adverse to what your expectations are or the volume of sale by you will be lower than the anticipated figures,
Since sale is the function of price and quantity. Hence, you face the sales risks based on these two factors.
Operating risk
Now, when we take costs involved in executing the sale, we divide the total costs into variable & fixed costs.
Variable cost is the costs that keep changes according to the volume of sales whereas fixed costs remain constant irrespective of the volume of sales.
When you subtract your variable and fixed cost from your operating income, the result is the operating income or EBIT (as shown in the table above).
This part of the statement i.e. the fixed costs, the variable costs etc will lead to the operating risks in the business. The risks involved here is that the variable costs may go up such as the raw material used may be scarce in quantity or the technical skill required in a labour may not be available. Similarly, the fixed costs may increase, in terms of the increased rent or the capital expenditure involved changes.
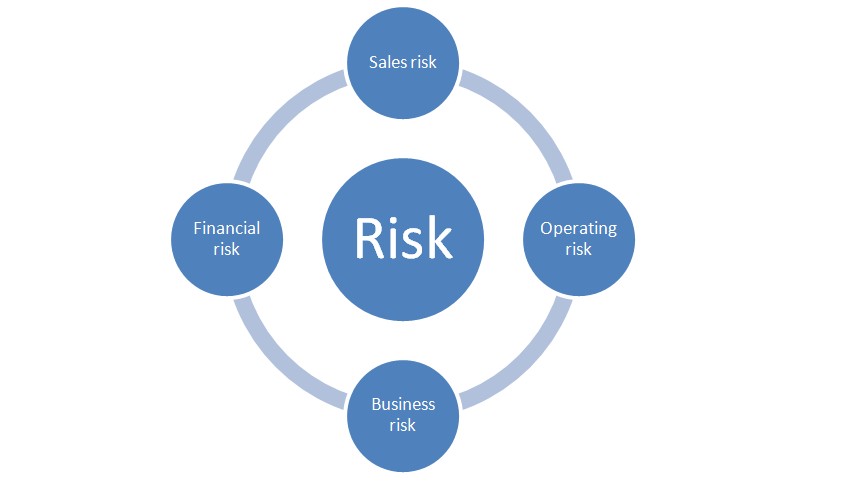
Business risk
Together, the sales and the operating risk lead to the business risks, as shown above.
Financial risk
After netting the interest from the operating income, we get the net income. Financial risks are related to the financial decisions of the company such as taking debt or loans for the business purposes.
Apart from the business risks involved, we must also know about the following other decision-making tools involved which are as follows:
Learn more about Business Risk Analysis and Leverage(Part-1) by watching the video below:
Leverage
After getting the idea about the different types of risk involved, let us first understand as to what is the need to segregate the costs into variable and fixed costs.
With the increase in the units of production, the fixed cost will remain unchanged whereas the variable costs will increase per unit of output produced. When we divide contribution by sales, we get the contribution margin.
The answer to this question will be understood while understanding the following concepts:
Fixed cost has already been incurred and will remain constant irrespective of the number of units produced. However, this contribution margin helps us to determine as to how soon will we be able to recover the fixed cost and come in the profit margin of the company. This is the reason of segregating the cost so as to understand the profit recovery posts the execution of sales. This is basically understood as the concept of operating leverage.
Leverage implies the use of fixed cost to maximize the impact for a given input
Consider your operating fixed cost is very low. This implies that you will be very quickly able to cover it by through your contribution.
For example: Operating fixed cost – Rs. 300/-; Contribution/ unit = Rs. 50/ unit. This means that by selling 6 units, you will be able to recover your fixed costs completely. After this whatever units are sold, the entire sales will be profit, contributing to the EBIT.
Operating leverage
Operating leverage is the use of operating fixed costs to maximize the impact on operating profit (EBIT) for a given change in sales
Given your fixed cost, once your sale increases, once you have covered all your fixed cost by selling a given number of units, after that with every increase in your sales, profit increases at a higher proportion. This is how the operating leverage works.
The higher the fixed cost, the higher will be the risk involved and vice versa.

Financial leverage:
Interest is also an example of a fixed cost, as specified in the table above. This implies that whether or not sales happen, we will be required to pay interest to our debt holders.
Interest is basically a financial fixed cost. Use of financial fixed cost to maximise your profit, given the change in your EBIT, is an example of your financial leverage.
In the table shown above, we have EBIT before the deduction of interest to arrive at net profit. If interest is low, then every change in sales will lead to change in net income and vice-versa.
Also Read: Business Risk Analysis – Break Even Point and Corporate Finance Decisions (Part-2)
Case study
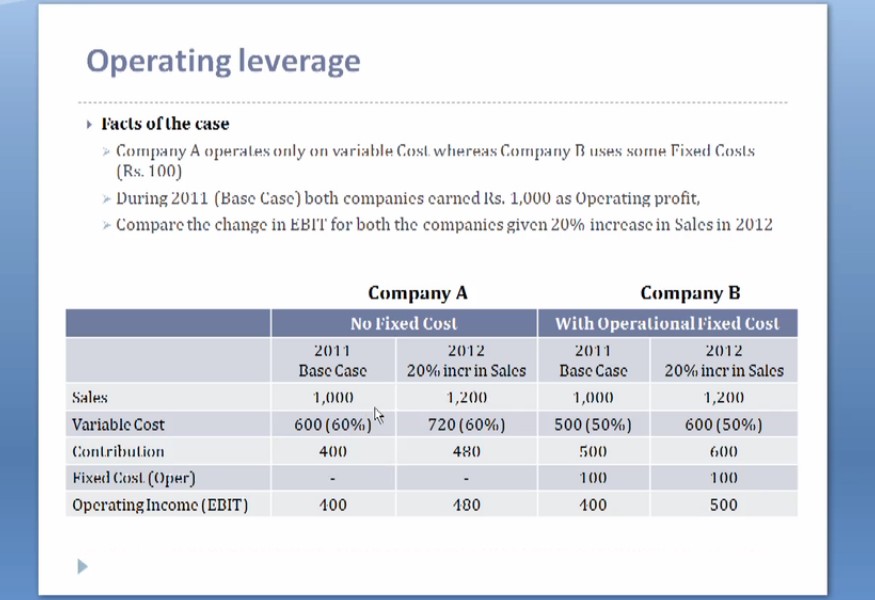
Analyse the above-mentioned example, to understand the operating leverage in both the situations mentioned below:
Bottomline:
Every company in its Annual Report mentions the various risks that the business faces such as Sales Risk, Operational Risk, Business Risk and Financial Risk. It is important to understand all these risks to properly comprehend the operations of the business and gauge its future potential. On the other hand, Operating Leverage and Financial Leverage quintessentially are double-edged swords. They maximise your profits but also maximise your losses when things aren’t going suitably.
This article introduces you to the above-said concepts at a rudimentary level. You, however, need to know the pragmatic application of all these factors to deduce if a company has the potential to generate wealth for you.
Whenever you learn a new financial concept, you should ask yourself, “How can this help me in my process of identifying a multi-bagger?” If you realise that you don’t know how, then don’t give up and just settle for whatever you know superficially. Dig deeper and deeper until you find that treasure full of gold.
In order to get the latest updates on Financial Markets visit Stockedge